By Heather Smith
In this tip article, you’ll use data to create a hosted feature layer and a hosted feature layer view in ArcGIS Online. You’ll also share the hosted feature layer with your organization and enable editing, and then share the view layer with the public and disable editing.
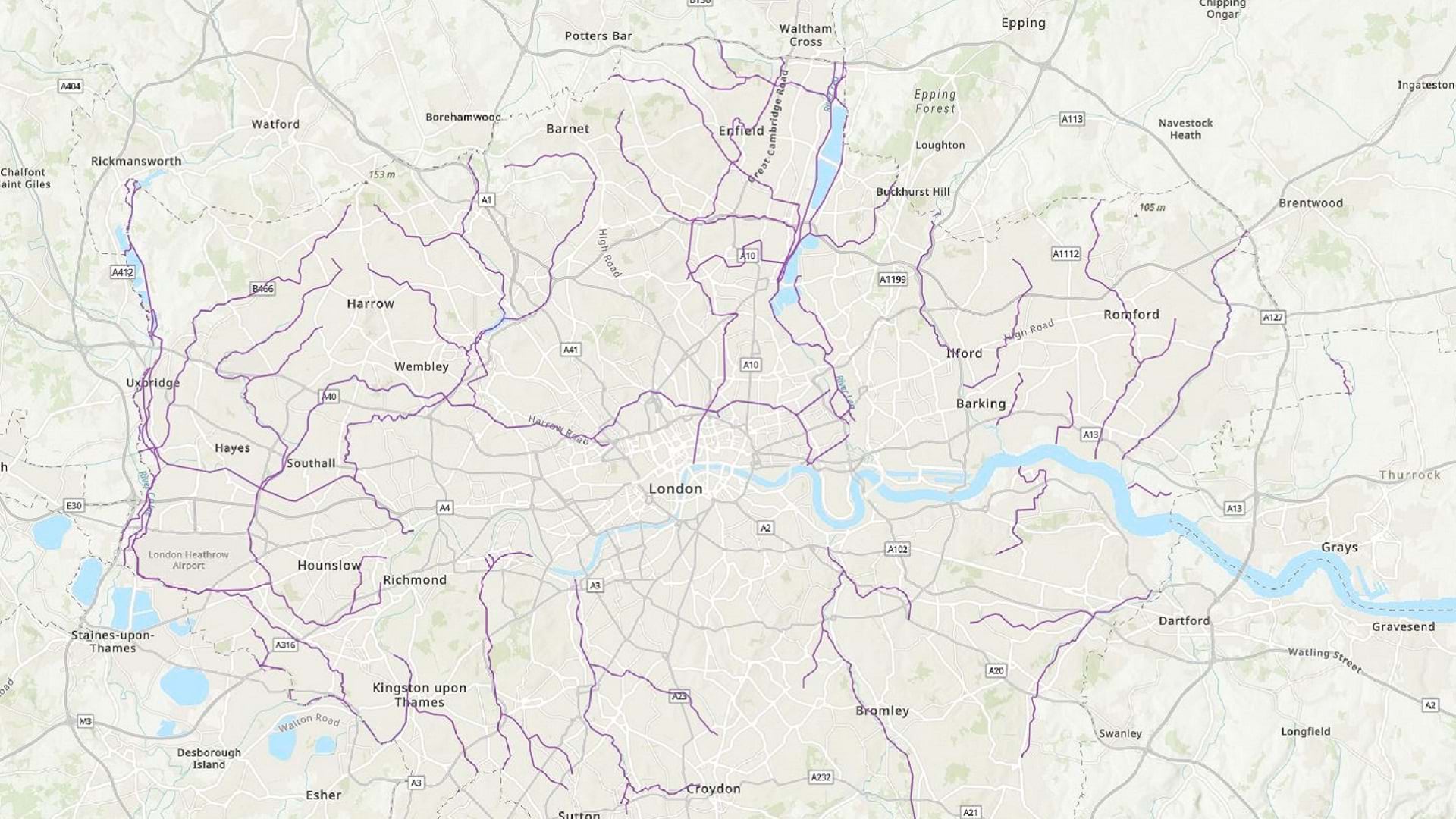
For this exercise, imagine that you have data that maps the water quality of streams in London, England. You want your colleagues to be able to edit this data as updates come in. However, you also want to share the data in a public-facing map, and you don’t want to allow the public to edit it.
