Drones offer high-resolution imagery anywhere on demand. By taking advantage of drone imagery, you can quickly address anything from vegetation encroachment on powerlines to the progress of a city works project. Skilled drone pilots can capture imagery anywhere whenever it is needed. Having your drone operations run smoothly and safely will allow you to make the most out of your investment in the time, labor, and hardware that is necessary for capturing drone imagery.
Coordinating a drone operation with many pilots, a fleet of vehicles, and many locations can come with its share of challenges. Even smaller drone programs with 1-2 pilots may have a need for accurate record-keeping and tasking. Who is flying when? Do they have permission to fly there? Can we task a team to fly to a particular location? How will we know when they are done? These questions can be answered by leveraging the interconnectedness of ArcGIS.
Collecting imagery with drones is a mobile workflow for a mobile workforce. ArcGIS has a suite of field apps that mobile teams have been leveraging for years. This article will walk through three ArcGIS field apps and how they can be used to help coordinate drone operations. The first workflow discussed is how drone flight requests can be supported using ArcGIS Survey123, then how ArcGIS Workforce can be used to task and track drone flights and finally, how ArcGIS Field Maps can be leveraged for in-field navigation and ground control collection.

Requesting and approving missions with Survey123
Survey123 allows you to design simple and intuitive smart forms and surveys that can be shared with anyone inside or outside of your organization. Surveys can be customized to fit mission requests specific to your organization. It also serves as a system of record; it keeps the details of all requests that have been made whether they have been approved or not. Common fields like name and date can be added, but customizing the survey to be specific to a drone collection can be simple and effective. Some examples of Drone specific fields could be UAS (Unmanned Aerial Systems) model, FAA (Federal Aviation Administration) Part 107 Certificate license number or an acknowledgment if the mission is in controlled airspace. An added advantage is the ability for requestors to create polygons that represent proposed mission sites.

Survey requests can feed into your GIS (Geographical Information Systems) dashboards and apps to display how the requests relate to planned or past missions, existing imagery, controlled airspace, or other geographic features important to your organization.
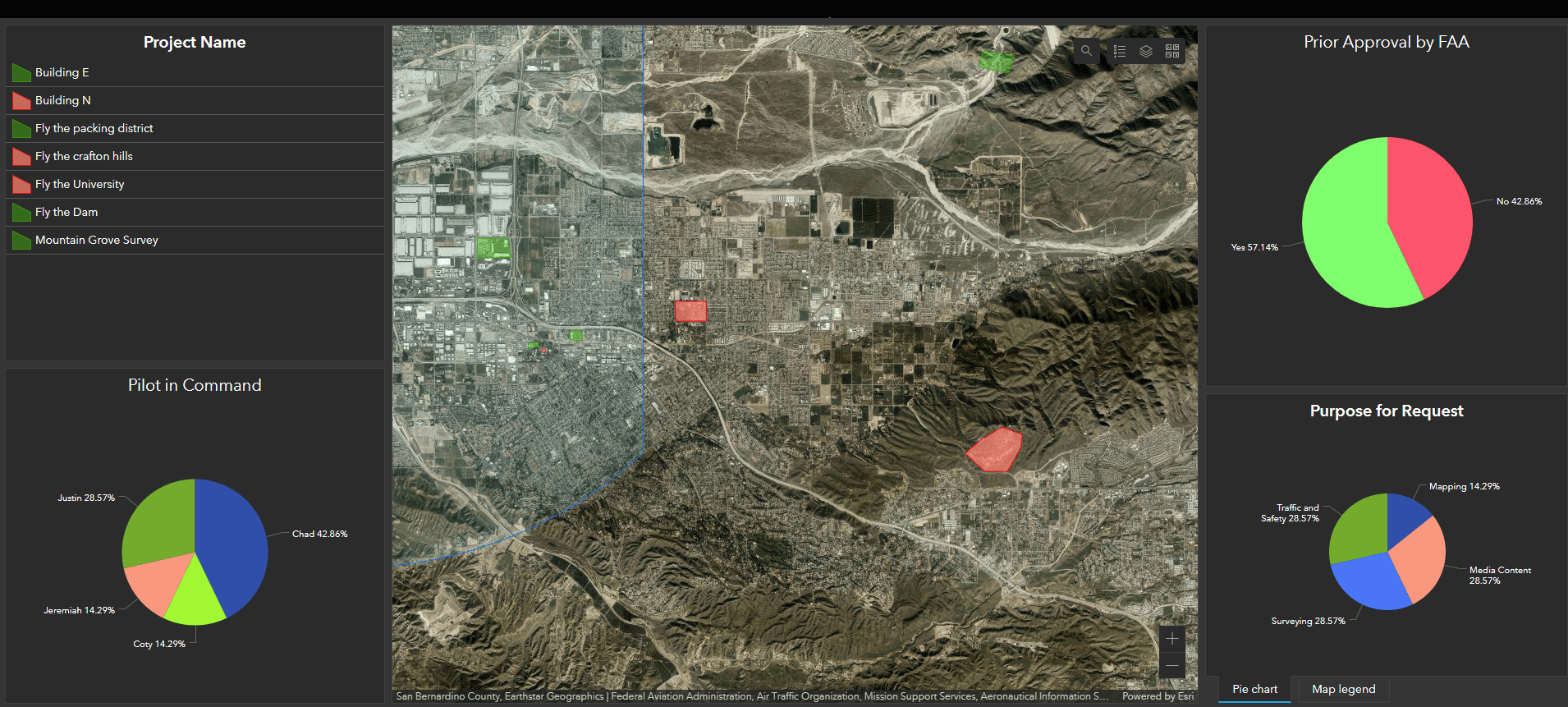
In this example we can see which missions have been approved, the pilot in command, and the purpose of the mission. We can also see where missions are in relation to each other and in relation to controlled airspace. The beauty of this comes from the customizability. Surveys and dashboards can be customized to fit your organization’s needs. Survey 123 can be a powerful organizational tool for managing mission requests. Next, we will look at tasking pilots with ArcGIS Workforce.
