Many organizations use ArcGIS Enterprise to host and share massive quantities of authoritative content across the organization.
An organization’s members may include hundreds of publishers that may in turn create thousands of web services, many of which reference authoritative data that is stored in an enterprise geodatabase.
To manage the status of these geoinformation assets, administrators need event-based solutions to track system resources for these items as well as their relationships and dependencies with other assets, such as associated database connections.
For this scenario, Yundi and Bill show how a knowledge graph can be used to visualize relationships between web maps and services and their dependencies on other enterprise assets, such as geodata.
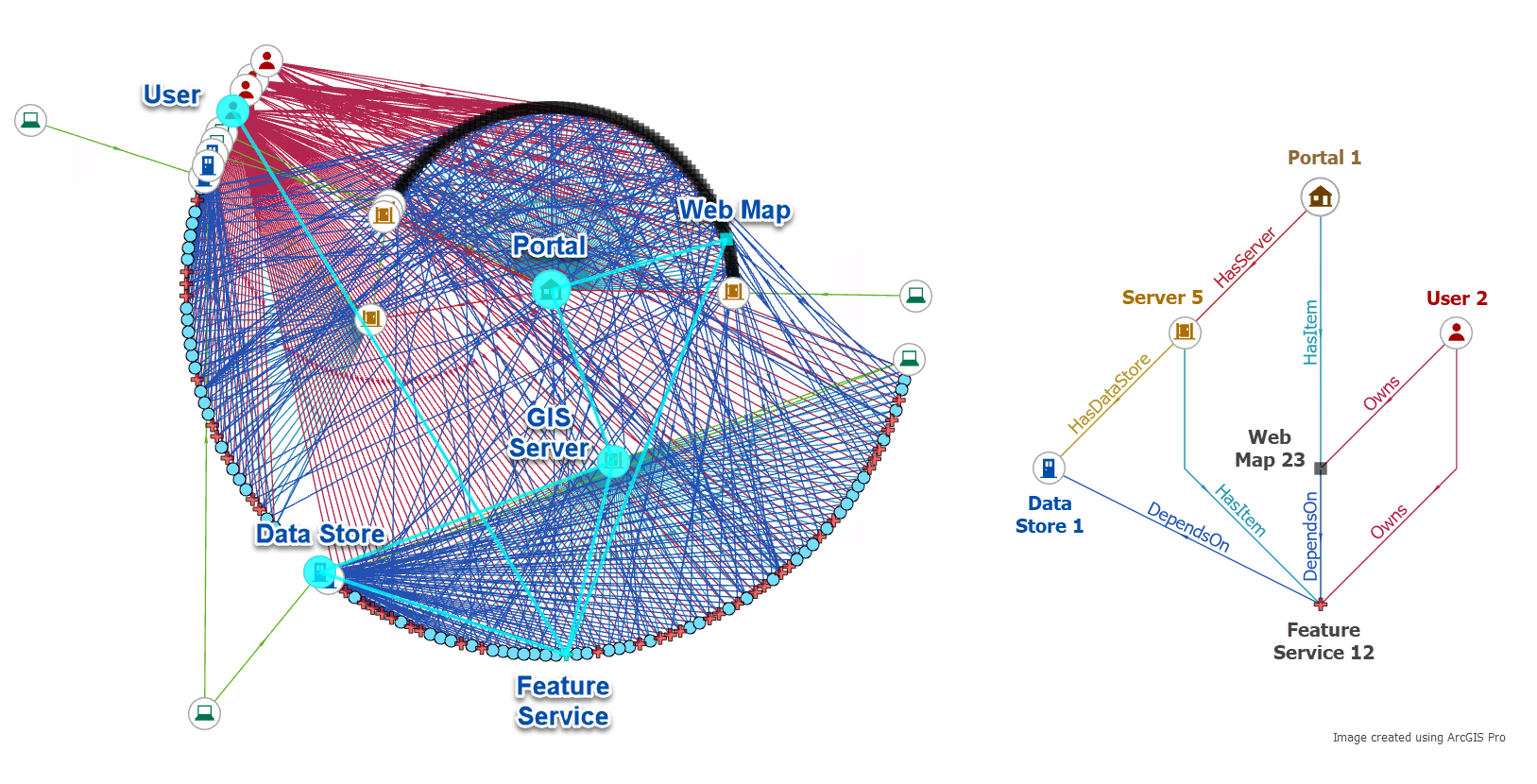
Query a knowledge graph for geoinformation assets
First, Yundi uses a notebook to query a knowledge graph for geoinformation assets and relationships. In her demonstration, she:
1. Uses a notebook to connect to the knowledge graph.
2. Queries the knowledge graph to identify which web maps and dependencies on service items (map and feature services and layers) will be impacted when a specific data store is temporarily offline for maintenance.
3. Returns a list of item owners along with a list of each impacted item they own, to contact them ahead of the scheduled maintenance.
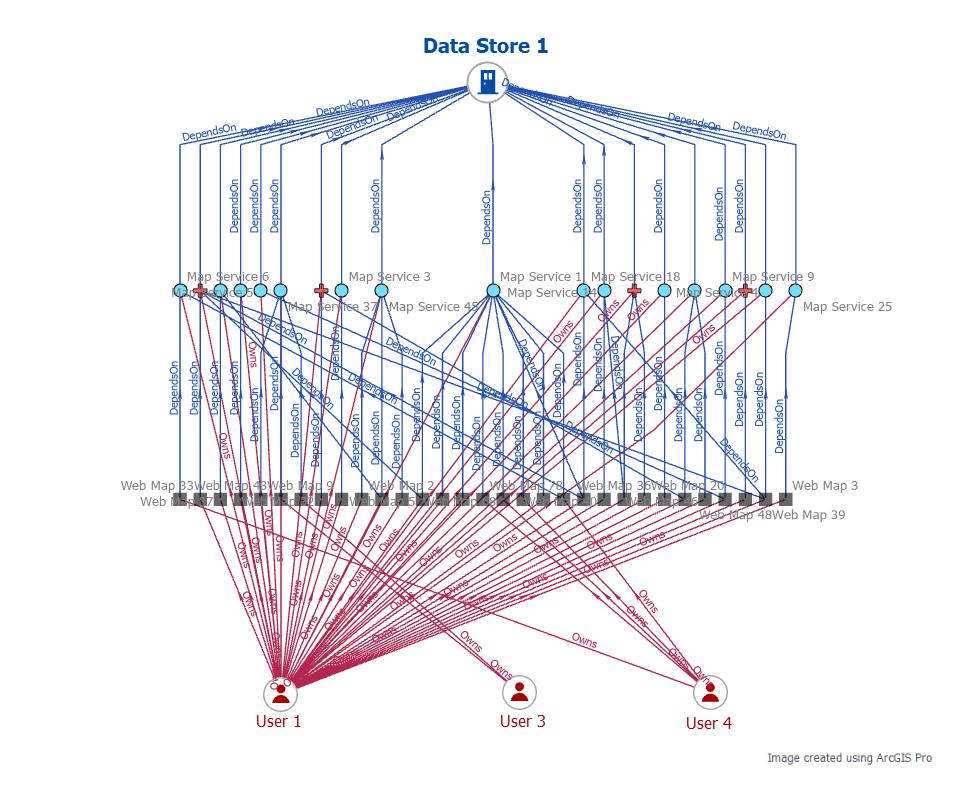
Next, to ensure the knowledge graph is in sync with the latest organizational items, Bill shows how to keep the knowledge graph up to date.
Real-time sync to monitor updates
Bill demonstrates how an administrator can monitor item updates, such as when they are created, updated, or deleted. From there, he shows how item relationships are surfaced to inform the administrator of underlying resources and connections to these items.
To accomplish this, he has automated a notebook using webhooks to run when items are created or updated. The notebook then processes the items by doing the following:
1. Extract the new item’s id and relevant details from the webhook’s payload.
2. When the published item is a map or feature service, it retrieves connection details from the server for the associated data store.
3. Connects to a graph store to update it with new entities and relationships.
4. Creates a new item entity along with additional attributes.
5. Creates entities and relationships to visualize and manage the connections across the items.
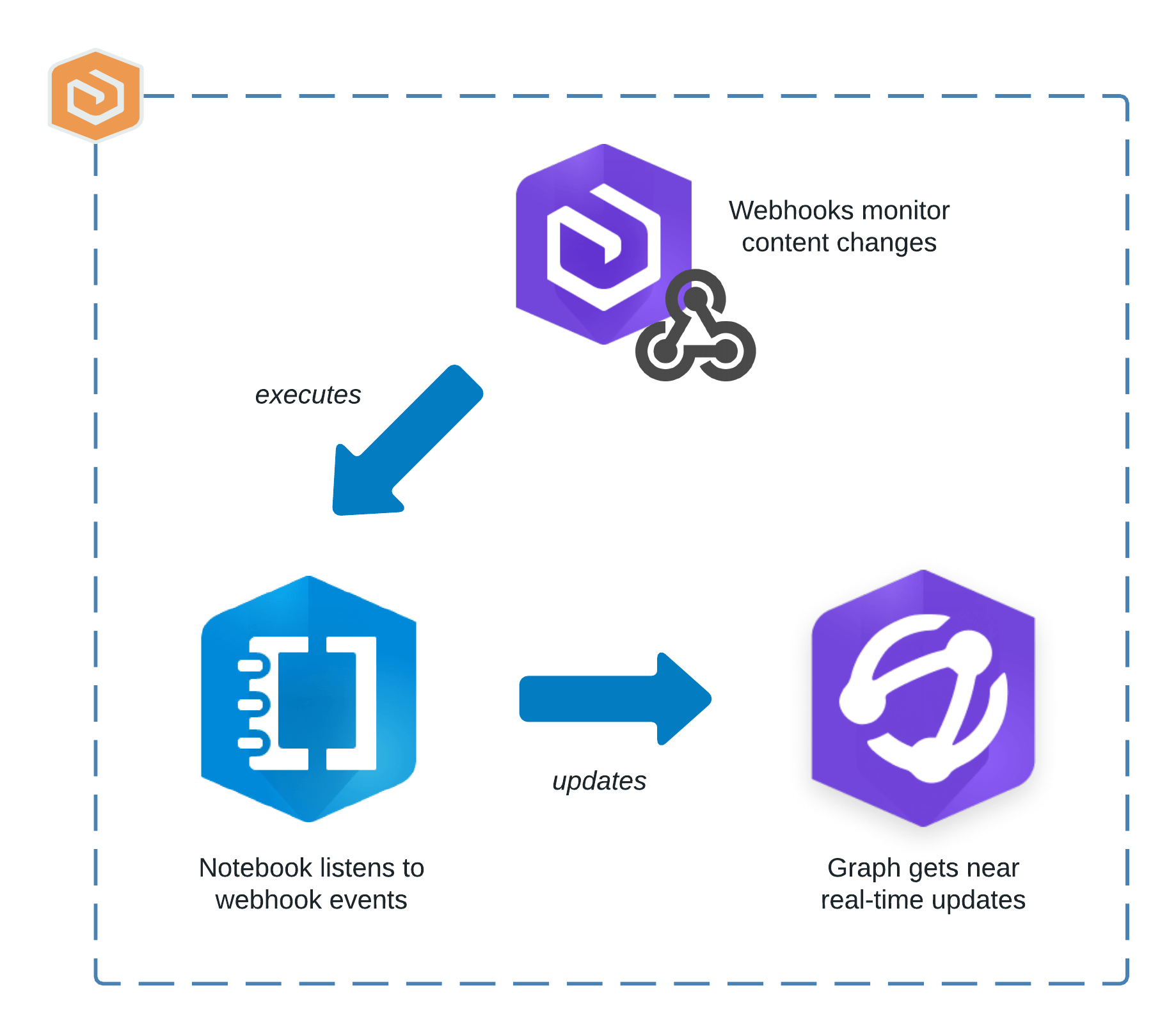
Yundi and Bill demonstrate how to monitor near real-time state of the content in an ArcGIS Enterprise organization using ArcGIS Knowledge and other ArcGIS capabilities. When an administrator anticipates scheduled system maintenance, they can use this information model to assess risk and to proactively work with the organization’s members to minimize impact and avoid disruption to their work.


Article Discussion: