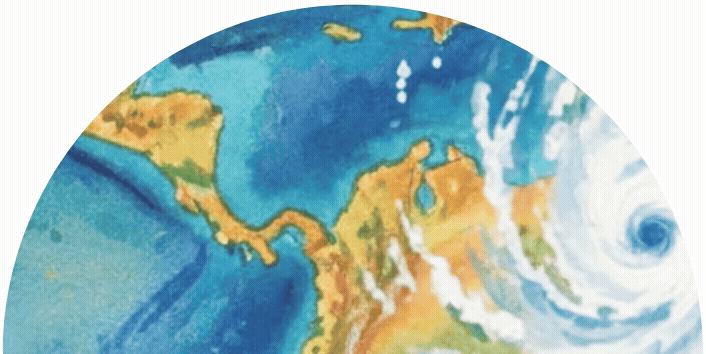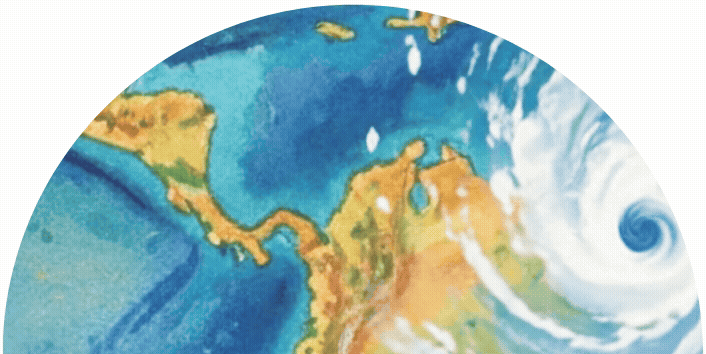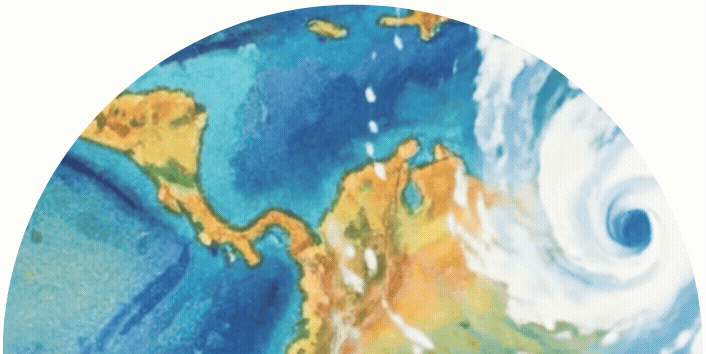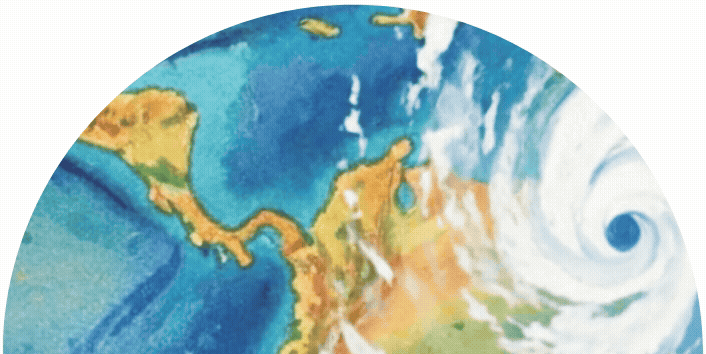
How can we map floods even when storm clouds block satellite views?
When devastating hurricanes, cyclones, and tropical storms flood the earth, traditional optical satellites often can’t capture the full picture. Storm clouds, heavy rain, and darkness create a visual barrier that leaves emergency responders and flood mappers swimming blind.
✨CLICK HERE REVEAL✨
(CLICK AGAIN TO HIDE)
But what if there was a way to peer through these obstacles and reveal exactly where water has spread across the landscape?
Enter Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR), remarkable technology that uses radar waves instead of visible light to create detailed images of Earth’s surface. Think of it as giving satellites “radar vision” that work 24/7, regardless of weather conditions.
Unlike optical satellites, SAR doesn’t rely on sunlight or clear skies. It actively sends out radar pulses and measures how they bounce back from different surfaces. Water has a unique radar signature, and it appears distinctly different from dry land, vegetation, or urban areas. This makes SAR incredibly powerful for detecting water and flood boundaries, even during the height of a storm.
From Exploration to Action
Curious about diving even deeper into your analysis and maybe even getting your feet a little wet in the process?

ArcGIS offers sophisticated tools that transform SAR satellite data into actionable flood and waterbody maps. With ArcGIS Pro SAR analysis toolset and deep learning-based waterbody extraction models you can identify flood boundaries, turning hours of manual analysis into minutes of automated processing.
Whether you’re tracking permanent water bodies like rivers or monitoring emergency flood events, ArcGIS SAR technology offers powerful capabilities. The integration with ArcGIS means you can:
- Access global SAR data instantly through Living Atlas
- Compare before-and-after flood scenarios with intuitive tools
- Apply advanced water extraction algorithms with just a few clicks
Methods for Extracting Water from SAR Data
Explore the following methods that you can do to extract water insights!
Not sure which method to start with?
Each method offers a different level of complexity, flexibility, and speed, so your choice depends on your goals. If you want to quickly explore SAR imagery and compare flood conditions without needing to download data, the Sentinel‑1 Explorer (jump to section) is the simplest place to begin. If you need more control, customization, or repeatable workflows, the ArcGIS Pro geoprocessing tools (jump to section) provide a full analytical environment. If your priority is automated detection of waterbodies with minimal setup, the ready‑to‑use deep learning model is the most efficient option (jump to section). Start with the method that best matches your experience level and analysis needs, then explore the others as you expand your workflow!
| Method | Skill Level | Best For | Data Requirements | Strengths |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sentinel‑1 Explorer | Beginner | Rapid visual comparison of flooding before and after events | No downloads required; uses Living Atlas data | Fast, intuitive, browser-based; great for exploring global SAR data; interactive tools like Swipe |
| ArcGIS Pro SAR Geoprocessing Tools | Beginner to Advanced | Detailed analysis, custom workflows, and precise extraction | Requires downloading and preparing SAR data; DEM optional | Full control of processing steps; supports calibration, terrain flattening, and despeckling |
| Deep Learning Water Body Extraction Model | Intermediate to Advanced | Automated water detection at scale with minimal manual steps | Requires preprocessing of Sentinel‑1 SAR data and installed deep learning libraries | No model training needed; ideal for repetitive tasks or large areas |
Method #1: Sentinel-1 Explorer with the Water Index
Want to be able to quickly compare images before and after a flooding event? Well now you can, with the Sentinel-1 Explorer! But here’s where it gets really exciting! It offers a user-friendly entry point into SAR analysis. You don’t need to be a radar expert to tap into this technology. Thanks to ArcGIS Living Atlas, Sentinel-1 SAR data is now as accessible as checking the weather on your phone.
The real kicker? This global dataset stretches back to 2014, creating a treasure trove of flood history at your fingertips. Whether you’re a student, researcher, or emergency manager, you can access this data directly in your browser without downloading massive files.
↔️See the built-in Swipe tool and Water Index renderer in action! 💧
You can literally watch how flood waters spread across the landscape in Athens during this 2023 storm event.
- Click the following link to see Indonesia during the 2025 storm event.
- You’ll see the November 16th imagery precedes the flood, while November 28th imagery captures the aftermath.
- While in the Swipe mode, use the
 to “Drag to compare” the two dates. It is currently being rendered with the Water Index, which highlights water presence. The areas in blue show areas that have a high water index. Notice that the image on the right (post event) shows a higher water index.
to “Drag to compare” the two dates. It is currently being rendered with the Water Index, which highlights water presence. The areas in blue show areas that have a high water index. Notice that the image on the right (post event) shows a higher water index. - Use the Analyze button to change modes, with the Index mask button selected, see the index calculated to delineate and measure estimated surface area of things like water and water anomalies, see how to steps.
Download the data
If you’d like to directly download the SAR data after exploring, scene information is provided to download Sentinel-1 data. Alternatively, the Sentinel-1 RTC data behind the explorer can be accessed via ArcGIS Living Atlas.
- Directly open it in Map Viewer or ArcGIS Pro Desktop.
- Explore the same Processing Template options available in the Explorer within ArcGIS Pro or ArcGIS Map Viewer.
TLDR: A quick, way to compare SAR scenes and spot flooding directly in your browser.
Method #2: ArcGIS Pro SAR Toolset Geoprocessing Tools for Analysis
Since SAR data contains bands with non-visible wavelengths, a common way to analyze SAR data is to create a color composite to make the data easier to interpret. A color composite uses band combinations for the red, green, and blue display channels to create a color image. Additionally, read this StoryMap resource, SAR Analysis for Create Color Composite. Then you can see how to identify flooded areas in this tutorial section or read this documentation to learn how to interpret SAR data for flood mapping.

Alternatively, the geoprocessing tool, Extract Water, creates polygons by classifying radar backscatter pixels. To preview this tool in action, check out this ArcGIS Pro short video, Use the Extract Water Geoprocessing Tool in ArcGIS Pro. Additionally, read this StoryMap resource, SAR Analysis for Extract Water.
- Download SAR satellite data for any supported sensor data.
- Prepare the data:
– For offshore, use the Apply Radiometric Calibration tool to calibrate to Gamma nought
– For onshore, use the Apply Radiometric Calibration tool to calibrate to Beta nought, then use the Apply Radiometric Terrain Flattening tool to generate flattened Gamma nought
– (optional) Use the Despeckle tool and/or Remove Thermal Noise tool to mitigate noise - Input the prepared data and optional DEM.
- Click Run. You’ll see in the map that the tool creates polygons for water areas and will also create polygons for areas that are not water (land areas).
TLDR: A customizable workflow that lets you preprocess SAR satellite data from supported sensors and extract water with high precision.
Method #3: Water Body Extraction with a Deep Learning Model
Skip the hassle of training! Use this ready-to-use deep learning model that’s already been trained to recognize water bodies in SAR imagery. No need to spend months training your own model! Just download, install, and start mapping floods like a pro. This model is ideal for permanent water bodies, such as rivers. The tutorial “Map floods with SAR data and deep learning” provides step-by-step guidance for implementing these techniques in your own area of interest. From the tutorial, you’ll discover how to download Sentinel-1 data, apply the necessary processing steps, and extract meaningful flood information using the cutting-edge deep learning model and the Binary Thresholding technique.
Scroll below to preview the tutorial page
⬇️⬇️⬇️⬇️⬇️⬇️⬇️⬇️⬇️⬇️⬇️⬇️⬇️⬇️⬇️⬇️⬇️⬇️⬇️⬇️⬇️⬇️⬇️
TLDR: A ready‑to‑use model that automatically identifies waterbodies at scale.
The Future of Flood Resilience
As climate change intensifies weather patterns across the globe, tools like SAR become essential for building resilient communities. The ability to rapidly assess flood impacts, track water recession, and plan recovery efforts can mean the difference between effective response and prolonged disaster.
The next time storm clouds gather and traditional satellites go dark, remember: SAR technology is still watching, still mapping, and still providing the critical insights needed to understand and respond to our changing world!





Commenting is not enabled for this article.