Pacific Gas and Electric Company (PG&E) provides natural gas and electric services to more than 16 million people throughout Northern California and Central California. The utility, which has a rich history spanning 120 years, has extensive networks of gas pipelines and electric transmission and distribution infrastructure across 70,000 square miles.
PG&E has developed a comprehensive inspection and monitoring program to ensure the safety of its natural gas transmission pipeline system. To help with this, PG&E often creates customized apps—but this is time-consuming for the utility’s software engineers, according to George Nadar, principal technology architect at PG&E. So the company aimed to streamline the engineers’ workflow to save time and money. Working with Esri partner Infosys Limited, PG&E extended its existing ArcGIS deployment and implemented a no-code development platform that allows staff to quickly create on-demand applications—without the need for custom programming.
A Complex Network
PG&E’s electrical energy is generated from multiple sources such as wind, solar, hydroelectric, natural gas, and nuclear power. The resultant electricity is transmitted through the electric grid consisting of higher-voltage transmission powerlines and lower-voltage distribution powerlines that total 18,466 miles and 106,681 miles, respectively.
For natural gas, gas transmission pipelines transport this energy source over long distances via PG&E’s natural gas network. This network includes 5,650 miles of gas transmission pipelines and 45,200 miles of distribution pipelines that connect processing areas, storage facilities, distribution centers, and people.
Inspecting and monitoring this comprehensive network is complex. To create new processes for this and streamline related app development, PG&E turned to Infosys, an international software services company headquartered in Bengaluru, India.
“We decided to implement a faster, more user-friendly process for application development that is available to employees throughout the company,” explains Nadar.
Developing the No-Code Platform
Because PG&E is a longtime user of Esri technology, Infosys used the company’s existing technology as the backbone for the new platform.
“As part of the development work for the project, we added a number of software components to the PG&E geospatial framework to create the new system,” says Chandrakanth Arcot, lead GIS consultant at Infosys.
The additional software applications include ArcGIS Data Pipelines to integrate data for mapping and analysis workflows in ArcGIS Online, and to manage data and automate tasks in ArcGIS Enterprise. These applications help engineers update feature services when there is a change to the data in databases or object storage sources, perform Python script comparison as part of code reviews, and sync map data from different portals to share a single source of truth.
Software and services like Amazon AppStream, a service designed for scalable application streaming, and Snowflake, a cloud-based platform for data storage, provided flexible app deployment and advanced data integration and analysis.
Infosys ultimately produced an ArcGIS technology-based development platform that allows PG&E staff to create applications on demand, without doing any coding or custom programming. This has enabled employees throughout the company to make use of geospatial technology.
To ensure user adoption and maximize the platform’s effectiveness, Infosys incorporated features such as easy sign-in to the development platform, and resources like detailed how-to wiki pages for app building. A user-friendly decision tree helps users navigate the platform’s diverse toolset and choose the right tools for their apps. In addition, a wide range of sample codes and templates are available to accelerate application development and provide ongoing support and training.
Benefits of the New System
The new platform has helped PG&E develop numerous applications and widgets that offer real-time data analysis, improve data integration, and enhance operational efficiency. Examples of these applications include a decision support app that gives users insight into public safety power shutoff events’ impact on customers and facilities, and a centralized collection of remote sensing data.
PG&E can also use its new platform to quickly create operational dashboards and other visualization tools. These tools provide staff with situational awareness during natural disasters and other emergencies and improve response time.
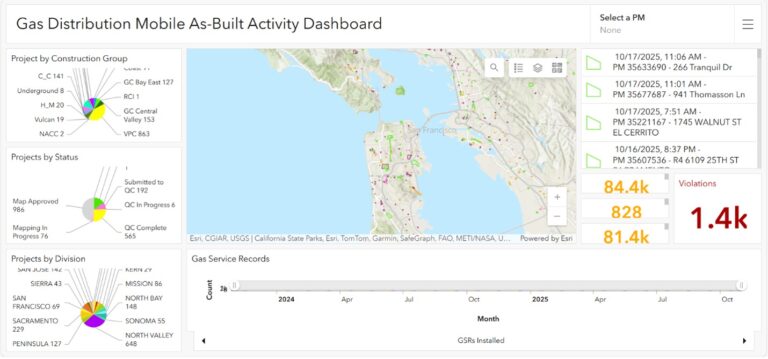
The no-code development process also supports real-time data analysis and enhanced data integration. Other benefits include accelerated project timelines and data-driven decision-making throughout the organization, resulting in increased efficiency.
PG&E’s ArcGIS technology-based platform has fundamentally transformed how the utility leverages geospatial intelligence and supports the of AI. For example, PG&E can leverage the platform to find potential grid failures through anomaly detection or optimize routing for field crews using machine learning algorithms. The new implementation can serve as a powerful model for electrical utilities, according to Arcot.
“By providing business users with accessible tools, comprehensive support, and seamless data connectivity,” says Arcot, “we empowered [staff] to become active participants in the GIS process, driving efficiency, innovation, and improved service delivery.”
