case study
Connecticut DOT Teams with UConn's Transportation Safety Research Center to Create a Highway Safety Analysis Program and Strategic Plan
Technology Paves the Path to Better Roadways
Federal transportation legislation mandates that all Departments of Transportation (DOTs) have the ability to conduct advanced safety analyses of their roadways to access funds from the Highway Safety Improvement Program (HSIP). Following a previous study that identified roadway safety deficiencies, the Connecticut Department of Transportation (CTDOT) partnered with the Connecticut Transportation Safety Research Center (CTSRC) at the University of Connecticut (UConn), which in turn partnered with consulting firm VHB to develop a modern data-driven roadway safety management system for the state using geographic information system (GIS) technology from Esri.
Prior to the Connecticut Roadway Safety Management System (CRSMS), CTDOT had a safety analysis strategic plan, which included the examination of a CTDOT safety analysis system, development of an overall vision for a future safety analysis system, and an implementation plan to allow for the adaptation of the future safety analysis system.
The objectives in creating a new strategic plan for CTDOT were to identify and address safety analysis issues and limitations and establish methods that meet the Highway Safety Improvement Program requirements and the specific needs of CTDOT. Key findings included the need for a GIS-based, advanced safety management system that implements the Highway Safety Manual (HSM).
Connecticut Roadway Safety Management System
Based on the recommendations of the strategic plan, the UConn/VHB team developed the award-winning CRSMS. To meet the requirements for GIS analysis and data visualization, the team built CRSMS on top of Esri ArcGIS Enterprise. CRSMS leverages Esri's robust ArcGIS Maps SDK for JavaScript for geoprocessing, data visualization, and web mapping.
CRSMS implements the six-step Roadway Safety Management Process (RSMP) introduced in the HSM. In addition to the six steps, CRSMS contains a Data Management module. The Data Management module is used to prepare roadway segments, ramps, and intersections for analysis; import or update the Safety Performance Functions (SPFs); and update other analysis parameters.
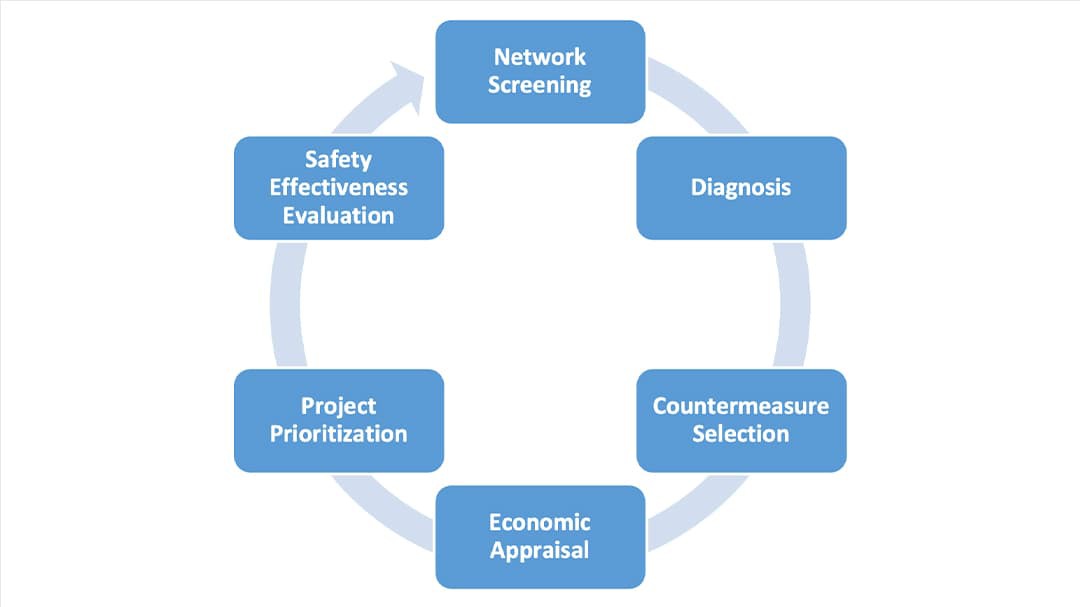
The six analysis processes included in the HSM and built out as modules of the system are as follows:
- Network Screening
- Diagnosis
- Countermeasure Selection
- Economic Appraisal
- Project Prioritization
- Safety Effectiveness Evaluation.
Step 1—The Network Screening module integrates maps while identifying locations with the highest potential for safety improvements. The module takes into consideration multiple safety performance measures and screening methods that allow for screening at different geographic levels.
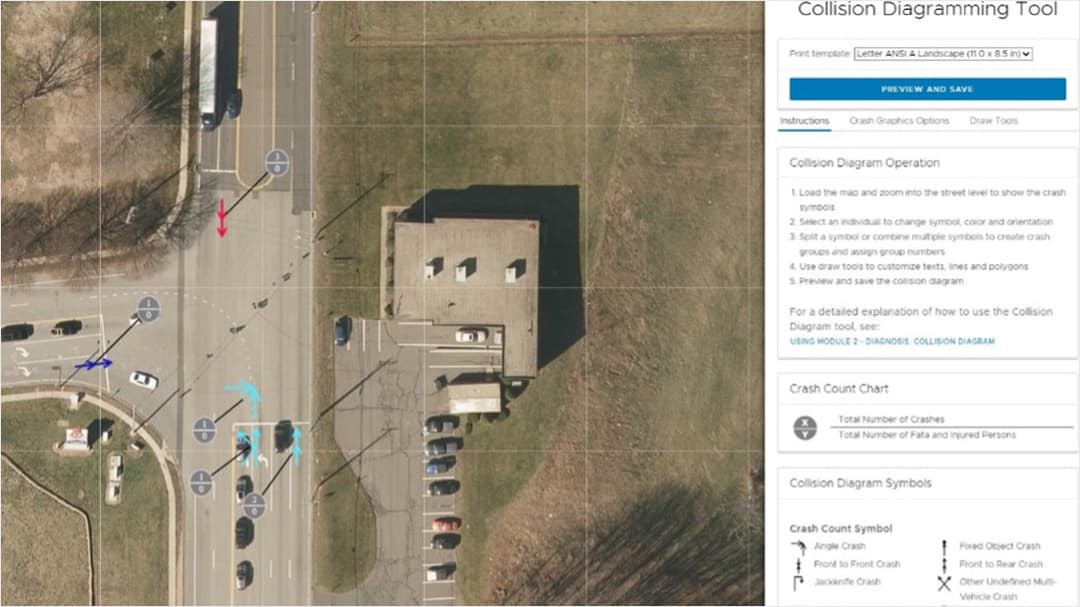
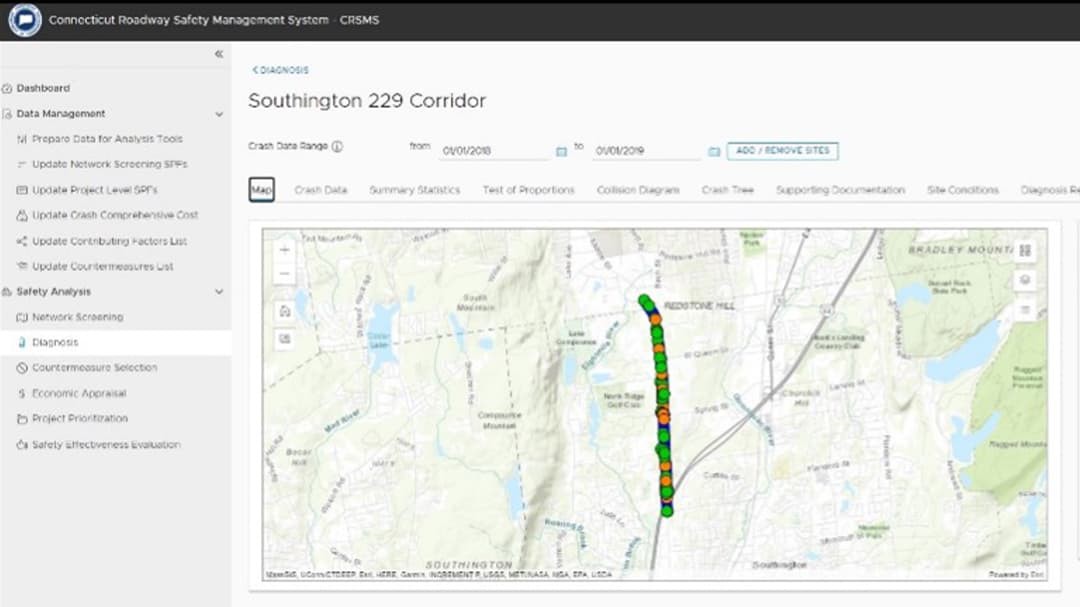
Step 2—The Diagnosis module has several useful tools, including Crash Map, Tabular Data, Summary Statistics, Crash Tree, Collision Diagram, and Site Condition View. The features allow users to identify crash patterns and the factors that contribute to the patterns.
Step 3—The Countermeasure Selection module gives the user the capability to compare engineering countermeasures that have the potential to reduce crash frequency or severity. The tool integrates thousands of the latest Crash Modification Factors (CMFs) from the CMF Clearinghouse and also allows the state to input its state-specific CMFs.
Step 4—The Economic Appraisal module enables users to view and compare the safety benefits of countermeasures along with cost, allowing for identification of the most cost-effective treatments. The tool also allows the user to create comprehensive engineering solutions by combining individual countermeasures. Incremental cost-benefit ratios are used to compare solutions.
Step 5—The Project Prioritization module creates less biased and more data-driven decision-making by implementing integer programming optimization for prioritizing competing projects with limited budgets.
Step 6—The Safety Effectiveness Evaluation module evaluates the change in crashes from the implemented safety solutions, showing how effective budgets and resources have been assigned for safety improvements. The tool provides flexibility in directing the different levels of safety effectiveness evaluations, (i.e., program level, project level, and site level).
CRSMS Implementation and Capabilities
A key component of the CRSMS is that it is built with Esri ArcGIS and integrates Model Inventory of Roadway Elements (MIRE) data elements for roadways, ramps, and intersections. CRSMS is designed as a single-page web application with a secure login system. Users log in through their web browser and gain access to the system based on their assigned rights.
Esri technology is embedded throughout the CRSMS but is most noticeable to users through the Network Screening, Diagnosis, and Safety Effectiveness Evaluation modules. The CRSMS Network Screening module is the most robust network screening platform on the market, providing users with the ability to screen their road network, ramps, and intersections using seven different performance measures. They can use interactive web maps to select study areas and visually present the results.
The Collision Diagramming tool within the Diagnosis module is one of the more built out components, leveraging the JavaScript API. The tool hosts a sketching platform to create easy-to-build and easy-to-read collision diagrams through an interactive GIS viewer.
CRSMS Launch and Capabilities
CRSMS was launched to CTDOT in stages and is now fully deployed. The Network Screening and Diagnosis modules were released to CTDOT in 2019, and the remainder of the modules were released in 2020. CRSMS has gained national attention and, in 2019, received the Best Practices in Traffic Records Award by the Association of Transportation Safety Information Professionals. CRSMS's implementation of the HSM and use of GIS technology make it very desirable to DOTs. Given the interest by other state DOTs, there is an open solicitation through the Transportation Pooled Fund Program to study the implementation of the tools in other states.