To achieve greater levels of scalability, performance, and reliability, organizations are increasingly seeking cloud-based options to support their enterprise geodatabases. And across the SAP HANA continuum, organizations have a range of flexible deployment options. For example, SAP HANA Cloud, the database management foundation of SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP), has emerged as a new option to support ArcGIS Network Information Management Systems.
Organizations understandably want to confirm the viability of new configuration options before adopting them. In response to this need, we conduct structured system testing with a focus on end user experience. In this case, we tested with a Gas Network Information Management System using a geodatabase configured with SAP HANA Cloud. The test results help us to evaluate the system’s behavior and its ability to support users executing real-world workflows.
Scroll on to review our initial test results demonstrating that SAP HANA Cloud is a viable option for an enterprise geodatabase.
How we test
Many customers find test studies published through the ArcGIS Architecture Center to be helpful in examining how a given system configuration performs and supports end users under a specified load. But have you ever wondered how and who actually does the testing?
Esri has a small Office of Technology and Innovation group, and we define a set of real-world workflows to be executed against a specific system design and configuration. But beyond that, we partner with an amazing team at Cybertech who sets up our testing environment, works with us to define a testing strategy, executes load tests and user experience tests, and shares their findings. Then we transform that data into insights, often in the form of a test study.
Initial test results for configuring an enterprise geodatabase with SAP HANA Cloud
While we don’t have a formal test study using SAP HANA Cloud yet, our preliminary tests have demonstrated interoperability between ArcGIS Enterprise and an enterprise geodatabase configured with SAP HANA Cloud.
During our tests, we executed core workflows that represent foundational gas utility network management activities. These are the same manual and automated workflows described in previous test studies, which were run against a design load simulating an organization with 15 editors and 200 web viewers.
At a high level, the results show the system’s ability to support the workloads, without errors. In the diagram below, the orange line represents CPU utilization (%), the gold line represents % disk utilization, and the purple line represents memory utilization (%). You can see that at design load, system resource usage across all system components is very low.
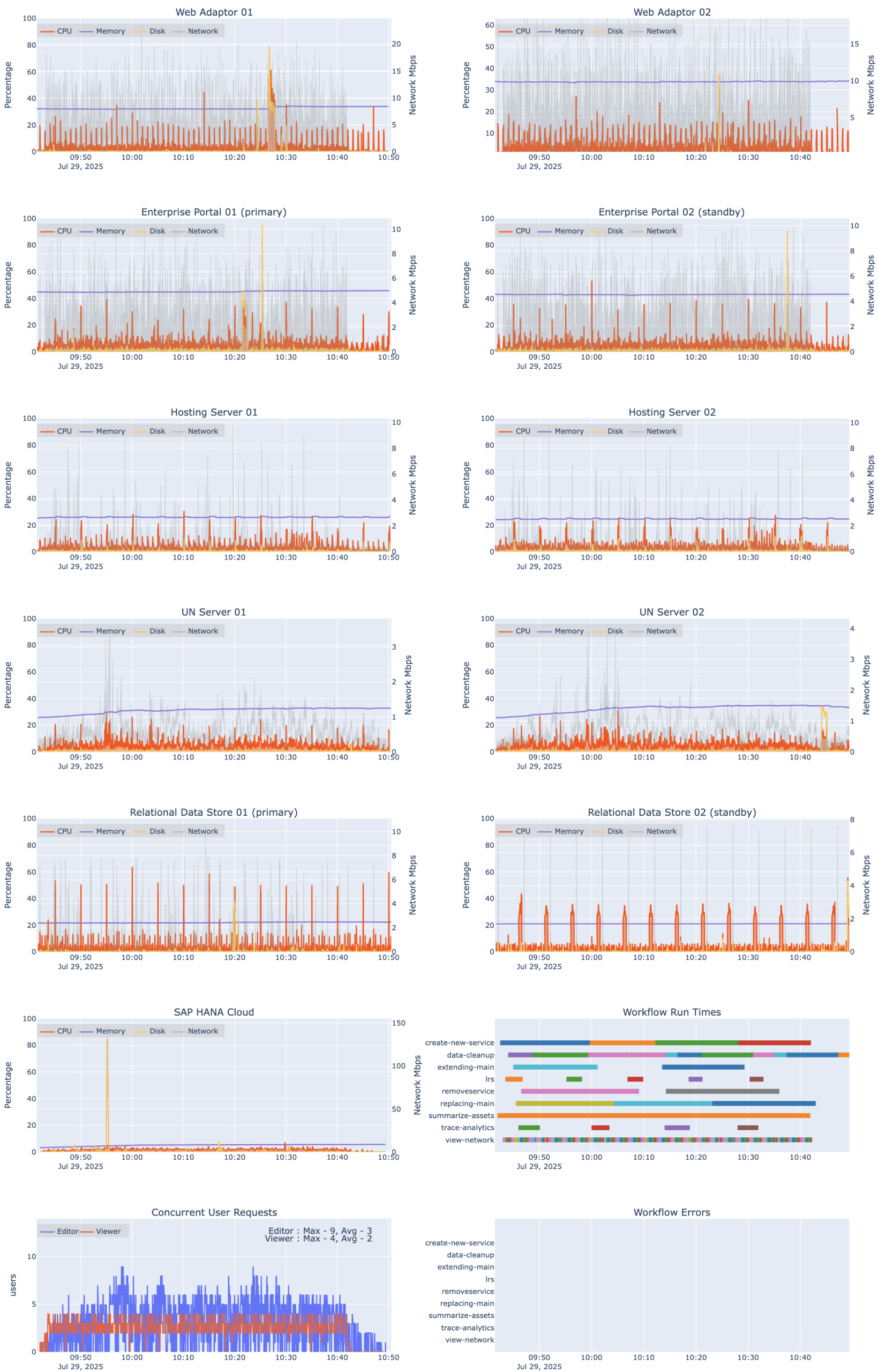
The lower left chart in the diagram shows concurrent user requests, where blue is from editor requests and red is from viewer requests. An abnormal test would show open requests in an upward trend, indicating that requests are not closing while new open requests are building. However, this chart shows the system is responding normally, with requests opening and closing as expected. This combined with the error chart showing no errors indicates the workflows are being successfully executed.
This initial test provided valuable metrics that will inform future designs that leverage HANA Cloud and other database-as-a-service options.
Final thoughts
As with any cloud deployment, it’s crucial to consider network latency, especially between ArcGIS Enterprise and the enterprise geodatabase components. The same is true for SAP HANA Cloud. For optimal performance, your SAP HANA Cloud geodatabase environment must reside in the same region as your ArcGIS Enterprise components. Placing these key system components in different regions can lead to noticeable performance degradation, resulting from increased network latency when exchanging data across significant distances.
To summarize, these results show that SAP HANA Cloud is a viable repository for customers pursuing a database-as-a-service offerings for their enterprise geodatabase.
With careful consideration and application of recommended design practices, organizations can confidently leverage SAP HANA Cloud to modernize their GIS infrastructure and support business-critical operations in the utility sector. Check out additional test studies evaluating Network Information Management Systems with an enterprise geodatabase configured with SAP HANA here:
- Network Information Management System: Gas Utility (SAP HANA)
- Performance Usability Comparison with SAP HANA deployed in SAP Private Cloud Edition
Please share your feedback - help us make these resources better!
➡️ You can also find our full catalog of test studies and blogs here
➡️ If you have questions or keep the conversation going, consider joining our LinkedIn group





Article Discussion: