This blog article shows the complete process of deploying an enterprise geodatabase in an Oracle database. You’ll learn about databases, ArcGIS support considerations, preparing your Oracle database to be used in ArcGIS, and tools and spatial components. This information is for database or geodatabase administrators in organizations using Oracle.
Install or upgrade to a supported Oracle database version
If you plan to install an Oracle database or upgrade a database version, review the following upgrade considerations:
Ensure that the Oracle version used by your organization is supported by all the ArcGIS clients’ versions you plan to use. This maintains optimal performance and workflow functionality.
- Check the What Oracle database versions are supported by ArcGIS Enterprise and ArcGIS Pro? knowledge article
Choose an Oracle database version with long-term support to minimize the frequency of upgrades.
- Check the Release Schedule of Current Oracle Database Releases article
Install the Oracle Database Client at a release that is compatible with the Oracle version, to allow the ArcGIS client applications to communicate with your database.
- Check the Oracle Instant Client Downloads list
Note: Follow the ArcGIS clients and DBMS upgrade considerations blog article which illustrates a common workflow example that many organizations use when upgrading their systems.
Configure Oracle database for deploying an enterprise geodatabase
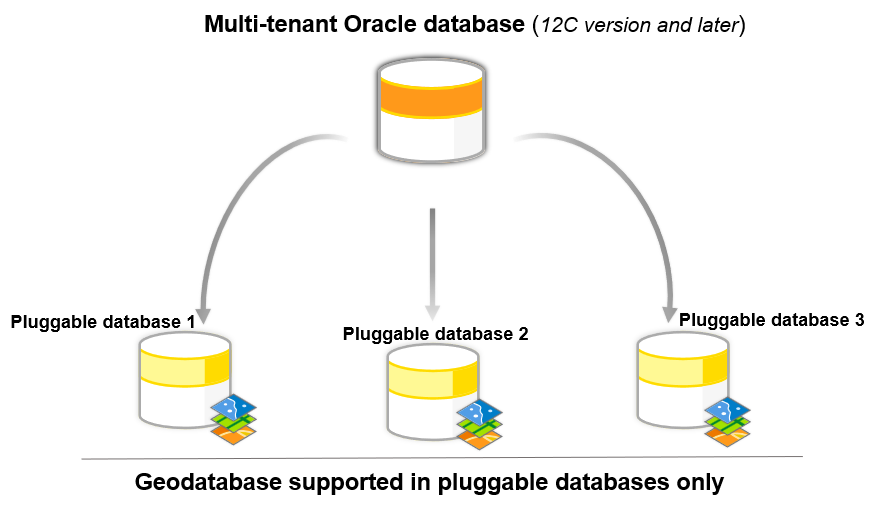
Oracle’s multitenant architecture has a container database (CDB), which can store multiple pluggable databases (PDBs). A PDB is a portable collection of schemas, schema objects, and non-schema objects that appears to an Oracle Net client as a database. In Oracle multitenant architecture, you can create geodatabases in a PDB only.
Considerations for memory and initialization parameters
Keep the following in mind:
- The Oracle Text component must be installed. The Text component is installed by default in Oracle; however, if you did not perform a default installation, the Text component may not have been installed. This component is needed for certain ArcGIS functionalities, particularly for creating and querying geodatabases with full-text indexing.
- Memory tuning – Although the default setting will work for creating an enterprise geodatabase, the following options should be taken into consideration for improving performance.
- SGA must not swap – Swapping the SGA to disk significantly degrades performance, as the purpose of the SGA is to hold frequently accessed data in memory for rapid retrieval. The SGA should be configured to fit within the available physical RAM. We recommend that the SGA size should generally not exceed two-thirds of the server’s physical RAM. This allows room for other processes and the operating system.
- Avoid excessive paging – Excessive paging, when parts of memory are constantly moved to and from disk, indicates that the SGA or other memory structures are too large for the available physical RAM. This leads to slow performance.
- Configure enough virtual memory – While the SGA itself should not swap, the system still requires adequate virtual memory and swap space. Oracle often recommends swap space to be at least three to four times the size of your physical RAM, although other sources suggest different ratios depending on RAM size. This swap space acts as a safety net for less frequently accessed data and other processes, but the critical point is to prevent the SGA from using it.
- Explicit quotas on tablespaces – Users who create Oracle objects (e.g., sde, data owners) need access to tablespace storage. This can be managed by granting the UNLIMITED TABLESPACE privilege, which grants unrestricted space across all tablespaces. Due to the risk of exhausting the storage or crashing the database, this should be reserved for DBAs only. The recommended option is to assign quotas, which is a safer and more controlled approach. Users are given specific space limits on designated tablespaces (for example, GIS_ADMIN gets quotas on GIS_DATA, not on SYSTEM). DBAs may assign unlimited or no quotas to geodatabase owners, allowing flexibility while keeping data organized and protected. For less experienced users (e.g., editors/viewers), limited quotas help manage space usage. Quota assignments should align with user roles and business needs.
- Database parameters – The following parameters must be changed as user that has sysdba privileges.
- OPEN_CURSORS: The default value for open_cursors in an Oracle database is 300. The recommended value is 2000 or higher. If it is set to a higher value before creating the geodatabase using the Create Enterprise Geodatabase geoprocessing tool, the open_cursors setting between the Oracle database and the geodatabase will be synchronized. However, if the Enable Enterprise Geodatabase tool is used or the value of the open_cursors parameter is changed after creating the geodatabase, you must update to open_cursors setting in geodatabases in Oracle.
- Execute privileges on packages – As the sysdba user, you need to grant the execute privilege on the following packages to the public role to create or upgrade the geodatabase:
-
dbms_lob
-
dbms_lock
-
dbms_pipe
-
dbms_utility
-
dbms_sql
-
utl_raw
After you create or upgrade the geodatabase, you can restrict privileges on these packages by revoking them from the public role and granting them to each individual user who connects to the geodatabase, including the geodatabase administrator. Note that you cannot grant the execute privilege to a role and grant the role to all the users because privileges granted through user roles are not applicable when running Oracle packages.
Connect to an Oracle database in ArcGIS Pro
Once the Oracle database is installed and configured, you will make a connection to the database using ArcGIS Client. To connect to Oracle from ArcGIS clients, you must install an Oracle client on the ArcGIS client machines. You will need a 64-bit client for ArcGIS Pro and ArcGIS Server.
After installing the client software, set environment variables that reference the Oracle client directory. This is required so that the ArcGIS clients can use the Oracle client libraries to connect to the Oracle database.
- In Microsoft Windows, set the PATH environment variable to the location of the Oracle client installation. See the Microsoft Windows documentation for instructions on setting the PATH environment variable.
- To install Oracle for ArcGIS Server on Linux, set the LD_LIBRARY_PATH system variable.
Once the Oracle client is installed and the environment variables are configured, you can connect to the database.
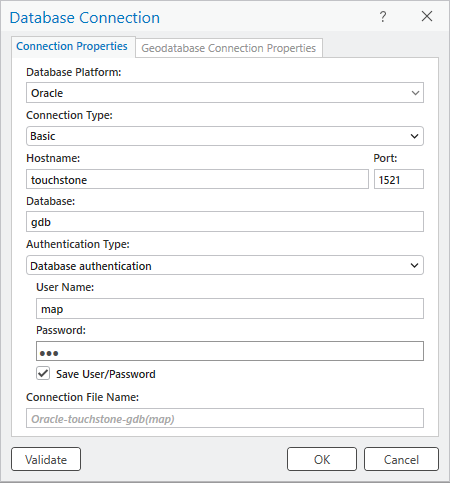
If connecting from ArcGIS Pro, you can create a database connection using the Database Connection dialog box.
Create an Oracle geodatabase
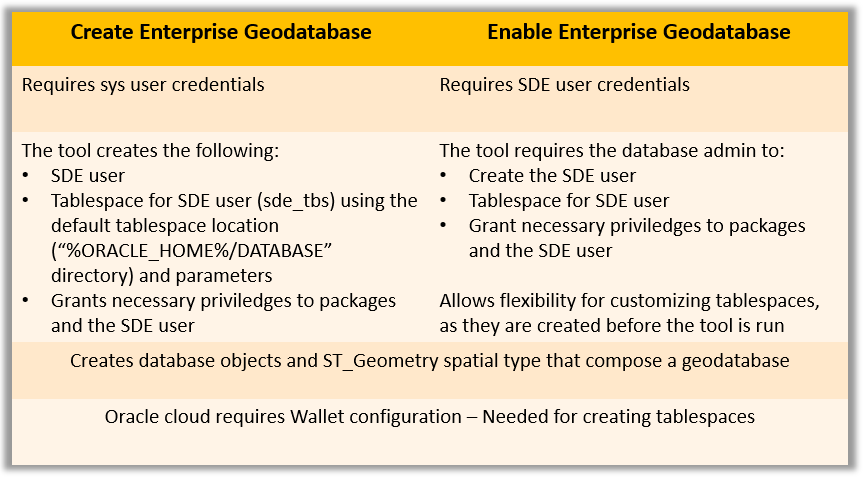
In ArcGIS Pro, two geoprocessing tools can help you create a new geodatabase in Oracle; the Create Enterprise Geodatabase and the Enable Enterprise Geodatabase geoprocessing tools.
Both the tools create an oracle enterprise geodatabase when run against an existing pluggable Oracle database, however they require different privileges and initial set up. The table summarizes the requirements for the two approaches.
Configure Oracle extproc
As part of the geodatabase installation, an Esri ST_Geometry spatial data type is created in the Oracle database. The Esri ST_Geometry spatial data type is the default geometry storage type for geodatabases in Oracle. You also must configure the Oracle external procedure agent (extproc) to access the Esri ST_Geometry libraries before you do any of the following:
- Run ST_Geometry SQL functions from SQL clients.
- Define a query layer that runs SQL functions on ST_Geometry columns.
- Query binned feature layers in ArcGIS Pro.
- Publish a web layer that references data in the Oracle database.
- Run the Select Layer By Location geoprocessing tool with the Intersect (DBMS) option.
The ST_Geometry SQL functions in Oracle use a shared library that Oracle accesses through the Oracle extproc. You must configure the Oracle external procedure framework, which requires access to the physical file ST_Geometry library—ST_SHAPELIB—to perform the tasks listed above.
The ST_Geometry library is created for specific operating systems. You can download the library file specific to your operating system and client version from My Esri.
The Oracle instance must have access to the ST_Geometry library. Place the library on the Oracle machine in a directory that the Oracle instance can access. Follow the steps for your specific operating system (OS) to configure the extproc using the shape library that matches the supported OS of your Oracle database.
Manage users and roles
After the geodatabase is created, you can set up users. The users may be data-owners or readers. Oracle separates who can log in (authentication) from what they can do (authorization).
- Create roles to simplify permission management across multiple users.
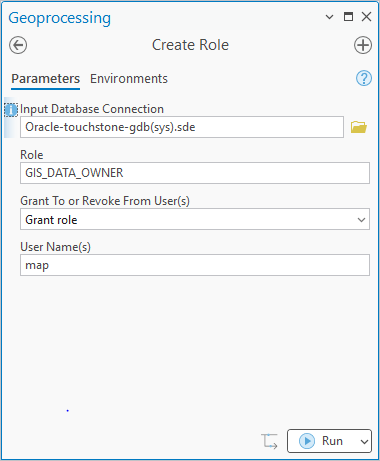
- Use the Create User tool to ensure new users have appropriate privileges to own data.
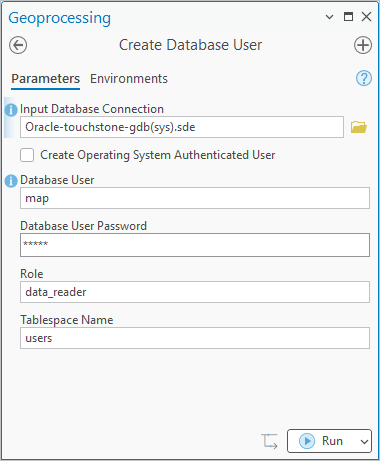
If a read-only user is needed, you have to create the user using DBMS tools.
Note: Follow the Privileges for geodatabases in Oracle topic to learn more about privileges for geodatabases in Oracle.
Create and manage datasets
Once your geodatabase and users are in place, you can create datasets or register existing data with the geodatabase. Registering your data opens the door to all the advanced capabilities of the enterprise geodatabase, including versioning, topology networks, attribute rules, and more.
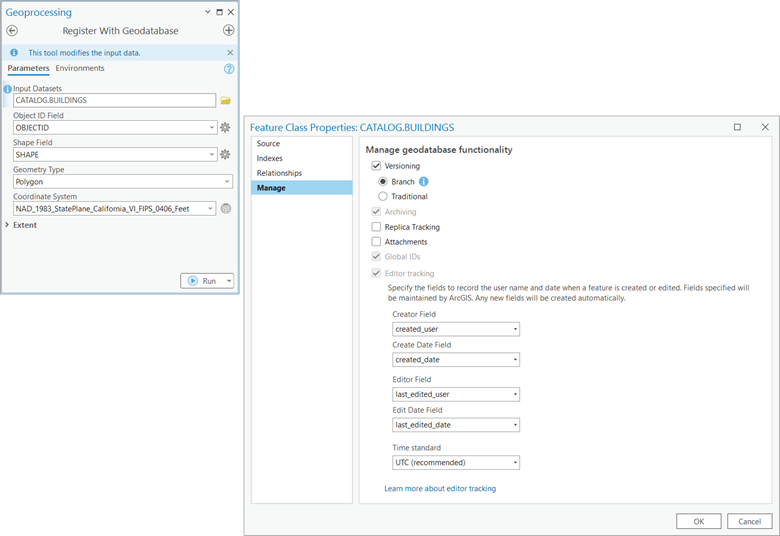
ArcGIS tools help simplify privilege management by making sure all the supporting tables for each dataset receive the correct permissions.
Use ArcGIS tools to manage privileges— Geodatabase datasets may be a collection of database objects. Granting read to write privileges on these datasets using ArcGIS tools it ensures that privileges on ancillary tables for the dataset are handled correctly.
Deploying an enterprise geodatabase in Oracle requires choosing a supported Oracle version, configuring your database for optimal performance, installing the right client tools, and setting up the geodatabase with the correct privileges and spatial libraries. After that, you can organize users, build datasets, and support your organization’s workflows. With this set-up process, you can use Oracle for enterprise-level GIS, and your geodatabase can grow with your organization’s data requirements.
Additional resources
- For an overview of enterprise geodatabases, watch the Enterprise Geodatabase: An Introduction technical workshop presented at the Esri User Conference 2023.
- To learn how to configure a database connection with Oracle on Linux, follow the Monthly Linux Tip blog article.
- Follow the example workflow to upgrade ArcGIS clients and the database version in an organization in the ArcGIS clients and DBMS upgrade considerations blog article.
- For more content on geodatabase and spatial data management, check on the Geodatabase Resources Hub.



Commenting is not enabled for this article.