We designed ArcGIS deep learning tools to work seamlessly with training data in the PASCAL VOC (Pattern Analysis, Statistical Modeling and Computational Learning, Visual Object Classes) format. While we recommend creating and managing your training data directly within ArcGIS to ensure full compatibility and reliability, we understand that you may need to work with datasets originally labeled in other formats.
To help you work with your existing datasets and streamline your deep learning workflows, we’ve developed a suite of Python scripts that convert metadata from several common formats into ArcGIS-ready PASCAL VOC formats.
Why PASCAL VOC?
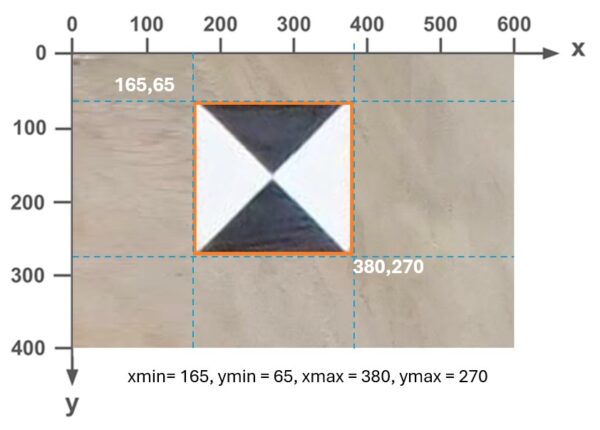
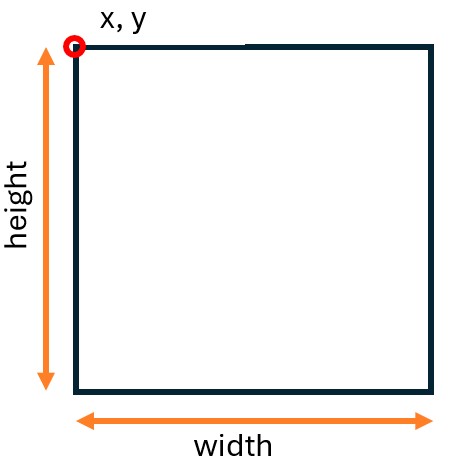
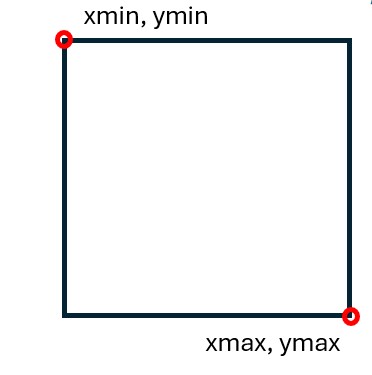
The PASCAL VOC format is a computer vision standard that keeps things simple. Its XML files specify bounding boxes using absolute pixel coordinates ( <xmin>, <ymin>, <xmax>, and <ymax> ) rather than percentages or ratios.
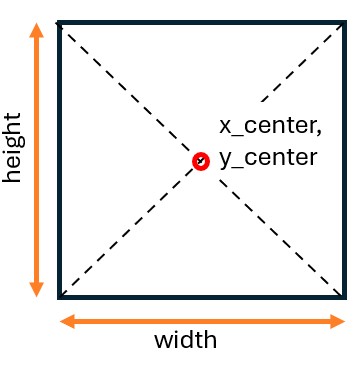
These absolute corner points differentiate PASCAL VOC from other formats. While external data varies in file type (JSON, TXT, etc.) and structure, the biggest difference lies in how they define the bounding box. Many formats record normalized values (0.0 to 1.0) or relative dimensions (center point, width, height) instead of pixels. Because ArcGIS tools require the PASCAL VOC standard, you must convert these external datasets to absolute pixel coordinates to use them successfully.

Click here to view technical specifications for key external datasets
YOLO (You Only Look Once)
File Type: |
 |
COCO (Common Objects in Context)
File Type: |
 |
Azure Machine Learning
|
 |
TFRecords
File Type: |
 |
Convert to PASCAL VOC
External object detection training data must be converted to the PASCAL VOC absolute pixel standard for use in ArcGIS. Our Python scripts automate this transformation.
Use the links below to download the relevant conversion script and documentation:
Work with the converted data
Once you’ve finished the conversion and have your new PASCAL VOC XML files, follow these steps to finalize your dataset and begin training:
• Replace labels—Replace your original labels folder in your dataset with the new folder containing the converted PASCAL VOC XML files.
• Verify structure—Ensure your main dataset folder (for example, trainingdata) contains only the two required subfolders: images and labels.
• Train your model—Use the Train Deep Learning Model tool and specify your main dataset folder (the one containing the images and labels subfolders) as the input.
You don’t need to start from scratch if your data isn’t in Pascal VOC. This streamlined approach helps you transform your existing datasets so they work within ArcGIS.




Article Discussion: