Spanish Airports and Air Navigation Streamlines Aeronautical Charting
Highlights
- Aena produces better charts in less time with GIS.
- Obstacle analysis for runways at Madrid Barajas Airport takes one day instead of the traditional six.
- Aena provides a central authoritative database to serve digital products and services over the web.
More than 190 million passengers pass through airports in Spain each year. Air transport in the country is managed by Spanish Airports and Air Navigation (Aena) public authority, headquartered in Madrid, Spain. Aena's mission is to guarantee safe, fluid, effective, and economic air travel. Its Aeronautical Information Division is in charge of disseminating the crucial aeronautical information necessary for safe and efficient air navigation for the Spanish airspace and 47 airports across the country. This mission requires Aena to publish several cartographic products.
The authority maintains 1,000 charts that are updated every 28 days. These charts are produced at the Aeronautical Information Service to deliver air navigation and safety-related data to pilots flying in Spanish airspace. Typically, more than 50 charts need to be updated every working week. A considerable amount of effort is spent on chart cleanup and quality check operations.
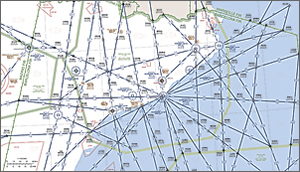
Aena relies on ArcGIS and Esri Aeronautical Solution to create aeronautical charts with detailed information for instrument flight.
Different aeronautical charts containing the same data need to be provided to cover the needs of different end users. This leads to editing tasks that are often highly repetitive and necessitates lengthy quality control processes. Maintaining coherence between all the products is time consuming. These tasks make keeping up with the current map production cycle among the biggest challenges Aena faces. The organization is under constant pressure to ensure that all products are accurate and up to date using the diverse information coming from various data originators.
Due to international agreements, there continues to be a need to produce and distribute paper printed aeronautical charts. However, there is a growing demand for access to digital products as well. Aena's legacy systems required separate systems for cartography and digital transmission of data in the industry interchange standard for aeronautical information, Aeronautical Information Exchange Model (AIXM) format. Aena lacked a true central database that could manage both requirements. It needed a system to produce high-quality charts both digitally and on paper, as well as the ability to post the charts on the web for publication. After researching available solutions, the Aeronautical Information Division selected ArcGIS technology as part of the agency's aeronautical information management system, named INSIGNIA. The technology implemented includes ArcGIS and Esri Aeronautical Solution. The technology solutions provide Aena with the flexibility it requires to manage complex, critical aeronautical information in a spatial environment that is centered on an aeronautical geodatabase.
The system allows the design, production, and printing of high-quality charts to Aena specifications, conforming to International Civil Aviation Organization standards. These charts include detailed instrument approach procedures, which are documents to be followed by pilots for particular types of approach to runways. Prescribed altitudes and headings that are to be flown, as well as any obstacles, terrain, and potentially conflicting airspace, are depicted. Standard instrument departure charts can also be created and provide flight crews with information to facilitate their departures from airports. Enroute charts provide detailed information used for instrument flight and include information on navigational fixes, such as waypoints, intersections, standard airways, airport locations, and minimum altitudes for flight. The system also supports interoperable messaging using AIXM.
Publishing the data using ArcGIS Server in a geodatabase makes it possible for Aena to use Open Geospatial Consortium, Inc.-standard technologies like the Web Feature Service (WFS), providing the ability to publish maps and charts via the Internet without fear of users changing the data. This opens the door for a completely new range of products and services, allowing an improved, more efficient, and safer use of aeronautical information. Aena is thus able to transition from the productcentric services it provides today to the datacentric services of tomorrow.
The transition to GIS for data management and cartography was a major cultural shift for the organization. Despite this, Aena is already receiving benefits from its improved processes and workflows. For example, performing the obstacle analysis used to produce some aeronautical charts for the four runways at Madrid Barajas Airport takes only one day instead of the six it did before.
The ArcGIS geoprocessing tools and geodatabase-centric map production have automated tasks and enhanced workflows, leading to reduced production hours and dramatically increasing cost-effectiveness by improving overall data management and usage. Aeronautical Solution has allowed high-quality cartographic products to be generated using more automation from the central geodatabase. This improves the coherence between products and allows Aena to create more and more tailored products that meet the specific needs of its clients. With the ArcGIS system, Aena has gained the flexibility needed to generate new cartographic products and deliver spatial services throughout the organization. It is able to do this with the same resources and is finding new commercial opportunities, creating a healthy business model.
For more information, contact Javier Fenoll Rejas, Aena (e-mail: jfenoll@aena.es).
Related Podcast
Cloud-Based GIS Solutions for Aeronautical Agencies
Marc Chiesa, president of CGx Aero in SYS, discusses aeronautical information management and GIS, providing examples of successful adoption in Norway, France, and throughout Africa. Listen to the podcast. [12:00 | 29 MB]