In today’s data-driven world, organizations are looking to optimize their geospatial data management workflows. Migrating data from ArcGIS Online to an enterprise geodatabase can be a transformative step that provides numerous benefits. For example, with enterprise geodatabases, you can take advantage of functionality that is unique to an enterprise geodatabase, such as versioning. Versioning allows multiple users to edit data simultaneously, in isolation from one another, with the option to review any conflicts. This helps organizations with many editors more effectively manage updates to their most critical GIS datasets.
Regardless of the motivations for migrating your data, having a good understanding of the available options is crucial to avoiding potential complications.
However, there are a few prerequisites to begin the migration process. First, you must own the features associated with your ArcGIS Online login or be an administrator, or the owner or administrator must configure the layer to allow others to export data. Second, you must determine what format to use when exporting data. There are multiple options with different benefits and drawbacks. You will also need an enterprise geodatabase connection with a database user who has permissions to add data.
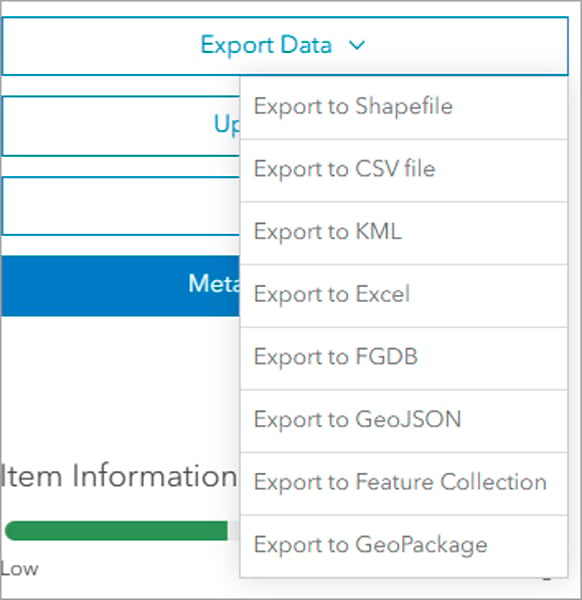
Export Data from ArcGIS Online
The Export Data menu is the primary option to download data from ArcGIS Online. This tool generates an item within your content in ArcGIS Online that encompasses the data from the selected layers in different formats. You can then download the data from that item to be used in ArcGIS Pro, Microsoft Excel, and elsewhere. The tool can be accessed from the item page when you want to download the full dataset.
There are multiple output formats to choose from. Depending on your workflow, you might choose one output format over the other.
- Use Export to Shapefile when most of your workflows are performed in ArcMap.
- Use Export to CSV file or Export to Microsoft Excel when you want to use the data in a tabular format or for data analysis. When you export point features to these formats, all attribute fields, and the x,y coordinates of each point, are exported. When exporting lines or polygons, only nonspatial attributes are extracted.
- Export to KML ensures you can use the data in ArcGIS Earth and Google Earth.
- Export to FGDB (file geodatabase) provides the most comprehensive export method. This is because it includes all the functionality applied at the feature class level, such as attribute domains, subtypes, contingent values, and attachments.
- Use Export to GeoJSON for the open data format that supports a seamless integration with JavaScript frameworks for exchanging and visualizing geospatial data on the web.
- Export to Feature Collection items are a subset of feature layers with focused and limited functionality.
- Use Export to GeoPackage when your analysis spans ArcGIS products and includes open data source software.
