In recent years, as wildfires have become more frequent around the world near developed areas and structures such as houses and roads, they have shifted from being merely an environmental threat to an existential one. Due to the growing ferocity of these wildfires, which in many cases makes them nearly impossible to manage, local governments have gone beyond equipping emergency services with response tools and begun focusing on prevention. Brush mitigation efforts, for instance, have proved essential in decreasing the chances of fires spreading to cities and critical infrastructure, ensuring the protection of residents as well as evacuation routes.
Southern European countries are among the most affected by wildfires every year. In certain areas, such as the Spanish region of Galicia, structural factors contribute to the proliferation of these fires. The ongoing depopulation of rural areas has led to the abandonment of agricultural land and its gradual conversion into forest. Consequently, forest coverage now accounts for almost 70 percent of the region, with more than 300 municipalities situated in its immediate surroundings.
GIS has become essential in enhancing wildfire prevention and minimizing its impact. A clear example of this is Xunta de Galicia, the regional government of Galicia. It has introduced a platform called Xesbio that is designed to manage the removal of dead wood and dry vegetation that builds up year after year.
Developed by Esri partner Vexiza using tools such as ArcGIS Web AppBuilder, Xesbio simplifies administrative tasks related to vegetation management. In Galicia, landowners are responsible for ensuring that plots near populated areas are properly maintained, which means both the regional government and local municipalities must monitor their progress before wildfire season to issue sanctions if necessary.
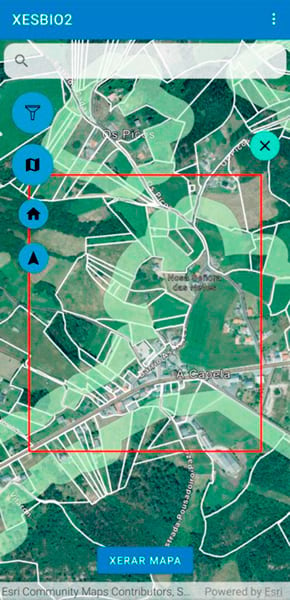
How ArcGIS Supports Risk Assessment and Vegetation Control
To assist workers responsible for verifying that parcels meet required standards, Vexiza developed a mobile field solution based on ArcGIS Runtime SDK for Android, enabling staff to record inspection data such as the presence of highly flammable biomass, along with photographs. Since many inspections are conducted in areas with limited connectivity, operators can work offline, and the data will synchronize once a connection is restored.
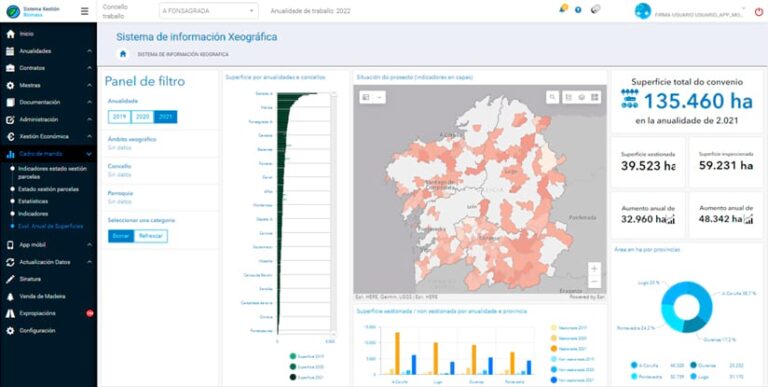
ArcGIS Web AppBuilder was also used to build dashboards that fully leverage GIS data. A key dashboard highlights the parcels that may pose a significant risk in the future based on automated criteria such as their location in areas that have previously experienced major wildfires. To achieve this, Xesbio is fully integrated with other ArcGIS ecosystems from Xunta, such as Xeocode, which is used for real-time wildfire management and from which Xesbio retrieves historical data.
Xesbio also integrates data collected during inspections, displaying the progress of cleaning tasks on the parcels on KPI cards and time-series graphs, while showing any parcels that are not yet in compliance on the map. This is further enhanced by the integration with available land records information, which includes details about parcel geometries, owners, and market value.
Moreover, since the regional government itself offers vegetation management services through a public entity, another dashboard allows users to check pending tasks on parcels that have signed agreements with that entity. This feature is particularly useful for identifying areas where work still needs to be completed, ensuring that every parcel is accounted for, and helping prioritize actions based on urgency and available resources.
This set of dashboards fully leverages the powerful customization capabilities of ArcGIS. Users can filter maps to display only the data that is most relevant to their specific needs, such as focusing on particular municipalities, provinces, or years. This level of customization ensures that each user, whether a local official or a wildfire prevention team member, can quickly access the insights they need without being overwhelmed by irrelevant data. As a result, decision-makers can enhance their analysis, identifying where resources are most needed.
Bringing Together GIS and Tools for Document Management
Within this ecosystem, additional parcel management tools are integrated with spatial information, allowing for a comprehensive and efficient approach to vegetation management and wildfire prevention. One of the key features of this system is the ability to handle contract agreements directly with landowners for biomass removal services.
The platform also allows for the issuance of official notifications to landowners whose parcels fail to meet fire safety regulations, prompting them to take action before wildfire season. These notifications are legally binding and can be tracked within the system, ensuring that no parcel is overlooked. Thus, local authorities can enforce regulations more effectively, fostering greater accountability and enhancing overall fire safety standards in the region.
By integrating ArcGIS technology into every stage of the wildfire prevention process and ensuring full traceability of all managed information, with every action taken on a parcel being recorded, Galicia has made significant progress toward a more resilient approach to managing fire risk, safeguarding its residents and critical infrastructure.