For this tip, you’ll need an ArcGIS organizational account with a publisher, facilitator, or administrator role (see options for software access).
Step 1. Publish a hosted feature layer
You’ll start by adding your data to ArcGIS Online.
- Download the London geodatabase. A file named London.gdb.zip is downloaded to your computer. Do not unzip it. The file geodatabase (.gdb) is a common data format for desktop GIS. It’s a container that can store multiple layers of spatial and nonspatial data. To use a file geodatabase in ArcGIS Online, you must upload a zipped copy of the .gdb file.
- Sign in to your ArcGIS organizational account.
- On the ribbon, click the Content tab.
- Click the New item button.
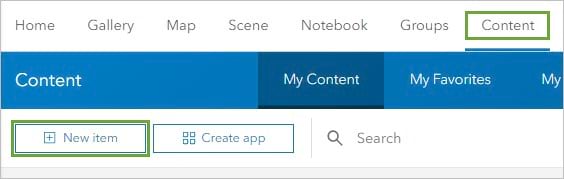
5. Drag the London.gdb.zip file to the New item window. (Alternatively, click Your device and browse to the .zip file.)
6. For File type, choose File geodatabase.
7. For How would you like to add this file, ensure that Add London.gdb.zip and create a hosted feature layer is selected.
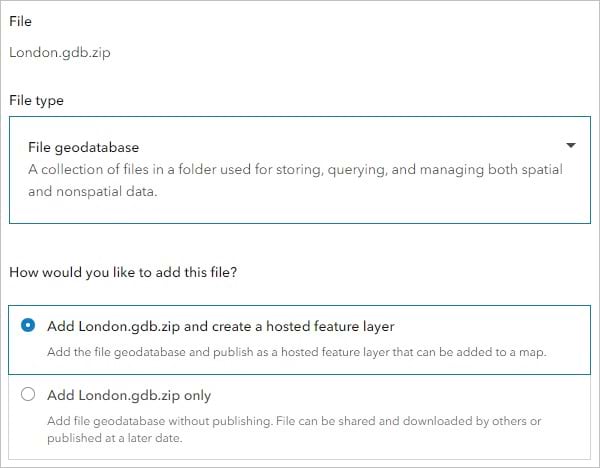
This option will create two new items in your ArcGIS Online account. One will be a copy of the file geodatabase. The other will be a feature layer created from the contents of the file geodatabase. You need the data in the feature layer format before it can be used to create maps in ArcGIS Online.
8. Click Next.
9. For Title, replace the text by typing “London Water Quality (gdb)”, followed by your name or initials (for example, London Water Quality (gdb) XX).
Note that you cannot create two layers in an ArcGIS organization with the same name. Adding your initials to a layer name ensures that other people in your organization can also complete this tutorial. Once a layer has been created, you can rename it in the map to remove your initials. This will not affect the name of the underlying data layer.
10. For Summary, type “Water quality of London’s rivers and other waterbodies from the Environment Agency”. (These details can be modified later.)
11. Click Save.
The item page for the new feature layer appears. The item’s name is London Water Quality (gdb) XX, and the item type is listed as Feature layer (hosted).
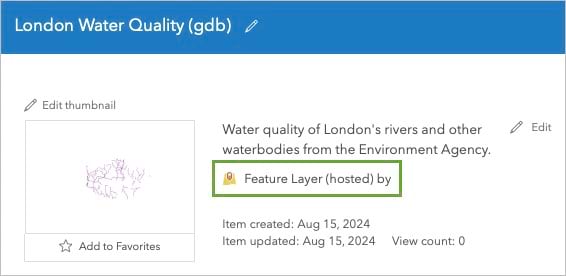
Hosted items are source layer items. They represent a dataset, whereas items that are not hosted only reference a dataset. If you delete a hosted feature layer, the data is also deleted. If you delete a feature layer that is not hosted, only the layer is deleted, and the data remains accessible for other layers to reference.
You will only see the (hosted) label when an item is hosted and it is owned by you. (If you have an administrator account, you will see the (hosted) label for items owned by anyone in your organization. You can read more about feature layers and hosted feature layers in the documentation.)
Because this layer is hosted and owned by you, you can manage the capabilities and schema of the data, rather than just the layer properties. You’ll take advantage of this later, when you enable editing.
Step 2. Enable editing
Because this layer is hosted and owned by you, you can always edit that data.
Next, you’ll share the layer with the other people in your organization and ensure that they can edit the data too.
- Click the Share button.
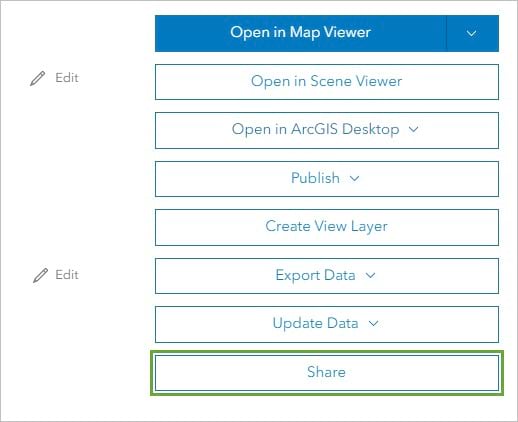
2. In the Share window, for Set sharing level, choose Organization.
3. Click Save.
Now, anyone in your organization can find and view this layer. You’ll update the Description section so that they can find more information about the data.
4. To the right of Description, click Edit.
5. Copy the following text, then paste it into the text box:
Source: https://data.london.gov.uk/dataset/water-quality-london-rivers-other-waterbodies
Date accessed: November 29, 2022
License: https://www.nationalarchives.gov.uk/doc/open-government-licence/version/3/
6. Click Save.

Next, you’ll enable editing on the layer.
7. On the ribbon, click the Settings tab.
8. Scroll down to the Feature layer (hosted) section and check Enable editing.
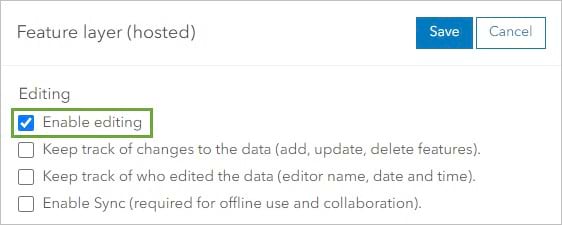
To learn more about the editing options, read the article on managing hosted feature layer editing.
9. Click Save.
Step 3. Create a hosted feature layer view
You now have a layer that people in your organization can view and edit. Next, you’ll create a layer that the public can view but cannot edit.
1. Scroll back up. On the ribbon, click the Overview tab.
Since you’ll be creating a new version of this layer, you will first change its name to make it clear which layer is for which purpose.
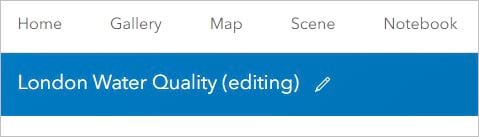
2. On the ribbon, next to the title, click the edit button.
3. Change the item’s name to the following: London Water Quality (editing)
4. Click Save.
Next, you’ll create a hosted feature layer view. The new layer view will not be a new dataset. Instead, it will reference the data from the London Water Quality (editing) layer. The layer view allows you to show the same data with different properties and settings. You need a layer view so that you can change the sharing and editing settings.
Note that you can only create layer views from hosted feature layers that you own.
For other feature layers, you can save a copy. This method won’t allow you to change editing settings, but it will allow you to change layer properties.
5. Click the Create View Layer button and choose View layer.

The Create View Layer window appears. The London Water Quality (editing) layer is selected in the Layers pane.
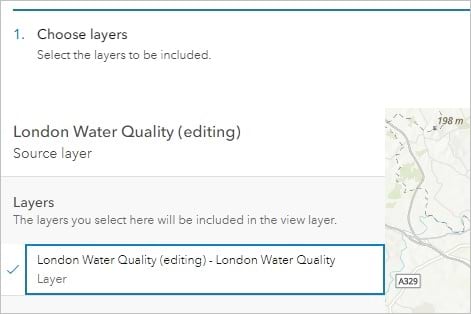
6. Click Next.
The next step, Define view, is optional and allows you to configure a filter, an area or interest, or fields. For this exercise, you don’t need to change any of these properties.
7. Click Next.
8. At the end of the Title text, add your name or initials (for example: London Water Quality (editing) view XX).
9. Click Create.
The item page for the new layer appears.
10. Change the layer’s title to London Water Quality. Click Save.
The item type is listed as Feature Layer (hosted, view).
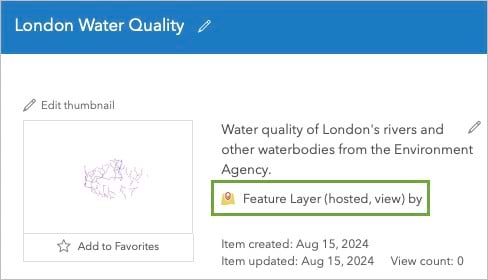
This layer view references the same data as the London Water Quality (editing) layer it was created from. When you or a coworker make updates to the data in the London Water Quality (editing) layer, those changes will also appear in the London Water Quality layer.
Next, you’ll update the sharing and editing settings.
11. Click the Share button.
12. For Set sharing level, choose Everyone (public).
13. Click Save.
14. On the ribbon, click the Settings tab.
15. Scroll to the Feature layer (hosted, view) section. Note that the Enable editing setting is unchecked and unavailable.
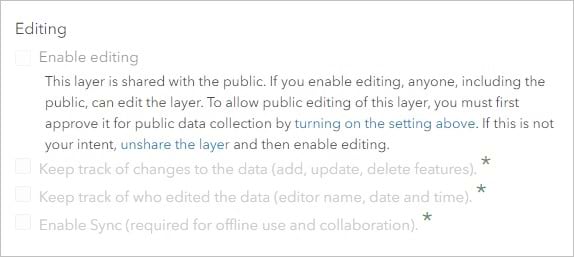
This setting became unavailable when you shared the layer with the public. You can still enable editing (if you first enable Public Data Collection), but it is unavailable by default to prevent you from accidentally allowing the public to edit the data.
Step 4. Review items
To finish, you’ll review the layers you created and confirm that they are shared appropriately.
- Scroll back up to the top. On the ribbon, click the Content tab.
2. Below Folders, make sure that All my content is selected.
There are three new items at the top of the content list:
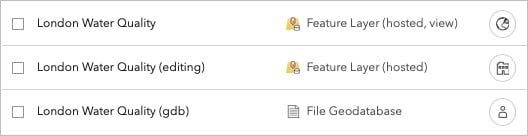
London Water Quality is a hosted feature layer view. It is shared with everyone. This is the layer you’ll expose in a public-facing map so that people can check the quality of waterways.
London Water Quality (editing) is a hosted feature layer. It is shared with your organization. This is the layer that you and your coworkers will edit as new water quality test results are reported.
London water quality (gdb) is a copy of the file geodatabase that you uploaded at the start of the tutorial. You can’t visualize this item on a map in ArcGIS Online. Its sharing level is set to Owner. No one needs access to this item except for you.
To summarize, you have now published a file geodatabase as a hosted feature layer and used it to create a layer view. You shared the layer with your organization and enabled editing so that your coworkers can update the data. You shared the layer view with the public and did not enable editing.
Next, you can send a link to the London Water Quality (editing) layer to your coworkers to confirm that they can edit the data. To confirm that editing is disabled on the London Water Quality layer, you can sign out of ArcGIS Online to simulate how a member of the public would interact with the layer.
This tutorial was last tested on April 23, 2025.