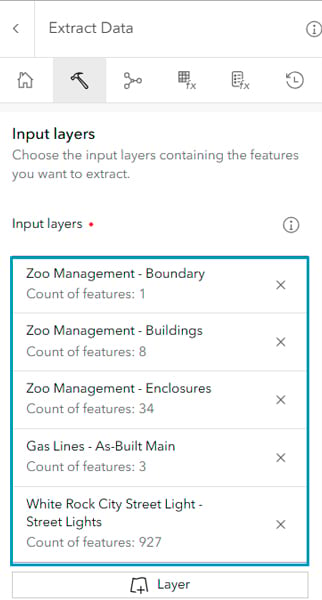
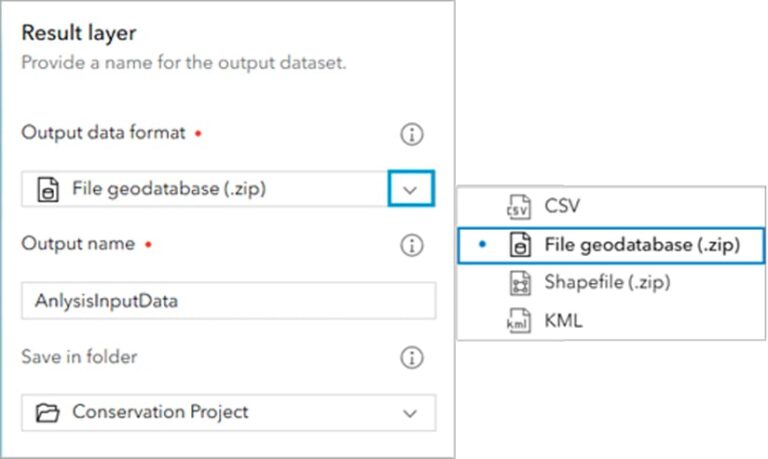
Alternately, you can access your data in Map Viewer using the Extract Data tool. This tool is located on the Analysis tab, and allows for more customization than the Export Data option on the item page.
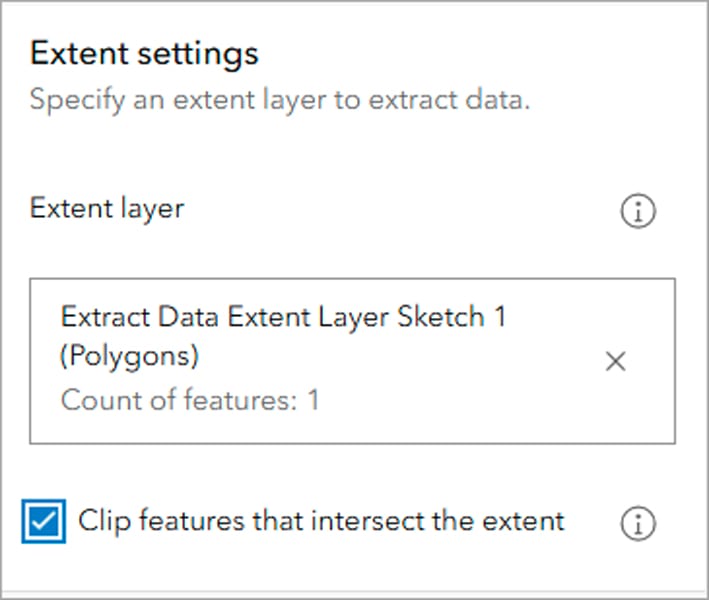
Using the Extract Data tool, you can extract data from multiple web layers from different sources as input. You can also specify an extent to extract data, with the option to clip features based on that extent.
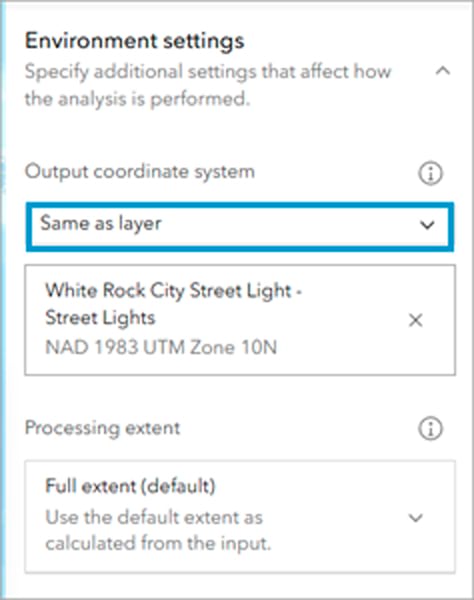
The Extract Data tool also comes with the ability to name the output file—which can only be a file geodatabase, .csv file, shapefile, or .kml file—and select the output folder. The Environment settings pane allows you to define the output coordinate system and the processing extent.
If the web layer you want to export doesn’t have the export option, ensure the Allow others to export to different formats option is checked.
Your output will be a hosted item containing a downloadable .csv file, file geodatabase, .kml file, or shapefile. You will then need to use the layer options to download the file locally before the data can be migrated to an enterprise geodatabase.
Import or Export Data from ArcGIS Online Using ArcGIS Pro
When accessing hosted feature camlayers in ArcGIS Pro, there are options available to import or export the data directly into an enterprise geodatabase.
First, it is necessary to connect to your ArcGIS Online account. You must be the owner of the data, or an administrator. If you are not the data owner or administrator, those users will need to share the dataset with you and configure the dataset to allow others to export the data. Sign in on the upper right corner of the ArcGIS Pro project.
To migrate the feature layer to an enterprise geodatabase, select your enterprise connection in the Catalog pane.
Click Import, then select Feature Class(es). The Feature Class To Geodatabase geoprocessing tool will open.
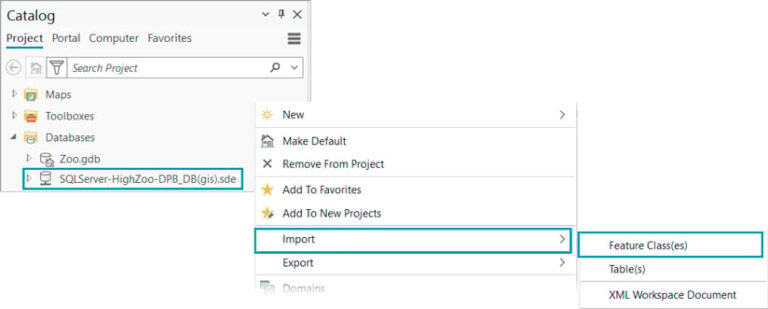
Note that choosing the Export option would also use the Feature Class To Geodatabase geoprocessing tool. A benefit of using Import is that it automatically populates the output enterprise geodatabase. Verify that the enterprise geodatabase connection is set for the data owner.
On the Feature Class To Geodatabase geoprocessing tool, select the browse button on the Input Features parameter. Select feature layers from ArcGIS Online or from a location downloaded from ArcGIS Online. You may need to extract the data first if the download is a .zip file.
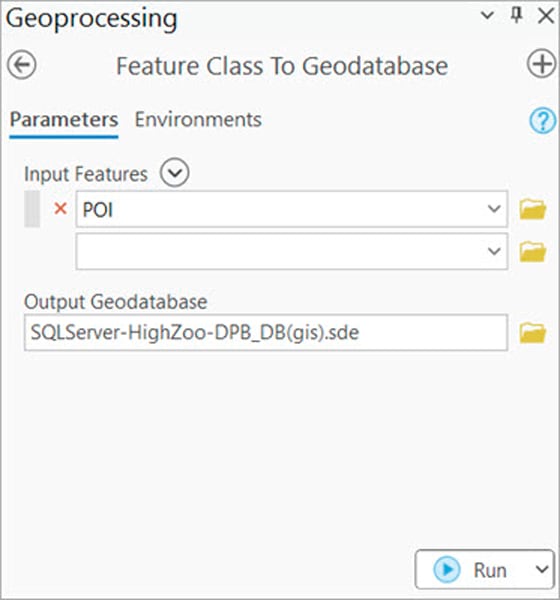
Verify the output geodatabase connection and environment settings before running the geoprocessing tool. For example, double-check the following options on the Environments tab:
- Preserve Global IDs
- Transfer Geodatabase Field Properties
- Import a subset of the data using the Extent environment

Export Features Option
Another way to migrate your data from ArcGIS Online to an enterprise geodatabase is within an active map in ArcGIS Pro. After adding the desired hosted web feature layer to the map, access the Export Features tool from the layer’s right-click context menu or from the Data tab on the ribbon. The output parameter can be set to convert the layer to a feature class directly in your enterprise geodatabase.
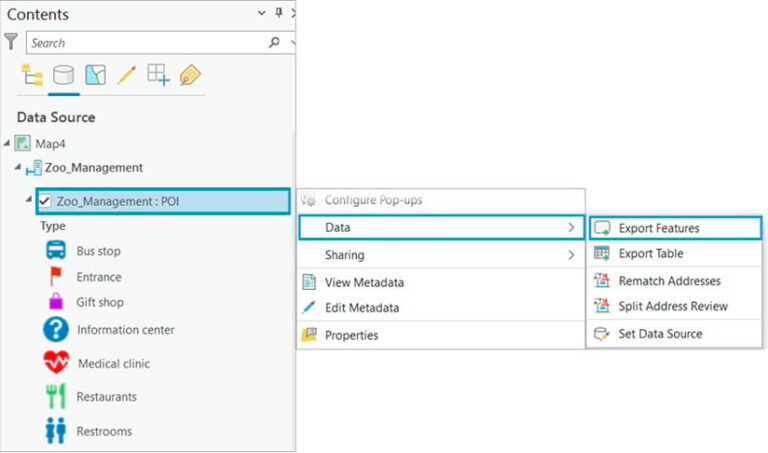
The tool allows for a single layer input, but you can customize it in several ways. Use it to define a SQL expression to select a subset of features; add, remove, reorder, and rename fields in the output feature class; or change field data type and merge field values into a single field.
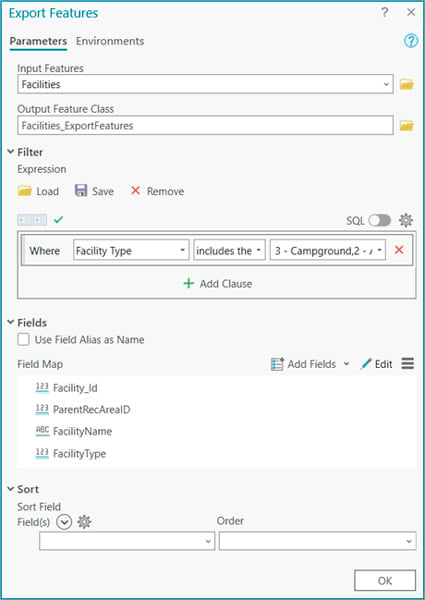
Finally, using the Environments tab, you can define a new coordinate system and preserve certain geodatabase functionalities such as the following:
- Maintain Attachments
- Preserve Global IDs
- Maintain fully qualified field names
- Transfer field domain descriptions
Note that you can also choose Export Table to export to a stand-alone table.
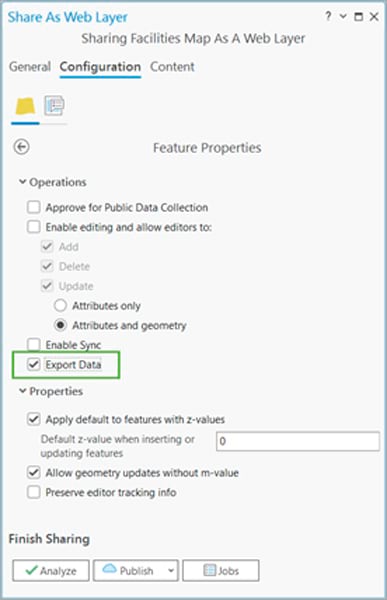
Sometimes the Export Features option will be grayed out on the web feature layer. Selecting Export Data avoids this situation. If you are a publisher in your organization and use ArcGIS Pro to share data with ArcGIS Online, enable the Export Data option during the publishing process. This controls whether a user other than the portal administrator or data owner can export the features from a web feature layer.
If you are not a publisher of the hosted layer or an administrator making changes to the existing web layer, try importing or exporting the data.
Download Data from ArcGIS Online Using ArcGIS API for Python
If you are a developer looking to eliminate manual steps or work with large volumes of data, you can download a copy of all your hosted web layers using ArcGIS API for Python. To extract data from one or more layers within a given extent, use the extract_data method. The extracted data format can be a file geodatabase, shapefiles, .csv, or .kml. Download and extract data with .zip files (such as File geodatabases and shapefiles) prior to using this method.
Downloading Services with Attachments
Downloading large feature services with attachments using the REST API can be challenging due to file size limitations. However, you can manage this by splitting the data into smaller batches. You can export subsets of the feature service data with attachments to a replica from a REST endpoint. Access this method from the View Details page. The Feature Service link opens the ArcGIS REST Services Directory page. A WHERE clause can be set to create a subset replica to an output URL. Once the replica creation is complete, download the .zip file and reference the data to migrate to your enterprise geodatabase.
When migrating data from ArcGIS Online to an enterprise geodatabase, there are multiple options to suit various workflow needs. Whether you are using the Export Data menu in ArcGIS Online, tools such as Feature Class To Geodatabase within ArcGIS Pro, or ArcGIS API for Python for large volumes of data, understanding and using these diverse options ensures that your organization can benefit from a seamless migration process and enhances your geospatial data management capabilities.



