We’re excited to share the powerful new and enhanced GeoAI capabilities available in the ArcGIS Pro 3.6 Image Analyst Extension. You’ll find that the entire training data pipeline has been refined, introducing powerful training data review tools that provide the confidence and efficiency needed to build the best deep learning models. This release is all about making your workflows easier and your results more accurate than ever.
Here’s a quick look at the powerful new capabilities across GeoAI workflows:
- New training data review tools
- New Transform Image Shapes tool
- Enhanced Grad-CAM for multi-classification
- Enhanced Auto Detect with multi-click
- New backend Deep Learning readiness check
- New 3D-RCNet model type
New training data review tools
Reliable GeoAI starts with reliable training data. To ensure the highest model accuracy, we’ve provided powerful tools to review your labels and training data. ArcGIS Pro 3.6 introduces a comprehensive set of quality assurance (QA) and quality control (QC) tools for your labels and exported training data.
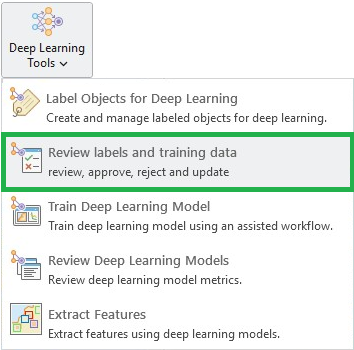
Manual review of labels
Since label creation is a critical but labor-intensive process, ensuring quality is essential for model performance. Labels often contain errors in class name or geometry. To streamline this manual QA process, we’ve dedicated a Label tab to centralize all the necessary tools. This tab allows you to quickly select single or multiple labels and take actions—such as review, approve, reject, and edit—directly and efficiently.
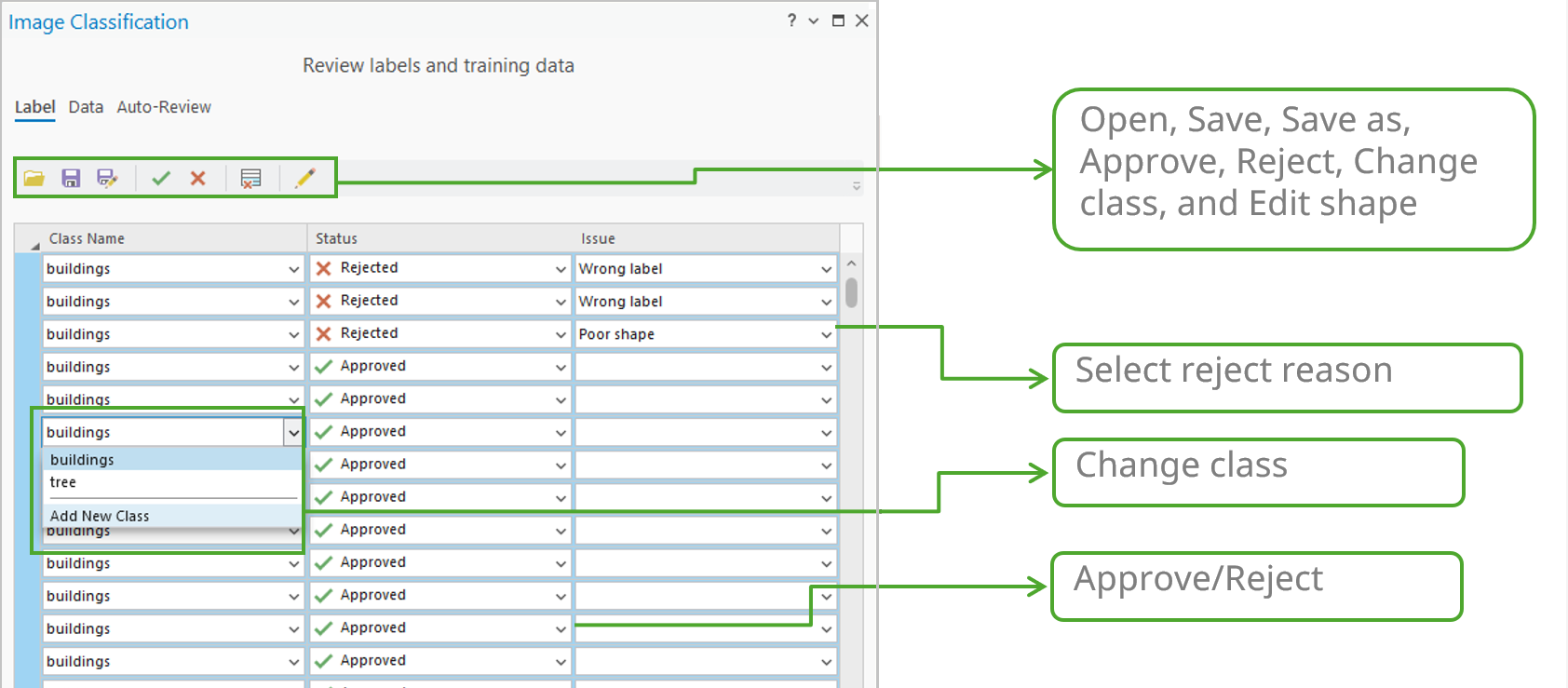
Automated review of labels
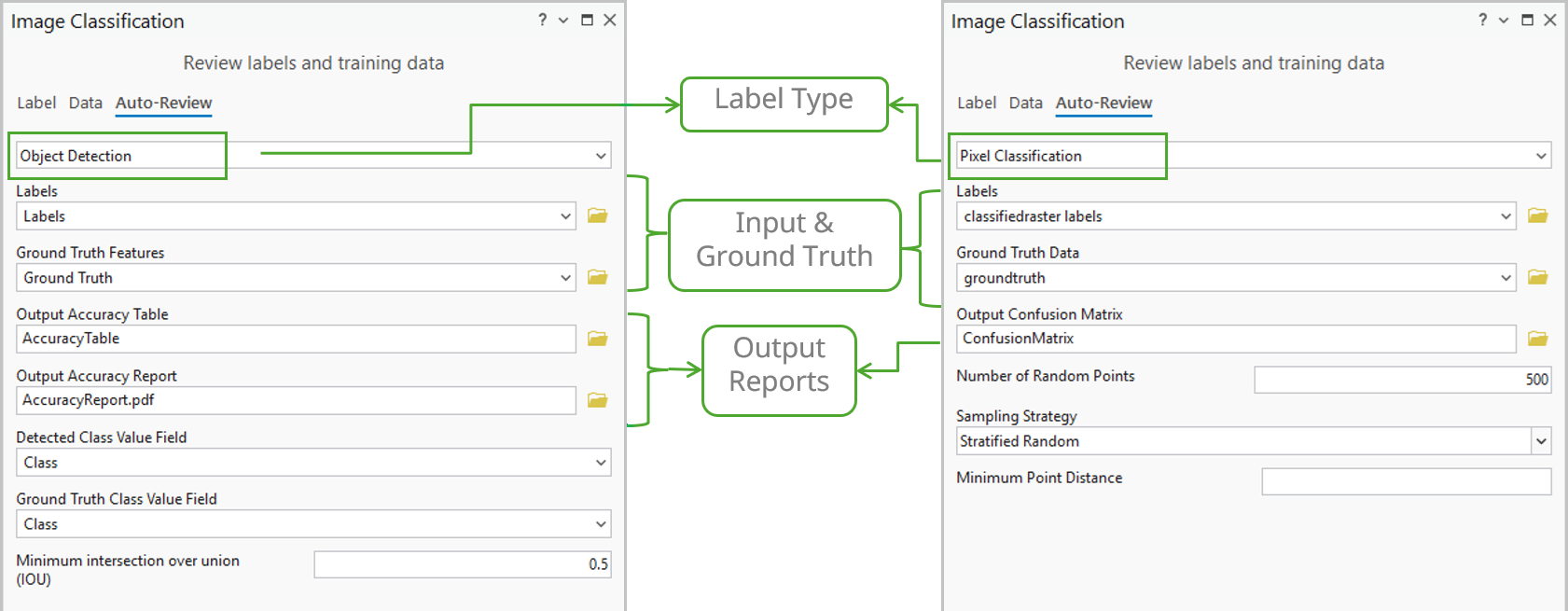
However, manual review may not be feasible for large datasets. To speed up the process, the new tools on the Auto-Review tab quickly assess label quality by comparing them against small ground truth samples.
- Object Detection —Provides essential accuracy metrics such as Common Objects in Context (COCO), mean Average Precision (mAP), and a Precision x Recall curve. The tool uses the Intersection over Union (IoU) ratio to identify and count true/false positives/negatives and generates a detailed quality report.
- Pixel Classification—Computes a confusion matrix based on errors of omission (false negatives, where a pixel that should have been classified as a class is missed) and errors of commission (false positives, where a pixel is incorrectly classified as belonging to a class when it does not), along with the IoU score. This process directly compares the results of your trained model against the ground truth reference data.
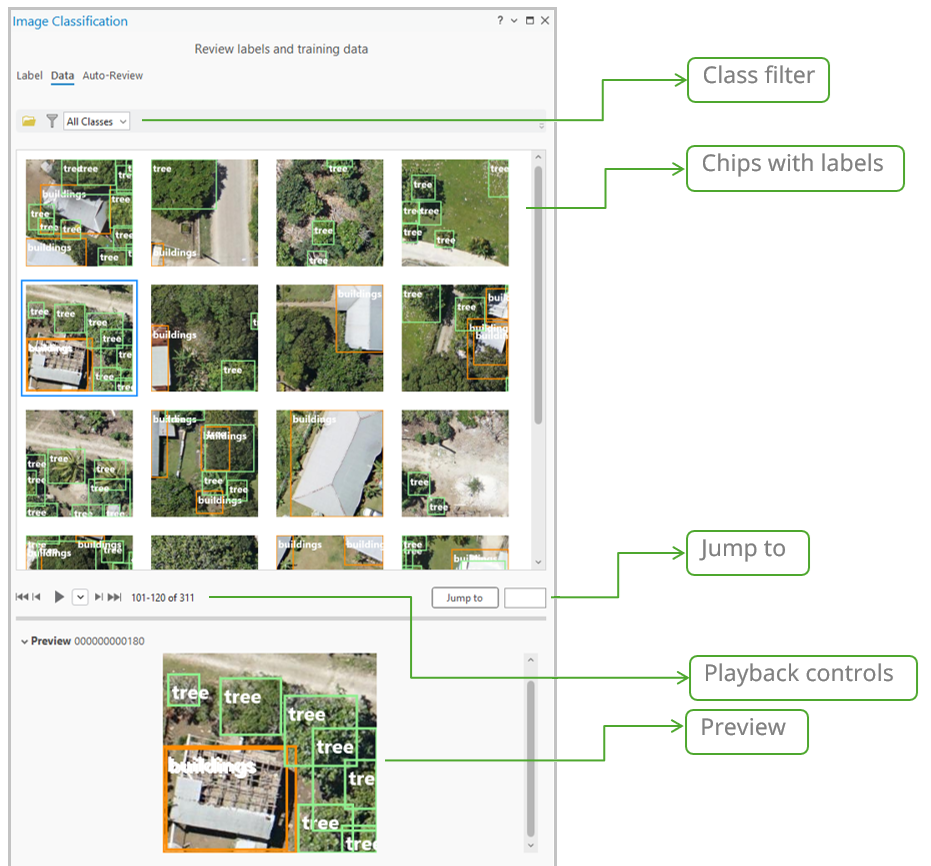
Training data review
The Data tab offers a quick visual QA review of your exported image chips. The main gallery shows image chips with class names with bounding boxes. Selecting a thumbnail displays it at full size for detailed inspection. This allows reviewers to quickly check for common issues such as incorrect chip size, missing or partial labels, or a lack of overlap. To help you review the image chips and labels more efficiently, the Data tab includes filtering, playback, and navigation controls that allow you to quickly screen the exported data. (Note: This visual tool currently only supports object detection training data.)
New Transform Image Shapes tool
Now in ArcGIS Pro, we’re giving you direct control over the geometry of your deep learning output. The Transform Image Shapes tool converts feature geometries between Image Space (the sensor perspective) and Map Space (the standard ground coordinate system). This is important for workflows involving oblique imagery or complex distortions. This tool ensures features detected in the raw image space are correctly placed and measured on the map after rectification. Ultimately, this guarantees the highest geometric accuracy for your final analysis.
Enhanced Grad-CAM
The Grad-CAM feature for Object Classification was introduced at the version 3.5 release, to highlight influential pixels for a single class. This functionality has been extended to now support multi-label classification.
Now, when classifying features into multiple categories, the tool generates multiple attachments in the output feature class—one attachment for each predicted label. This capability gives you detailed insight by showing the specific pixel regions that influenced the model’s decision for every individual class, dramatically increasing the interpretability of complex multi-label classification results.
Enhanced Auto Detect with multi-click
We enhanced the existing Auto Detect specifically for complex features. It now supports multi-click workflows for labeling structures, such as complex buildings or trees. You no longer rely on a single click. Instead, you provide the tool with multiple reference points, which allows it to integrate your input and generate a more accurate object boundary for complex shapes and objects.

New backend Deep Learning readiness check
Ensuring your Deep Learning environment is set up correctly is also crucial. We’ve included a simpler way to verify your setup: a new function that allows the backend to report whether your ArcGIS Pro Python environment is ready for deep learning workflows. This is a fast, definitive check that confirms that the necessary libraries are correctly configured and accessible to ArcGIS Pro.
New 3D-RCNet model type support
Hyperspectral Imaging (HSI) data enables the precise identification of materials based on their unique spectral signatures. Therefore, we are introducing the Hyperspectral3DRCNet (3D-RCNet) model in ArcGIS. This specialized deep learning model type delivers high-accuracy classification of complex HSI data, which is essential for advanced remote sensing applications. It uses an architecture that efficiently merges the strengths of 3D Convolutional Neural Networks (ConvNets) and Vision Transformers. It embeds the Transformer’s powerful self-attention mechanism into a novel 3D relational convolutional operation, ensuring superior performance and computational efficiency.
Wrap-up
ArcGIS Pro 3.6 focuses on improving your GeoAI workflow quality—from training data validation, to model interpretability, and advanced classification. We can’t wait to see the powerful GeoAI applications you build with these expanded capabilities.



Article Discussion: