For many ArcGIS users, ModelBuilder is an essential tool for automating their desktop GIS workflows. Now, ArcGIS Online users can access ModelBuilder directly within Map Viewer, bringing powerful, no-code automation tools directly into their software as a service (SaaS) ArcGIS capabilities.
ModelBuilder enables analysts to streamline spatial analysis without writing code, saving time and reducing technical barriers. Models are used to create multistep workflows that automate various tasks ranging from simple operations to complex analyses. For example, a simple workflow could involve merging datasets and summarizing data by area, while a more complex analysis workflow might include advanced pattern detection like identifying hot spots or outliers.
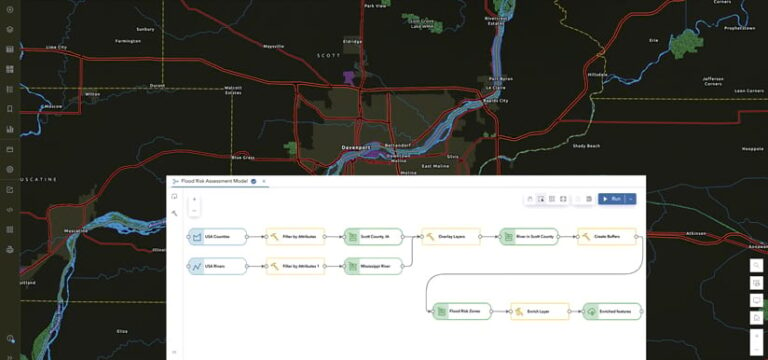
For novices and experienced analysts alike, ModelBuilder offers a user-friendly visual environment for creating, organizing, and sharing analysis processes. The following are some of the key benefits of using ModelBuilder.
Key Benefits
A No-Code Approach
The greatest strength of ModelBuilder is its ability to put together sophisticated analysis workflows without requiring users to have any programming knowledge. Users can visually connect data and tools to form a process, such as designating input datasets for selected tools, or employ the Auto Layout option to automatically arrange model components. The intuitive visual interface makes ModelBuilder a great entry point for analysts who are still building their coding skills and may want to explore workflow automation in the future.
Automate Analysis Workflows
ModelBuilder allows users to automate repetitive tasks by adding and connecting analysis tools and datasets. This reduces the need to run individual tools manually and ensures consistency in the results. For example, an urban planner can create a model that identifies suitable playground locations by automatically buffering school sites and overlaying the resultant buffer areas with appropriate zoning classification data—combining multiple tools running in a single workflow. Once the model is created, it can run repeatedly, saving the urban planner time and reducing the chances of human error.
Document and Communicate
A model provides a visual, step-by-step interface that allows users to see exactly how a workflow progresses. Users can examine the parameters applied for every tool employed in ModelBuilder, as well as the input and output for each step. This is particularly useful when users need to document or explain their methodology. For instance, a GIS instructor can use ModelBuilder to break down complex tasks into manageable steps to make it easier for students to visualize and understand how different GIS tools work together.
Improve Performance
During model execution, each tool only generates temporary intermediate datasets before the final output. This helps improve performance by preventing the creation of an output hosted feature layer after every tool. For example, if someone is running a complex spatial analysis with multiple steps—say, for data management tasks or spatial joins—ModelBuilder minimizes the overhead by ensuring that intermediate results are not written to disk. This can significantly speed up processing times.
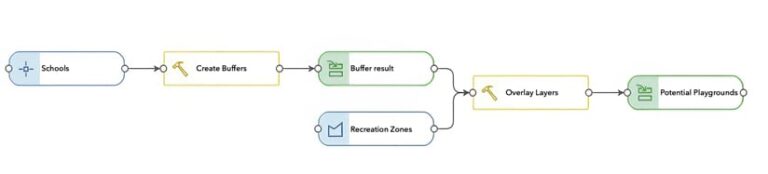
Share and Collaborate
ModelBuilder enhances collaboration by letting users share models within their ArcGIS Online organizations and even publicly. This sharing capability promotes collaboration and knowledge transfer, eliminating duplicate efforts across teams. For instance, a hydrologist who develops a watershed analysis model can distribute it to regional offices, ensuring that each team employs the same methodology while applying its own datasets. Similarly, environmental consultants can establish standard impact assessment models that maintain regulatory compliance across multiple projects, with each analyst able to view and understand the exact analytical steps being performed.
By using ModelBuilder, GIS professionals can simplify their workflows, improve productivity, and collaborate more effectively.
Get Started with ModelBuilder in ArcGIS Online
The integration of ModelBuilder into Map Viewer greatly enhances the analytical capabilities of ArcGIS Online.
ModelBuilder is available now to organizations with Professional or Professional Plus user types. Using ModelBuilder consumes credits based on the amount of time spent working within the ModelBuilder session. ModelBuilder supports most of the feature analysis tools in Map Viewer, including frequently used ones like Enrich Layer and Generate Travel Areas. Additional functionality is planned for future updates.
To learn more about leveraging analysis in ArcGIS Online and to explore the new ModelBuilder functionality, check out the help documentation.