
ArcGIS IPS enables indoor positioning by putting a blue dot on indoor maps, allowing you to locate yourself and others inside a building in real-time. When used with ArcGIS Field Maps, it enables indoor location awareness for asset inspections and location sharing for safety and security use cases. It also enables wayfinding when used with the ArcGIS Indoors Mobile app.
The May 2025 ArcGIS IPS release brings updates to ArcGIS Pro 3.5, enhancements to the ArcGIS IPS Setup 1.7 mobile application, and new features in ArcGIS Maps SDKs for Native Apps 200.7. This release aims to improve indoor positioning accuracy, particularly when the device is stationary or running on Android OS.
Features included with ArcGIS Maps SDKs for Native Apps 200.7
Adaptive radio positioning
To put it simply, indoor positioning within ArcGIS IPS is done by matching received radio signal strength values from nearby Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) beacons or Wi-Fi access points against positioning data stored in the Indoor Positioning Data Service (IPDS). The device’s location is calculated based on cross-referencing the real-time signal data and positioning data generated within ArcGIS Pro.
In this release, positioning accuracy has been improved using enhanced algorithms in indoor location data source (ILDS), also called IPS engine. The more ILDS is used for indoor positioning, the more statistics on received radio signals are collected and stored locally on the device. Now, ILDS uses them for more accurate matching against the data stored in IPDS, resulting in reliable positioning in extended or subsequent sessions.
A challenge with the radio signal strength matching principle is that indoor positioning accuracy can vary depending on the hardware used. Devices with lower-quality sensors often struggle to detect weaker signals, such as those emitted from BLE beacons that are farther away from the device’s current location. Devices with highly sensitive built-in sensors are more capable of detecting both strong and weak radio signals equally well. Sensor performance on iPhone devices is consistently high across models, whereas Android devices, due to their wide variety, may include models with lower-quality sensors. The survey-based positioning data generated using phones with highly sensitive sensors may include weaker signals that some Android phones may interpret incorrectly. This can lead to reduced positioning accuracy on lower-end Android devices.
Note: Refer to the list of recommended devices for ArcGIS IPS.
The new adaptive radio positioning algorithm addresses this issue by continuously adapting the incoming radio signals and aligning their characteristics with the reference positioning data stored in IPDS. This facilitates a more consistent indoor positioning performance across all Android devices. The adaptive radio positioning feature is available only on Android devices. As specified in the recent ArcGIS Pro documentation, to enable it, IPDS shared from ArcGIS Pro 3.5 must include the beacons’ locations along with other information, such as their transmitter ID and associated level ID.
Stand still filter
Radio signals are prone to continuous fluctuations, meaning their values can vary even when the device remains stationary. This may result in a jittery or unstable position when standing still. The standing still filter suppresses these updates when the user remains in one place, making the blue dot stay stable.
Improved startup
In Native Maps SDKs 200.6 and earlier, if location services were not enabled or if the required permissions weren’t granted, ILDS would still initialize but will output no positions.
With the new updates introduced in 200.7, ILDS waits for each sensor and data provider to be activated. If all sensors (BLE, Wi-Fi) and data providers (Apple IPS, GNSS) used for indoor positioning cannot be activated, ILDS will fail to start and report an error. The sensors used for indoor positioning depend on the map’s configuration and the type of positioning data (BLE or Wi-Fi) associated with it.
If one of the sensors cannot be activated or suddenly stops working on the mobile device, ILDS raises the appropriate warnings.
Features included with ArcGIS Pro 3.5
Adaptive radio positioning support
To enable adaptive radio positioning, introduced in the previous section, the Indoor Positioning Data Service (IPDS) must include information about beacon locations along with their relevant attributes, which IPS Engine takes advantage of to improve the estimated position.
ArcGIS Pro 3.5 introduces a new IPS Beacon Features parameter in a survey-based method in the Generate Indoor Positioning Dataset tool to support that feature. This parameter is already present and required in a survey-less method.
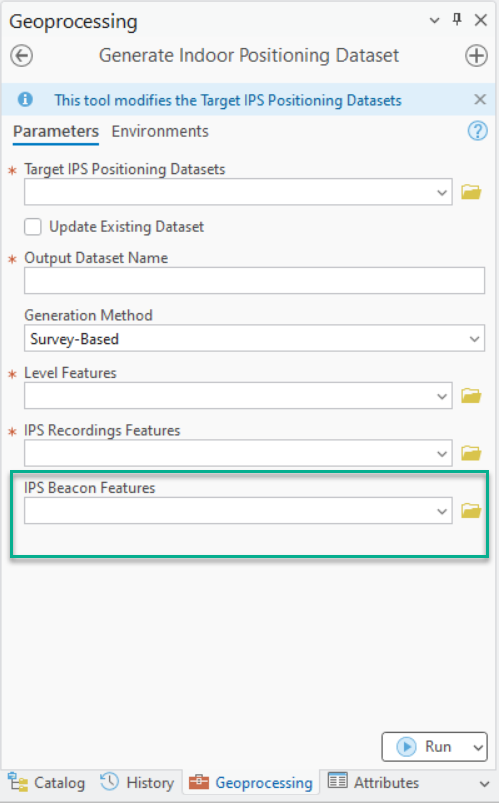
If beacon features are provided in a survey-based method, the generated IPS positioning dataset in IPS_Positioning_Datasets feature class includes the attachment with the necessary beacon information to support adaptive radio positioning. Since IPS Beacon Features is a required parameter in a survey-less method, the attachment is always generated.
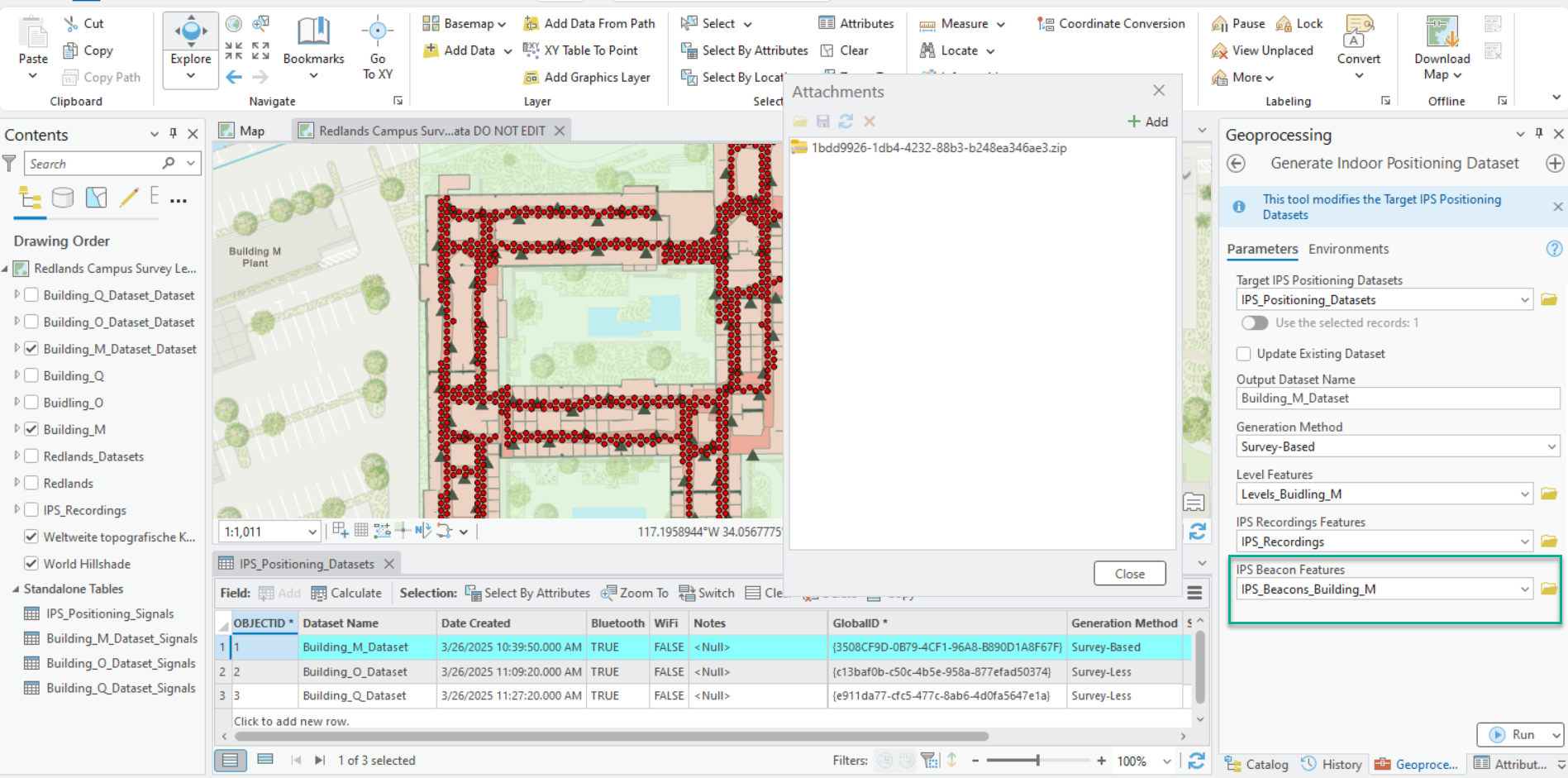
Once the IPS positioning dataset is generated, it can be shared as an Indoor Positioning Data Service for use by IPS Engine.
ArcGIS IPS Setup 1.7
Reconfigure ILDS parameters
Indoor positioning configuration parameters were introduced in ArcGIS Pro 3.4 to empower IPS administrators to refine and set custom configurations for their web maps when and if needed. These parameters can be applied in ArcGIS Pro in the map properties when sharing or configuring the IPS-aware map. These default or custom values are used when initializing ILDS.
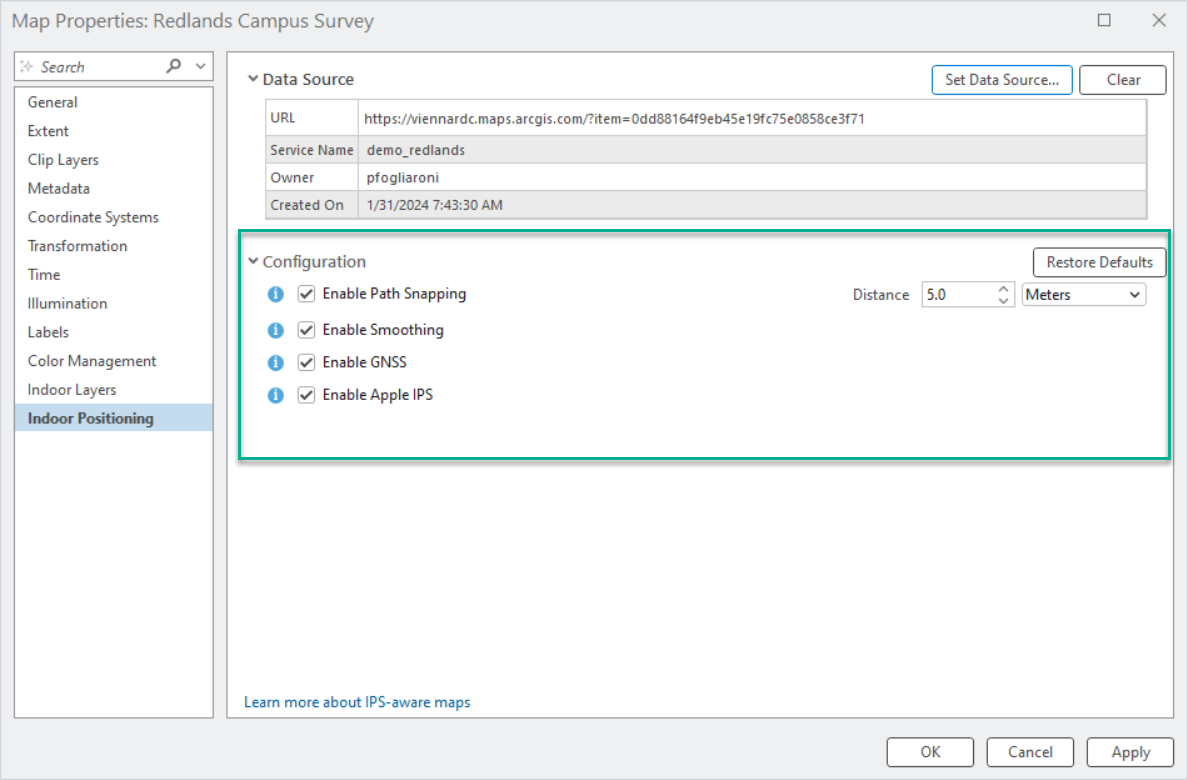
In this ArcGIS IPS Setup release, configuration parameters such as Path Snapping Distance, Use GNSS, and Use Apple IPS are also accessible to onsite indoor positioning system testers and technicians within the mobile app. These parameters enable the fine-tuning of IPS engine settings, helping to evaluate and optimize indoor positioning performance.
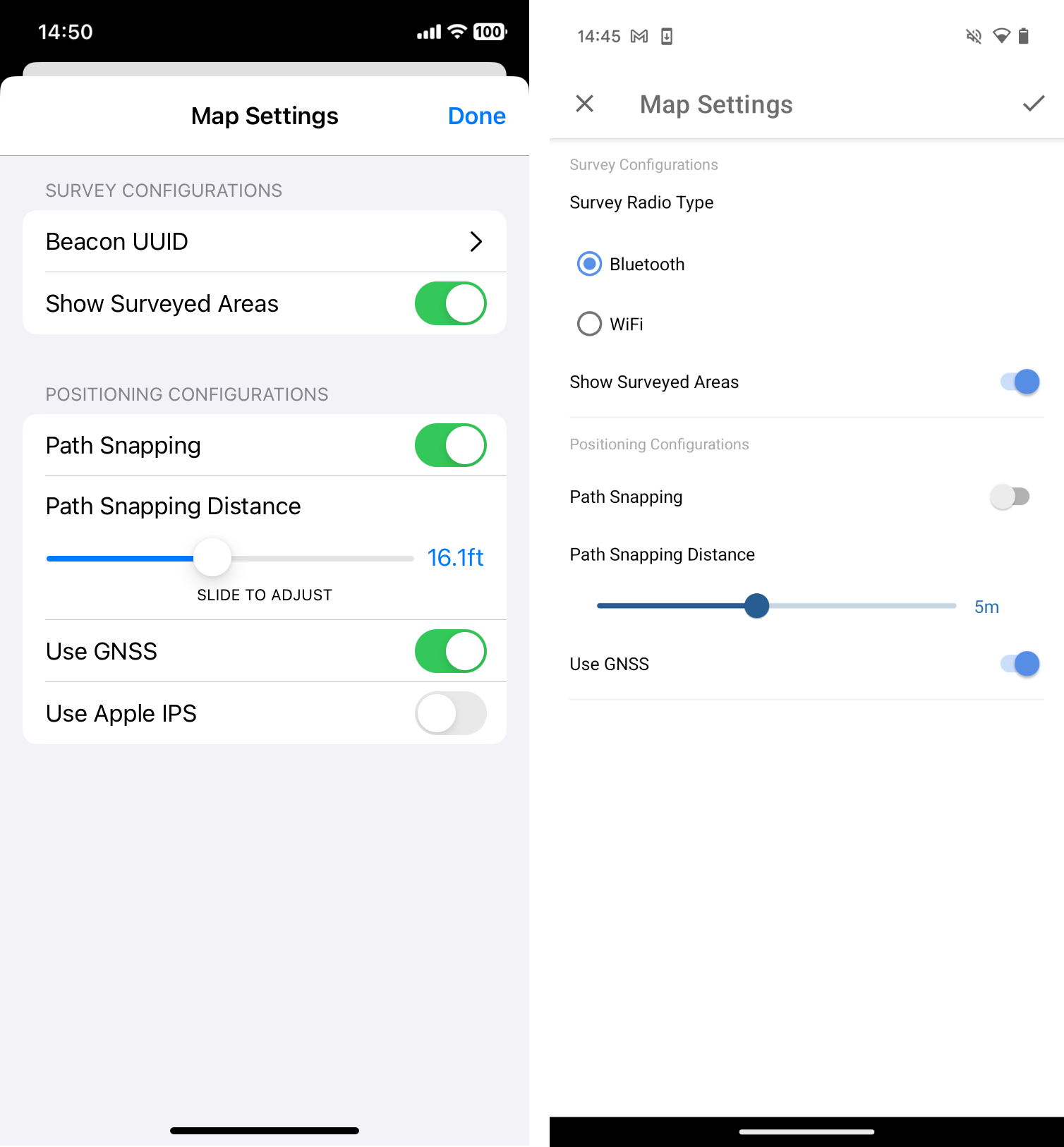
Changes made in the configuration within ArcGIS IPS Setup are local, meaning the custom parameters are consumed by the IPS engine only on that specific (test) device. In the future, users with appropriate privileges (e.g., IPS-aware map owners or organization admins) might be allowed to sync those changes with the hosted IPDS, applying the selected custom configuration to all users of the map.
The last enhancement ArcGIS IPS Setup brings in the 1.7 release is additional information about the positioning data powering a specific IPS-aware map. This information is presented in the Indoor Positioning Data section of map details accessible from the app’s map list.
For more information, please visit the ArcGIS IPS product page. Ask questions and stay up to date by joining our Esri Community place.

Article Discussion: