Commercial airports today face the challenge of accommodating an increasing volume of passengers and aircraft. This surge necessitates the expansion of both airside and landside infrastructure and services. Planning, building, and maintaining facilities to accommodate growth while also providing excellent customer service requires substantial revenue.
The majority of airports revenue is derived from two sources: aeronautical and non-aeronautical charges. Because these income streams are influenced by location-based factors, it is essential for airports to integrate tools that can optimize this relationship. To manage these location-based revenue streams effectively and ensure long-term sustainability, smart airports are increasingly leveraging Geographic Information Systems (GIS). In this blog, we will explore how airports can optimize indoor space management, harness real-time data, and implement innovative solutions to enhance both operational efficiency and passenger experience.
Managing Efficient Aircraft Locations
Airports use the interactive Aircraft Parking app as a planning tool to situate and track true-to-scale 2D digital models of commercial aircraft. This app helps visualize how to maximize space utilization and track where aircraft, identified by unique tail numbers, are parked and for how long. Airports charge airlines a fee to park these planes overnight, while they are in maintenance, or if they are taken out of service (mothballed).
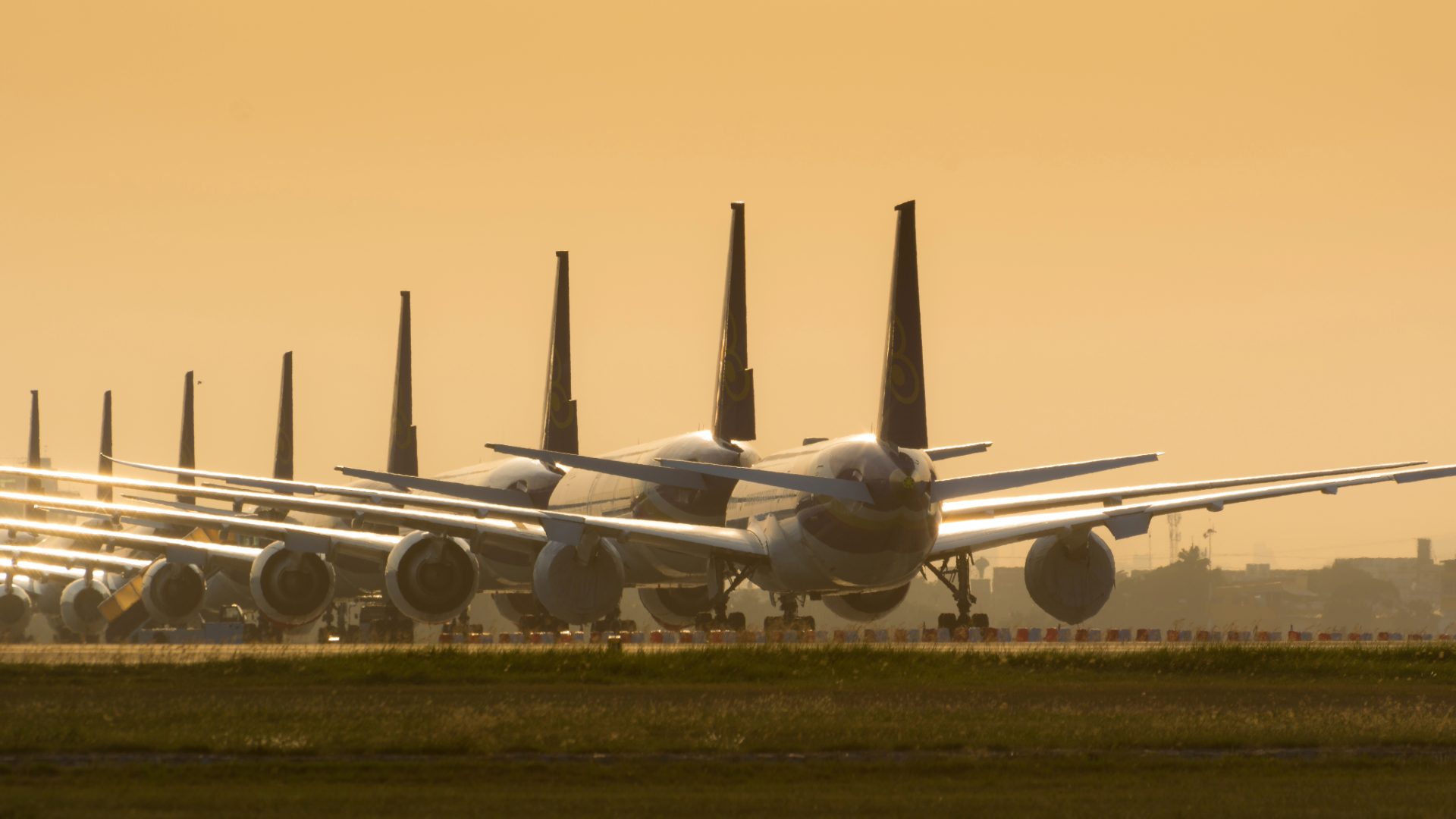

For example, during the height of the Covid-19 pandemic, when travel was halted, many commercial aircraft were temporarily mothballed due to the dramatic decline in air travel. Airport planners utilized a GIS application to maximize ramp space by situating aircraft shapes in areas that could accommodate planes based on their wingspan, weight, and fuselage length. Different plans were developed considering the potential types of aircraft parked in these spaces. Placement, orientation, and attribution (tail number, aircraft type, carrier, date in/out), and tracking rental rates were made easy with this web app.
A dashboard was used by managers to visualize the location of mothballed aircraft, how long planes had been parked, and the rent the carrier was being charged to store their aircraft. ArcGIS Field Maps was used by field crews who would verify daily aircraft locations along with photographs so that the data would be up to date.
This application has evolved into a tool that airports can use in everyday operations to assist in gate assignment / management, for overflow, overnight parking, diversions due to maintenance or bad weather, and for long-term storage of aircraft undergoing refurbishments.
Optimizing Indoor Space Management
Airports generate significant revenue from leasing spaces to vendors in the terminals and across the airside. Managing these spaces is a complex, full-time task, as lease spaces and floor plans change regularly, and lessees/vendors come and go. Maintaining an up-to-date system of record inside terminals poses challenges to property managers and teams responsible for managing interior real estate. Furthermore, having real-time access to map-centric lease information has been a persistent challenge. Many airports still rely on spreadsheets, cumbersome paper-based systems, or systems that exclude a map to track lease spaces and activity, which is not efficient.
Indoor GIS provides the foundation for airports to optimize their indoor operations, enhance passenger experiences, and improve overall efficiency. Leveraging indoor mapping and location intelligence, ArcGIS Indoors provides a comprehensive view of airport facilities, assets, and operations in floor-aware 2D and 3D environments. An indoor digital twin, or 3D accurate representation of indoor spaces, is particularly helpful with lease management at airports.
Using ArcGIS Indoors, airports are streamlining their space management by mapping lease spaces. Many airports are deploying floor-aware maps and apps where lease spaces are linked through the space’s unique “address” or ID to 3rd party lease management systems like Amadeus PROPworks and others. With these links established, ArcGIS Indoors enables property managers to view detailed, floor-aware interior plans that accurately represent the layout of lease spaces. Additionally, valuable information can be calculated or enriched with external sources such as exhibits, floor plan layout, use type, square footage, lease terms, and revenue, can be configured in Indoors Viewer.
By having this detailed authoritative information readily available in a digital format, space planners can easily visualize and analyze lease spaces and activity. Indoors Space Planner is an app that allows you to visualize and plan occupant assignments in indoor spaces, such as quickly identify available spaces, occupancy rates, lease terms, and other important details. For example, airports use the browser-based Space Planner to plan current and future changes to the workspace.
Advancing Space Management by Taking Real-Time GIS Indoors
ArcGIS is open and designed to integrate well with other enterprise systems and sensors like Wi-Fi and CCTVs. With these sensors, airports gather anonymous passenger location information which is used to visualize and understand occupancy rates and fluctuating volumes of foot traffic. Real-time GIS enables anonymously mapping and tracking of passenger movement through terminals, giving decision makers a keen understanding of density and volumes of customer traffic. By analyzing real-time passenger flow and asset and facility usage data on an indoor map, decision makers can identify bottlenecks and optimize space allocation. This helps them draw informed conclusions that increase revenue and operational efficiency. Additionally, this information supports data-driven decisions about rental rates based on the traffic a given lease space sees over time. Spatiotemporal data can be visualized and analyzed within ArcGIS, providing valuable insights into the performance and utilization of lease spaces.
Another key benefit of indoor GIS is its ability to improve the passenger experience. By providing indoor wayfinding, airports can help passengers easily navigate through terminals, locate amenities, and more efficiently find their way to their gates. Managing passenger travel inside the terminal can increase loiter times, giving passengers the opportunity to shop, visit concessions, and ultimately spend more money during their time in the terminals. Additionally, clearly communicating travel time reduces uncertainty, affording passengers more time for leisure and freedom to spend time in other places.
Improving parking is essential for enhancing the passenger experience and growing revenue. By utilizing both indoor GIS and real-time GIS, airports can optimize their parking facility operations. ArcGIS is utilized to map multi-level parking garages, allowing facility managers and planners to access parking availability and historical usage through dashboards. It also provides tools to improve space planning and management, which can be used to optimize the airport’s office, operational, and parking spaces. These dashboards help viewers understand parking utilization, visualize occupancy patterns, and select suitable spaces for reserved parking.
Real-time GIS, powered by ArcGIS Velocity, enhances airport parking operations by analyzing real-time data from various sources to monitor parking space availability and occupancy levels instantaneously. This capability enables facility managers to make quick, informed decisions that improve traffic flow and reduce congestion in and around parking areas. Additionally, integrating ArcGIS Velocity with smart parking systems allows airports to communicate current availability to passengers via mobile apps or digital signage, significantly enhancing their experience. The ability to visualize historical usage patterns through interactive dashboards further aids airports in identifying peak times and optimizing pricing strategies.
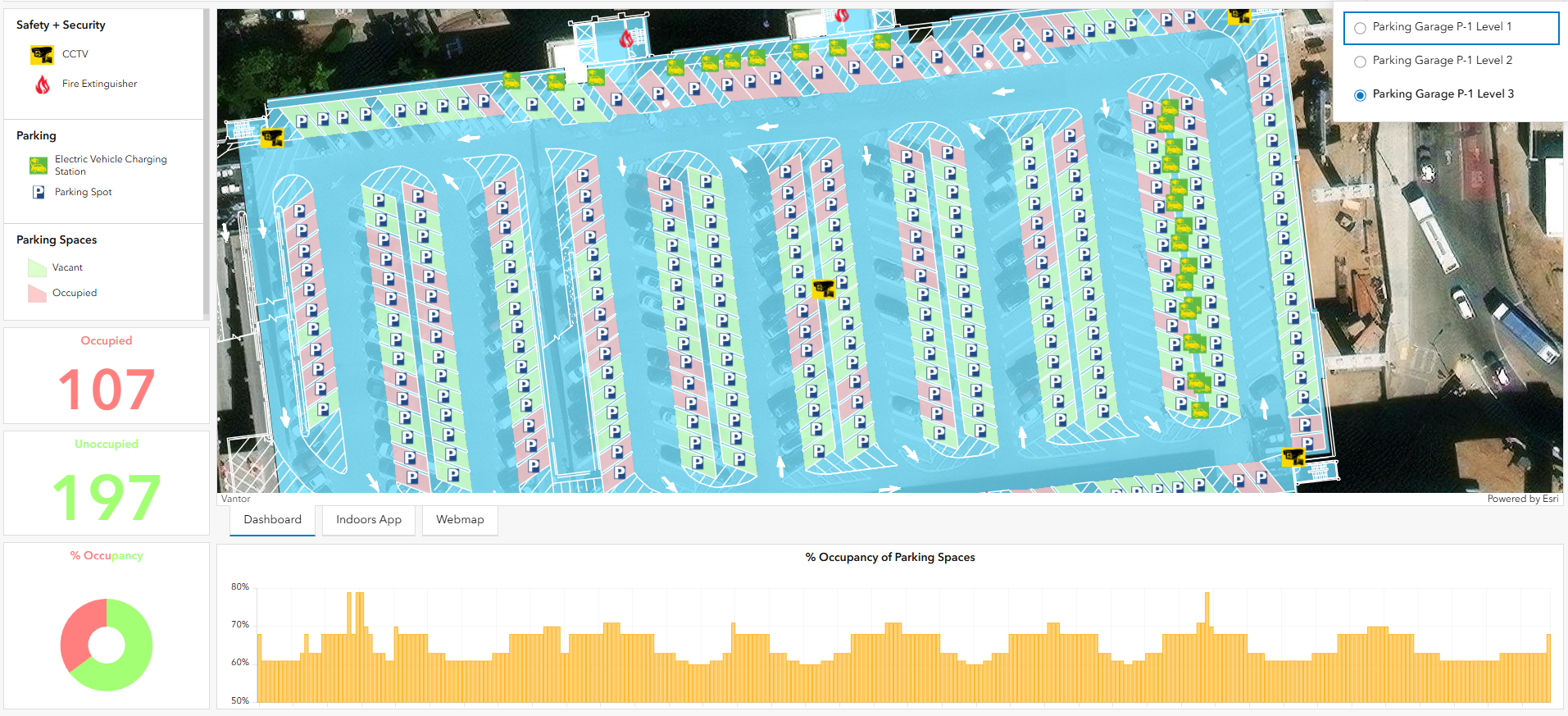
Comprehensive maps with asset locations and information provide the foundation for efficient field operations. To create and maintain these maps, curators of indoors data can use ArcGIS Pro or a purpose-built web app to create, edit, modify, and update physical spaces and information about them. Mobile and field workers can use Survey123, FieldMaps, and similar apps to collect and update asset data and report issues or maintenance needs for EV charging stations and other garage assets. Routine maintenance, like repainting space numbers, is made more efficient by reporting and tracking this work with a mobile app. An application that passengers can use to reserve a parking space is also in the suite of tools that airports can quickly deploy.
Conclusion
The integration of GIS in airport operations is revolutionizing revenue management and operational efficiency. By leveraging ArcGIS, airports can optimize space utilization, streamline lease management, and enhance the overall passenger experience. These smart solutions not only improve the management of aircraft and indoor spaces but also provide valuable insights through real-time data analysis. This enables airports to make informed decisions, ultimately boosting profitability, and ensuring long-term sustainability. As airports continue to adopt and innovate with GIS technology, they are well-positioned to meet the growing demands of modern air travel while maintaining high standards of service and efficiency.



Article Discussion: