RESOURCE
How GIS supports Intelligence Preparation of the Battlefield (IPB) and Joint Intelligence Preparation of the Operational Environment (JIPOE)
Intelligence agencies use ArcGIS tools to create dynamic information layers that are easy to share with commanders and staff. Discover how you can use GIS in all four stages of the process for intelligence preparation of the operational environment.
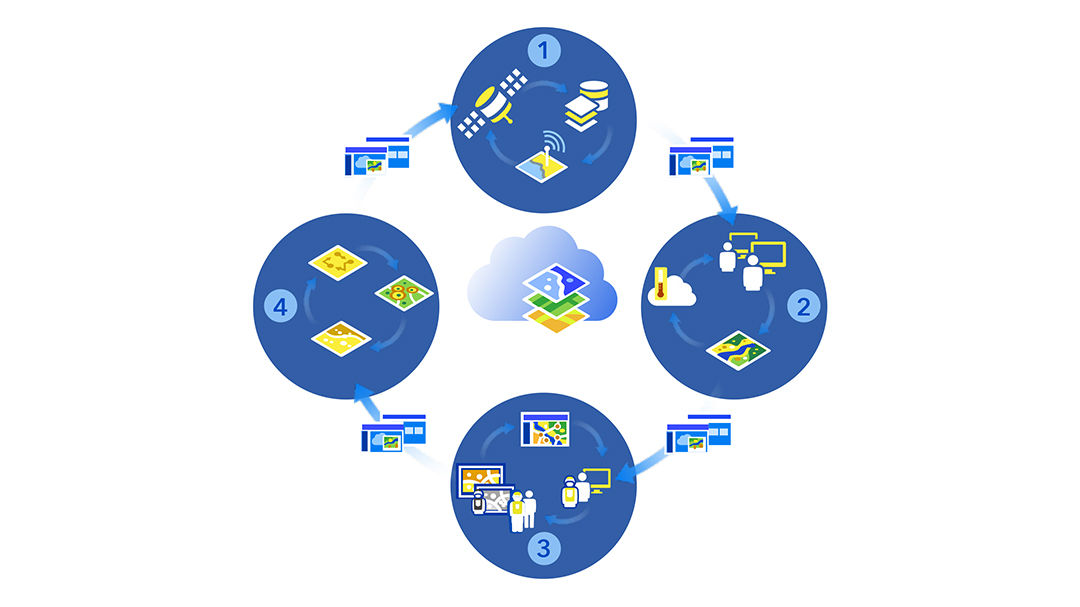
Define the operational environment
ArcGIS is used as the standard tool for managing all foundational geospatial intelligence (GEOINT). In addition, ArcGIS Living Atlas of the World is the foremost collection of geographic information from around the globe. Intelligence analysts can use ArcGIS to manage this foundational data and build a comprehensive geographic view of the political, military, economic, social, information, and infrastructure (PMESII) elements of the environment. As a unit spends more time in an operational area, the unit's knowledge of the environment improves. This information is captured and shared as new foundational data. In addition, as units are relieved in an operational area, this standard and nonstandard data can easily be transitioned reducing the learning time.
Describe the operational environment
Analysts use ArcGIS to understand the impact the operational environment will have on military capabilities. Geospatial analysts use predefined workflows in ArcGIS to understand the impact of terrain, meteorological, and oceanographic factors. Analysts map out relevant sociocultural factors and system nodes and links to develop a system perspective of the adversary. This information can be dynamically shared in maps, diagrams, link charts, and matrixes.
Evaluate the threat or adversary
Intelligence agencies use ArcGIS to evaluate threats and adversaries. They also leverage foundational intelligence information about enemy order of battle. Analysis tools can be used to visualize the capabilities of weapons systems, collection capabilities, and maneuver forces. Historical information can be reviewed to understand capabilities and limitations. Systems analysis can be leveraged to understand centers of gravity and key nodes. This information creates a foundation that can be used when determining and evaluating courses of action.
Determine course of action
Intelligence analysts use ArcGIS to share the information captured through the intelligence preparation process with all staff and subordinate commanders, giving them a holistic view of the operational environment. This foundational information is leveraged during the collaborative process of developing courses of action. ArcGIS supports collaborative planning—carried out in person or remotely—by providing shared services and standard tools for course-of-action (COA) sketching, threat analysis, and synchronization. During the action development process, structured tools can be used to capture standard information such as the following:
- COA sketches
- Situation templates
- Event templates
- High-value targets
- Named areas of interest
The process for JIPOE is cyclical—as more information is collected, each phase is repeated to support planning and operations. Using GIS, this process can be accelerated, and information can be shared in real time between each phase in the process. The products created can be shared with planners to support their iterative processes.