ArcGIS Data Reviewer is an extension to ArcGIS Pro and ArcGIS Enterprise that automates, simplifies and improves data quality management workflows. The release of ArcGIS Pro 3.5 and ArcGIS Enterprise 11.5 expands on the validation methods that automate the detection of poor-quality data. These include a new check for supporting attribute rule-based data validation and a significant expansion in the validation checks that support interactive evaluation of data quality.
Continue reading to learn more about what’s new in the ArcGIS Data Reviewer May 2025 release.
Don’t have time to read the blog article? View the video below instead.
Data Reviewer checks in attribute rules
Valency Check
The Valency check is now available in attribute rule-based workflows for ArcGIS Pro 3.5 and ArcGIS Enterprise 11.5. This check validates relationships between points or nodes of polyline features that intersect with a specified number of other polyline features. The check is commonly used in industries that maintain linear assets such as water, wastewater, and gas utilities.
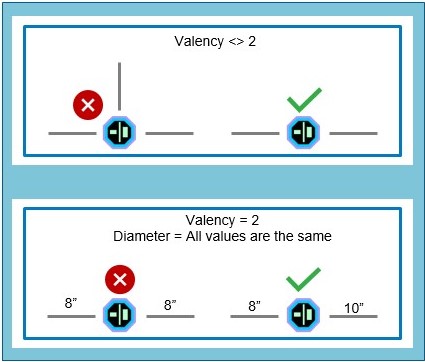
Watch the video to see how the Valency check is used to identify errors in a water utilities scenario.
Data Reviewer checks for ad hoc validation
In ArcGIS Pro 3.4, a new workflow for automating the detection of poor-quality features was released. The Run Data Checks tool is easy to use, often requiring only a few mouse-clicks to identify poor quality data. In the ArcGIS Pro 3.5 release, an additional twenty-eight (28) checks were added to this interactive quality control workflow.
Watch the video to see how this new workflow is used to identify errors in indoor maps.
Feature Integrity Checks
Assess a feature’s integrity with the Duplicate Vertex, Evaluate Part Count, Evaluate Vertex Count, and Nonlinear Segment checks.
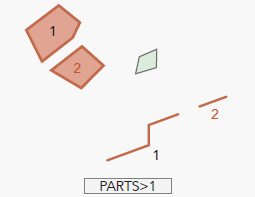
The Evaluate Part Count check is a frequently used check that identifies features that contain multiple parts. In water utilities, multipart features are problematic when conducting tracing operations.
Linear-referenced Feature Integrity Checks
Evaluating the integrity of linear-referenced events is now supported with the Find Event Gaps, Find Event Overlaps, Find Orphan Events, and Invalid Event Measure checks.
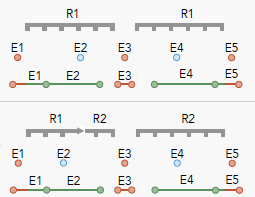
The Invalid Event Measure check finds linear-referenced events that contain invalid measure values. The check identifies invalid measures on events within the same route or across multiple routes.
Assessing Feature Attribution
Improve workflows by assessing a feature’s attribution with the Regular Expression, Relationship, and Unique Field Value checks.
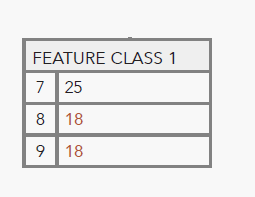
The Unique Field Value check identifies duplicate attribute values in defined fields. In address data management, a requirement of NextGen-911 is that each addressing feature (road centerline, site structure address locations) be assigned a unique identifier value that is not duplicated in the same dataset.
Identifying errors in polygon features
Identify specific errors and conditions in polygon features concerning their area, perimeter, gaps, overlaps, and thinness with the Evaluate Polygon Perimeter and Area, Polygon Gap is Sliver, Polygon Overlap is Sliver, and Polygon Sliver checks. Identify errors related to holes, unclosed rings, and unnecessary shared boundaries in polygon features with the Find Polygons with Holes, Unclosed Polygon, and Unnecessary Polygon Boundaries checks.
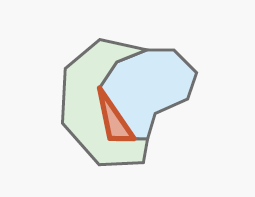
The Find Polygon Gap is Sliver check finds gaps between polygon features that are slivers based on their shape and, optionally, size. Sliver gaps between polygon features often result from creating polygon features without proper snapping settings or from editing shared boundaries without topology.
Identifying errors in polyline features
Assess the quality of features modeled in your GIS as polyline features with the Evaluate Polyline Length, Monotonicity, and Polyline or Path Closes on Self checks. Identify errors related to a polyline’s spatial relationship to other features with the Find Dangles, Find Disconnected Polylines, Unnecessary Nodes, and Evaluate Intersection Count checks.
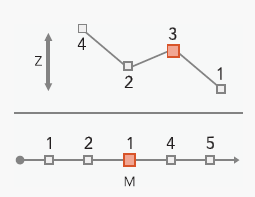
The Monotonicity check identifies features that contain z-values or m-values that are not strictly increasing or decreasing in value. This check is commonly-used in surface transportation to identify routes which contain non-monotonic M values that create issues when linear referencing events.
Z-enabled Feature Checks
Identify errors in Z-enabled features with the Adjacent Vertex Elevation Change, Difference Z at Intersection, and Evaluate Z Values checks.
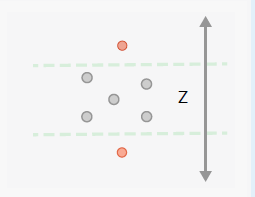
The Evaluate Z Values check returns features with z-values that fall within specified parameters, ensuring they are within an expected range.
For more information, please visit the Data Reviewer product page. If you have any questions, or ideas on what you’d like to see in future releases, join our Esri Community.
Interested in getting started today? Start a 21-day trial for free now.
Article Discussion: