Publishing and Using a Geoprocessing Model
New Functionality with ArcGIS Server
This tip was originally posted by Jeremy Bartley, a contributor to the ArcGIS Server Blog. Read other tips and comments.
One of the exciting new aspects of ArcGIS Server 9.2 is the ability to publish geoprocessing models and scripts to the server. A model can be published either as a tool that can be used directly on top of any map service or with an associated map service so that you can control the symbology of the generated layer.
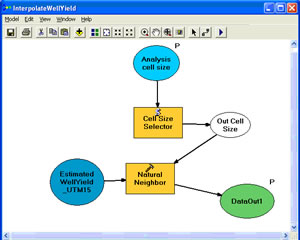
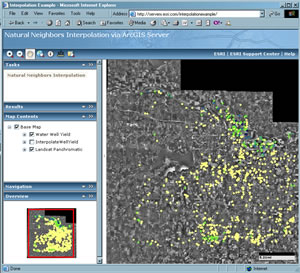
To illustrate the power of geoprocessing on the server, I built an example that uses a map service and an embedded model that allows users to execute an interpolation on the server and view those results in the Web mapping application. The map service contains a point dataset describing the potential water yield from water wells drilled in Douglas County, Kansas (data courtesy of the Kansas Geological Survey and the Kansas Geospatial Community Commons). The model takes in the water well dataset and a user-defined cell size. This information is passed as input parameters to the Natural Neighbors geoprocessing tool. The output is a raster dataset. The output is then rendered using a predefined layer symbology file (or Layer file).
If you looked closely, you may have noticed that the model includes an embedded Python script. This script allows me to put a limit on the input cell size parameter. I want to allow the user to set the cell size (in meters) of the output raster dataset from within the Web application. However, I want to make sure that the user does not enter so small a cell size that it will negatively affect the speed of the Web application. The script ensures that if the user enters anything less than 30 meters, the application will default to a cell size of 30 meters.
Here are some key steps to remember when publishing a geoprocessing tool embedded in a map service:
- Create a map document (MXD) with the input layer and any other background layers that you want in your map service.
- Create a toolbox in your project directory.
- Add a new model to your new toolbox.
- The model should use one of the layers in the map document as an input parameter.
- Ensure that your map document and input map layers are at the same projection.
- Your output dataset should be written to the scratch workspace.
- Set your toolbox scratch workspace environment variable equal to a directory that is visible to your ArcGIS Server Object Container (SOC) account.
- Move your finished model to your ArcMap table of contents. This is called a tool layer.
- Execute the model from within ArcMap and verify the results.
- Turn off the output layer in ArcMap and publish to the server.
The easiest way to publish a map service with an embedded geoprocessing service is to publish the map document by right-clicking on the map document and choosing Publish to ArcGIS Server. ArcGIS Server will see that the map service has a tool layer and will load that tool as a geoprocessing service.
Once deployed to the server, it is relatively straightforward to deploy the map service and associated geoprocessing task as a Web application using ArcGIS Server Manager. Check it out here: http://serverx.esri.com/interpolationexample. Try building and publishing your own models.