In the ArcGIS GeoAnalytics Engine 1.3 release (January 2024) we have several exciting new features to expand your big data spatial analysis workflows. This latest release introduces geocoding and network analysis functionality as well as various enhancements to existing functionality to help you enrich your data science workflows with spatial insights. These new features bring more of Esri’s industry-leading geospatial analytics capabilities directly to your big data – in a data lake, data warehouse, or ArcGIS.
Let’s take a look at the new features:
Geocoding
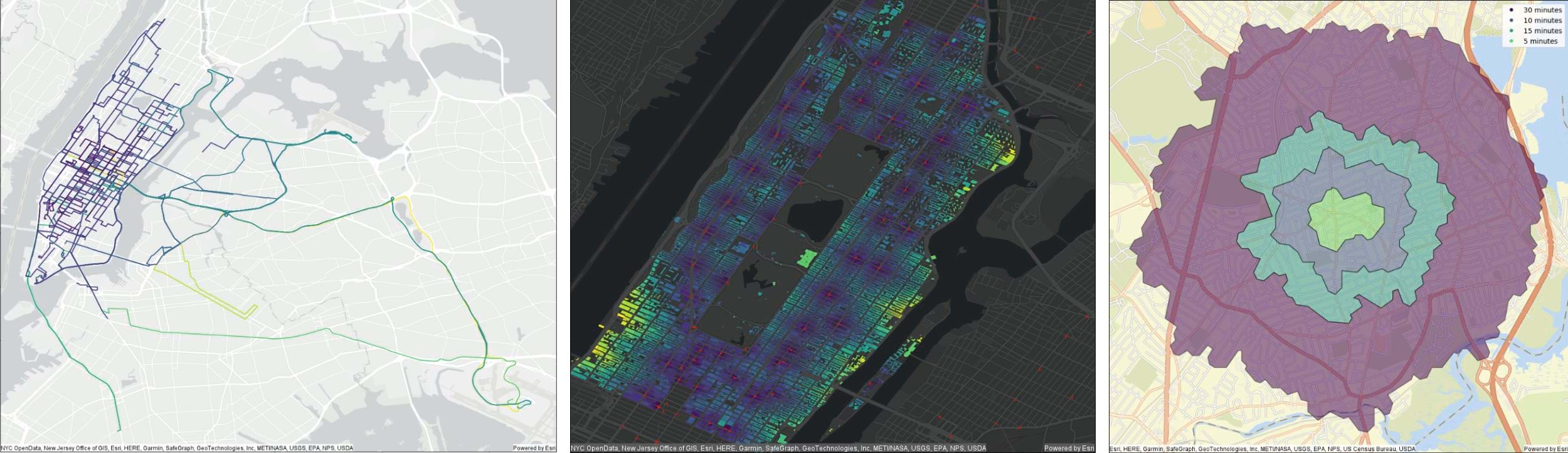
The 1.3 release introduces forward and reverse geocoding. Geocoding is the process of assigning a location, usually in the form of coordinate values, to an address. The Geocode tool takes a set of string values for addresses and converts them into geographic coordinates using a locator for reference. Reverse geocoding allows you to convert geographic coordinates to a readable address. It’s important to note that a locator dataset is not included with GeoAnalytics Engine at this time, so you will need to supply your own. For prototyping and testing purposes, you can find a sample locator file in the geocoding tutorial from ArcGIS Pro. More information can be found in the core concepts document for geocoding in GeoAnalytics Engine.
Network analysis
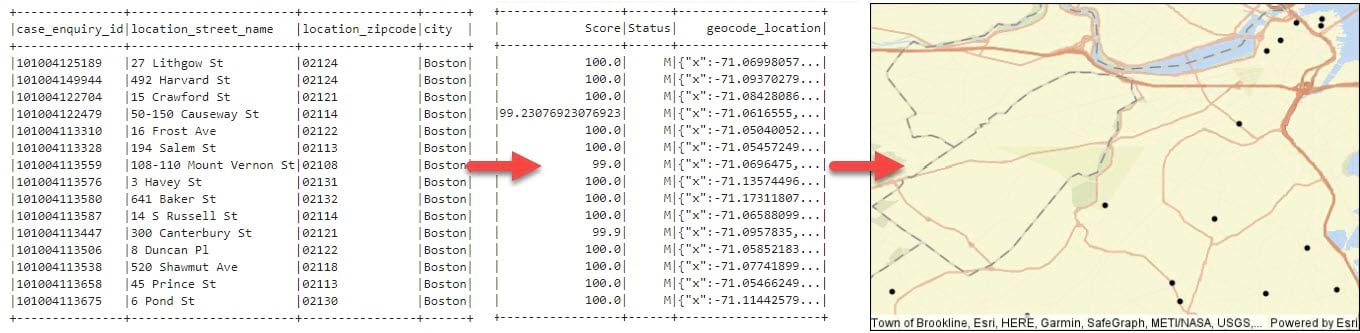
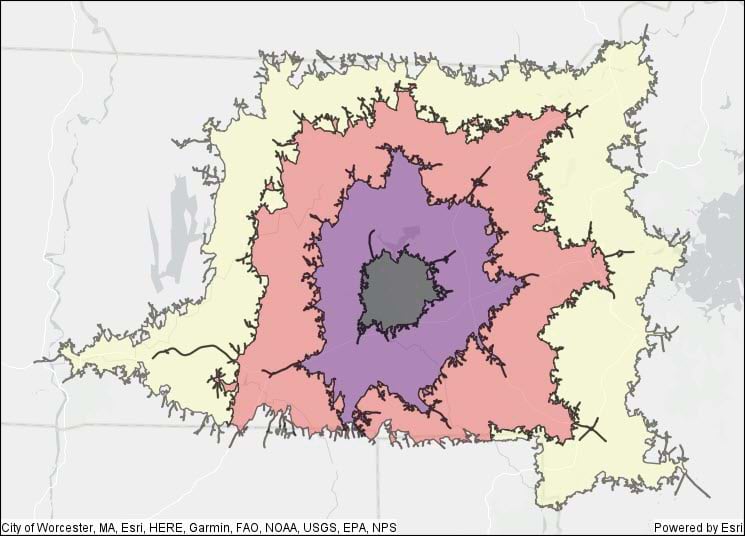
The 1.3 release also includes a full set of network analysis tools, including Create Routes, Create Service Areas, Generate OD Matrix, and Find Closest Facilities. These tools allow you to use a network dataset (roads, railways, utilities, etc.) to answer questions about connectivity and proximity to maximize efficiency in movement of goods, coordination of vehicle routing, or to better understand proximity along a connected network. Similar to geocoding, a network dataset is not included with GeoAnalytics Engine at this time, and you will need to supply a network dataset as a mobile map package (MMPK) or mobile geodatabase. More information about using network datasets in GeoAnalytics Engine can be found in the documentation on network analysis. You can find instructions on building a sample network dataset in the ArcGIS Pro documentation on how to create a usable network dataset. The network dataset from that tutorial can be converted to an MMPK using ArcGIS Pro and then used in GeoAnalytics Engine.
Feature enhancements
In addition to the new network analysis and geocoding tools, the 1.3 release includes significant improvements to performance, scalability, and reliability when reading and writing large feature services. Performance has been improved for geographic distance calculations and this release also adds support for the latest Spark runtimes.
ArcGIS GeoAnalytics Engine is updated two to three times each year to provide new features so you can make spatial analytics a seamless part of your data science workflows. We’re always looking to hear from you about the capabilities you need to enhance your big data workflows!
For more information on the latest features, check out the product release notes or stop by the GeoAnalytics Engine Community Site for resources on getting started, tips and tricks with various tools, and much more!


Article Discussion: