At the University of Rhode Island (URI), transitioning from a legacy computer-aided facility management (CAFM) system to ArcGIS Indoors in 2022 marked a pivotal shift in how spatial data was managed, visualized, and shared across campuses. Today, the university’s spatial services team and other key stakeholders are taking the next steps to embed GIS in the fabric of URI campus operations.
A legacy computer-aided facility management system served the university well for decades, supporting URI’s needs for space inventory and tracking movable assets. However, its limitations—especially regarding user-friendliness and interoperability—became increasingly apparent. ArcGIS Indoors offered a modern alternative, enabling URI to unify spatial data across colleges and divisions and provide intuitive access via desktop, mobile, and kiosk platforms.
Migrating to Indoors first required an enterprise GIS solution that would support not just Indoors but also a robust, enterprise-wide GIS implementation. This foundational work set the stage for deeper GIS integration across the campus, including developing a geospatial strategy, hiring a full-time GIS specialist, and publishing a basemap through the ArcGIS Community Maps program.
Building a Scalable Enterprise GIS
To enable these GIS efforts, URI needed a resilient and scalable system with capabilities that could expand with the university’s growing spatial technology needs. The spatial services team partnered with two university groups—URI Information Technology Services and the URI Environmental Data Center—to build and manage an ArcGIS Enterprise instance. These two groups built a fully scalable ArcGIS Enterprise instance in the Amazon Web Services cloud, currently running ArcGIS Enterprise 11.5 with Microsoft SQL Server 2022.
The ongoing ArcGIS Indoors implementation started with an Indoors pilot project in May 2022. The project was supported by Esri partner Paratum Solutions. The legacy CAFM system used proprietary floor plan editing software, so the implementation started without CAD data. After working through the process of migrating the floor plans to CAD and establishing CAD standards, Coast2Coast was hired to convert the floor plans in March 2024. The company is experienced in providing as-built and modeling services. The entire process took about five months.
The spatial services team performed quality control checks and imported the floor plans into the Indoors data model as the converted CAD files were received. During implementation, the Indoors data was already being used by public safety staff to manage university events such as commencement.
With support from Esri Professional Services, the team completed migrating the legacy CAFM data using the techniques developed during the pilot project. Overall, the Indoors implementation was less expensive than three years of licensing for the legacy CAFM system.
Supporting Campus Operations
With the geospatial foundation in place, the spatial services team then looked to support the needs of university departments that were focused on campus operations: the public safety department, the transportation and parking department, and the facilities group. The spatial services team built several GIS applications to manage authoritative data using tools such as ArcGIS Experience Builder, ArcGIS Field Maps, and ArcGIS Survey123. The resultant tools significantly improved URI’s ability to share authoritative data that is critical to campus operations across departments.
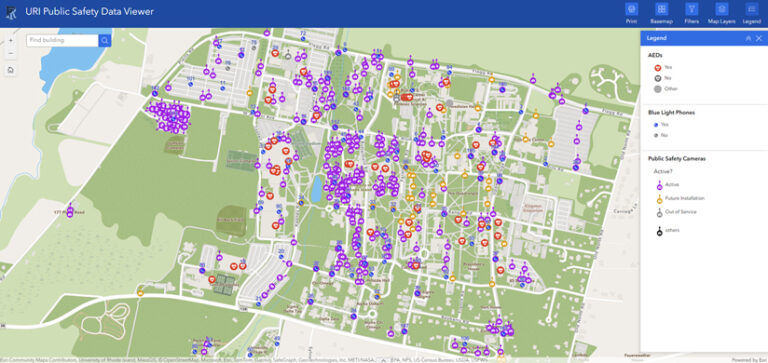
URI’s public safety department relies on a situational awareness dashboard that monitors emergency blue light phones in public areas, as well as security cameras and automated external defibrillator locations. The department also uses campus maps and Indoors floor plans to manage university athletic events, residence hall move-ins, and commencement.
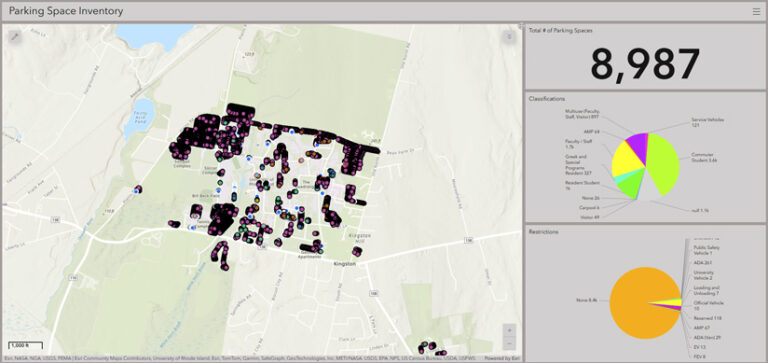
The transportation and parking department migrated URI’s parking inventory from Excel spreadsheets to ArcGIS and now manages the inventory using ArcGIS Field Maps.
The facilities group uses ArcGIS to track landholdings, manage utilities data, maintain construction maps, and integrate Smartsheet APIs to distribute updates on projects managed by URI’s Office of Small Projects through web applications.
Instead of manually managing siloed data in external locations, URI stakeholders are now managing and sharing authoritative data across the ArcGIS platform digitally. These capabilities are elevating ArcGIS as an anchor enterprise business system technology.
As URI built momentum tackling campus operations challenges, the spatial services team wanted to start solving problems for the broader campus community by taking advantage of distributed collaborations between ArcGIS Enterprise and ArcGIS Online instances. This allows the team to create public-facing web applications based on authoritative data managed in URI’s ArcGIS Enterprise instance—sometimes in an enterprise geodatabase.
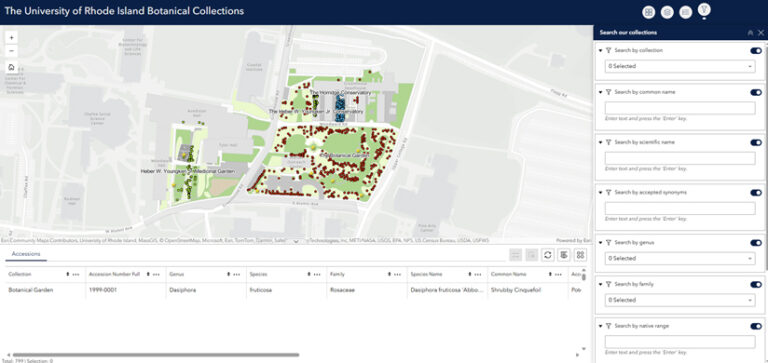
The first public-facing achievement was helping URI’s College of Pharmacy and College of the Environment and Life Sciences map the URI Botanical Garden collections. An enterprise geodatabase replaced an older database and underpins a public web mapping application for visitors to spatially view and interact with the data.
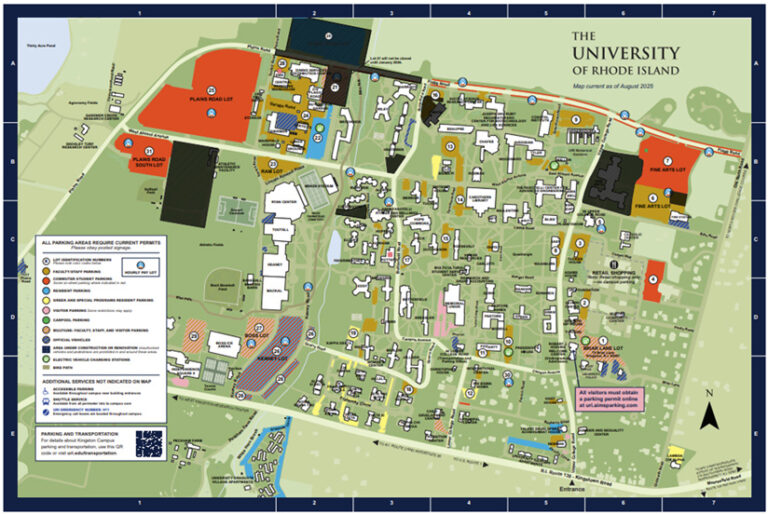
The spatial services team has also provided the university’s external relations and communications team with access to authoritative GIS data via the Adobe Illustrator plug-in. ArcGIS Maps for Adobe Creative Cloud enables the team to access and design with data-driven maps in Adobe Illustrator and Photoshop. The team uses the plug-in to generate a campus parking map. This provides URI’s publishing team with access to authoritative geospatial data such as basemaps, building footprints, parking data, sidewalks, trees, and pavement lines—while allowing for artistic license.
Spatially Visualizing University Data
One of URI’s most exciting GIS developments is the data visualization capability that the ArcGIS Indoors model facilitates. Previously, URI staff visualized data one floor plan at a time using the former computer-aided facility management system. Combining the ArcGIS Indoors data model with the ArcGIS platform allows users to visualize data across the entire university and drill down to the campus, building, or space level.
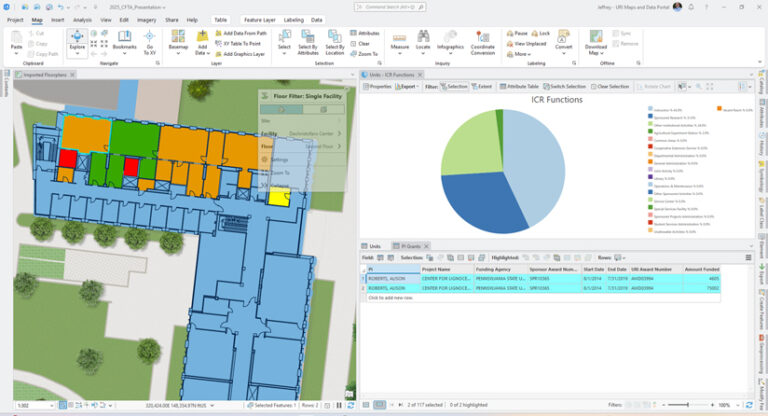
However, the visualization doesn’t end there. The spatial services team is also working on a pilot project for a digital twin. The team used base year data from a space survey for an indirect cost recovery rate negotiation to visualize how major research buildings on multiple campuses performed in terms of sponsored research activity. The team then used Indoors to see how the floors and individual research spaces performed during the space survey. This approach could be applied to many different types of data, including research expenditures, work order costs, and cleaning time.
The space survey data consisted of functions based on percentages for each room in the building. For example, a research laboratory might be functionalized as 50 percent sponsored research activities and 50 percent instructional activities. The team members took advantage of the unique unit ID to spatially relate the tabular space survey data with the rooms in Indoors. They then focused on the research spaces through a definition query for the research room types. Finally, the research spaces were symbolized based on the percentage of sponsored research activities.
By selecting the room, a user could also see all of the assigned functions in pie chart form and get a list of grant awards for the principal investigator assigned to the research space. This project allows the university to analyze the performance of a building and its individual research spaces regarding indirect cost recovery. More importantly, it demonstrates the power of the ArcGIS suite to visualize various datasets at the university, campus, building, floor, or space level.
Looking Backward—and Forward
The biggest challenge has been managing expectations. As the number of departments and stakeholders relying on your enterprise GIS program grows, the more you will deal with people who don’t fully understand GIS. They see maps, not data creation, collection, management, and visualization. They don’t understand why it takes Indoors to render the more than 500,000 lines of code in the details feature class. They just want them to be rendered much faster. You need to educate your stakeholders so that their knowledge grows alongside the enterprise GIS. A GIS team or department needs to focus on building the geospatial tools. It’s up to partner departments and stakeholders to manage their data using the tools that a GIS team builds, maintains, and supports.
What has been clear throughout the process of integrating GIS technology across URI is the importance of a strong spatial foundation. The first step to an endeavor like this is a geospatial strategy. URI spatial services started with rounding out the GIS team, building a scalable ArcGIS Enterprise environment, and creating a university basemap. These pieces continue to help build success.
The spatial services team is still working to improve the base-map, but it’s highly functional—even if it’s not the most artistic. The same is true of the entire enterprise GIS program. The work will never be finished. An enterprise GIS program is always growing and adapting. The same is true of a geospatial strategy. That’s why the spatial services team plans to revisit this strategy for a full refresh now that the ArcGIS Indoors implementation is complete. You always need a map to guide you on the next phase of the geospatial journey.
The transition to ArcGIS Indoors, combined with the comprehensive ArcGIS suite, has transformed how URI manages and shares spatial data. Authoritative datasets continue to grow while collaboration flourishes. With this approach, the spatial services team continues to chip away at existing data silos.
Going forward, the team plans to publish a new interactive university web map. URI is implementing ArcGIS GeoEvent Server to facilitate real-time mapping of university shuttles; the fire alarm status in buildings; and, in the future, parking lot capacity. The shuttles use TransLoc fixed-route and on-demand transportation solutions and the fire alarms use the Digitize alarm monitoring platform. URI is also evaluating how the university can leverage additional ArcGIS tools, such as the ArcGIS Data Interoperability and ArcGIS Workflow Manager extensions, to automate processes and integrate data with other university systems. With all these innovations and plans, ArcGIS is no longer just a tool at URI; it’s a strategic asset that drives innovation.


