In the ArcGIS GeoAnalytics Engine 1.6 release (June 2025) we have several exciting performance and usability improvements to enhance your big data spatial analysis workflows. This latest release includes updates to the Find co-traveler tool, the ability to write polygon and linestrings in vector tiles, expanded Scala API support, and improved performance for spatial joins and plotting. These improvements make it easier and faster to bring Esri’s industry-leading geospatial analytics capabilities directly to your big data – in a data lake, data warehouse, or ArcGIS.
Let’s take a look at the new features.
Enable Tool Functionality with Scala API
The ArcGIS GeoAnalytics Engine 1.6 release includes the addition of a Scala API for all tools in GeoAnalytics Engine. Users can now drive analysis tools using either Python or Scala syntax while utilizing the same underlying implementation. This complements the existing Scala API for SQL and track (TRK) functions.
Efficiently Identify Location with New SQL and Track Functions
The 1.6 release introduces two new SQL functions: ST_LineInterpolatePoint and ST_LineLocatePoint. These functions improve user ability to identify locations at fractional distances along linestrings. For instance, these functions can be used to identify the point that is 20% of the way along a linestring.
Additionally, SQL and Track (TRK) functions have been enhanced to make it easier to specify distance or duration parameters using ST_CreateDistance and ST_CreateDuration functions. This tool allows us to customize the distance and units for each row of data. For example, we can set unique distance requirements to define the “area of interest” based on location or attribute. In this example, we can also specify the distance using different units for each row in the dataset, such as miles or kilometers.

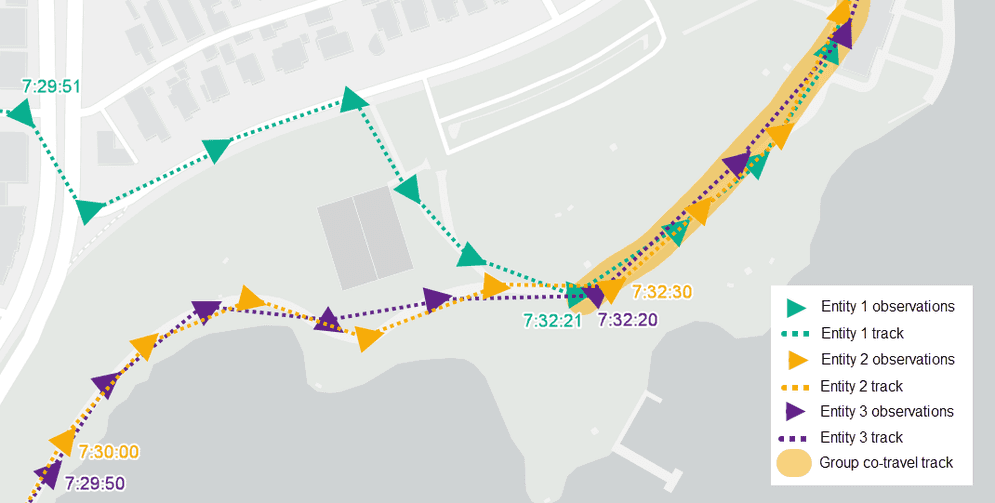
Identify Relationships Using Co-Travelers Group Mode
The 1.6 release introduces enhancements to the Find Co-travelers tool to enable finding groups of two or more entities co-traveling together for defined amounts of time. This is useful for uncovering relationships between individuals or groups. For instance, it can be used to identify vehicles or individuals travelling together, for crime analysis, or to uncover potential suspects that met up along routes for exchange of goods.
Write Polygons and Linestrings to Vector Tiles
Users can now write polygon and linestring geometries to vector tiles in addition to points. This allows for hosting and fast visualization of spatial data, no matter the geometry type. For example, aggregating point observations into high-resolution H3 bins and quickly host and visualize the bins in a web map.
Analyze and Visualize Results More Performantly
The 1.6 release of ArcGIS GeoAnalytics Engine also includes improvements to spatial join performance, as well as a new quantization option for faster plotting of geometries to aid in visualizing intermediate results of your analysis.
ArcGIS GeoAnalytics Engine is updated two to three times each year to provide new features so you can make spatial analytics a seamless part of your data science workflows. We’re always looking to hear from you about the capabilities you need to enhance your big data workflows!
For more information on the latest features, check out the product release notes or stop by the GeoAnalytics Engine Community Site for resources on getting started, tips and tricks with various tools, and much more!


Article Discussion: