Featured
Dynamic, intelligent infrastructure
Infrastructure isn't fixed; it's dynamic, intelligent, and even emergent.

A foundation for modern infrastructure
Modernizing infrastructure with resiliency, sustainability, and equity in mind requires a deep understanding of each asset's location-based relationship to environmental and human-made systems. GIS maps and analysis help leaders understand where to make infrastructure investments with the greatest impact and align with sustainability goals.
Resilient infrastructure
Resilient infrastructure helps communities resist and recover from stresses and supports positive economic, social, and environmental outcomes.
Sustainable infrastructure
Sustainable infrastructure requires solutions that anticipate future environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors.
Equitable infrastructure
Equity is a key consideration for infrastructure investments that must consider social, economic, and environmental well-being.

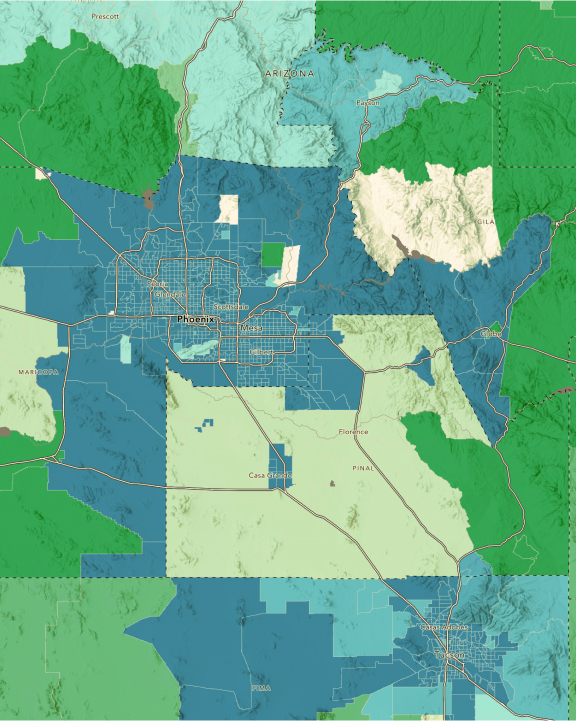
The geography of infrastructure investments
Modern infrastructure management requires holistic thinking on both micro and macro scales. A geographic approach to planning and operations helps leaders understand how infrastructure projects relate to surrounding environments. GIS is the nervous system for modern infrastructure management, connecting systems, workforces, organizations, and communities. ArcGIS is the cornerstone by which organizations modernize their networks and improve resiliency in a sustainable and equitable way.