Tasking drone pilots with ArcGIS Workforce
While missions can be requested in Survey123, they can be assigned and dispatched within the ArcGIS Workforce. As an app, Workforce is a mobile and SAAS solution that uses a geographic approach for better mobile workforce and coordination and teamwork. It provides real-time information and allows dispatchers to assign fieldwork on the fly. Workforce is a perfect fit for helping to coordinate a drone operation composed of mobile workers. It allows you to see the status of each project and each pilot.
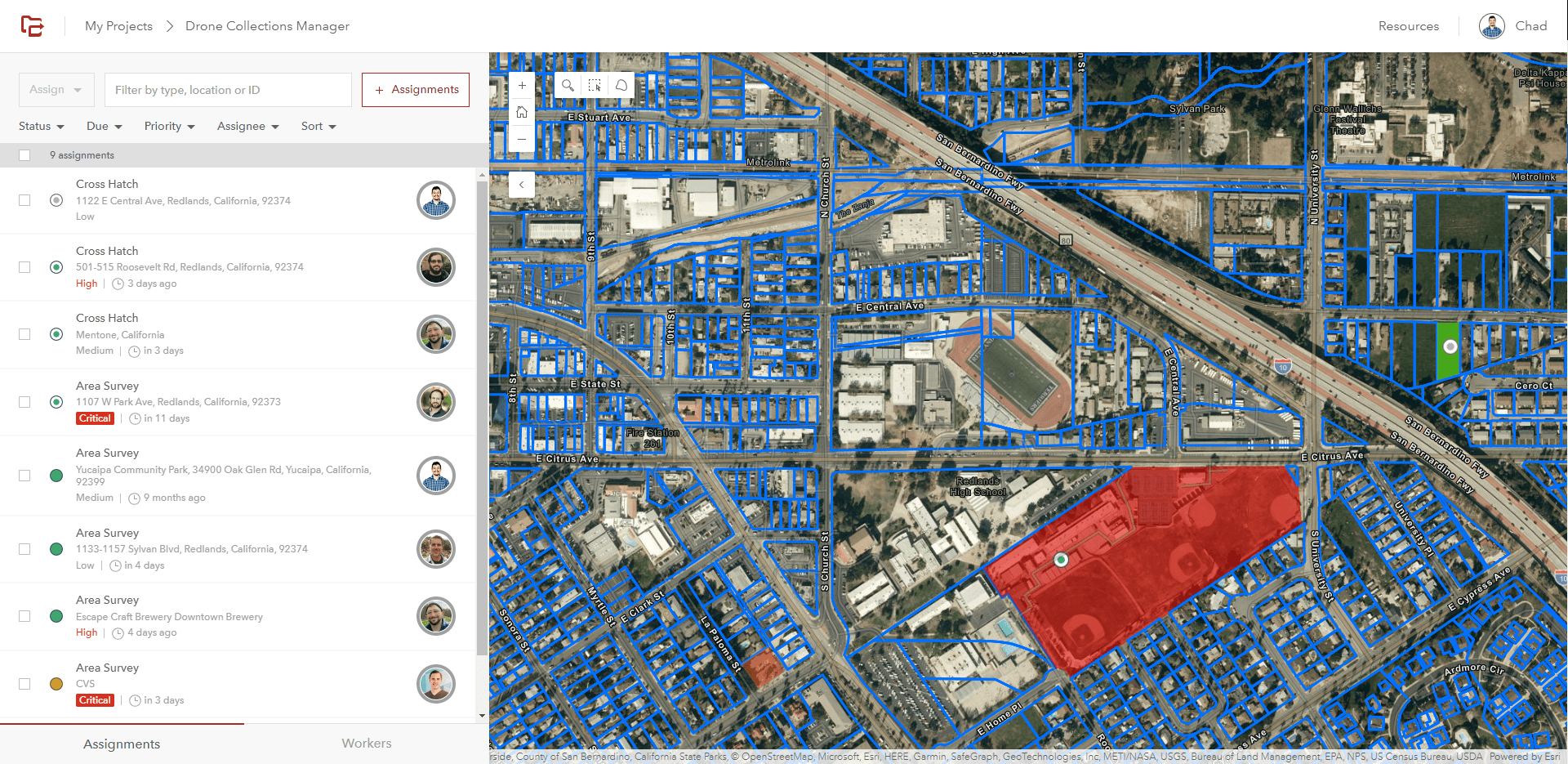
The app can leverage geographic features, like parcels in our example, to assign tasks based on a geographic area. Users are also able to assign custom polygons created in ArcGIS Online or even the requested polygons from Survey123 to serve as the bases for an assignment or a flight plan.
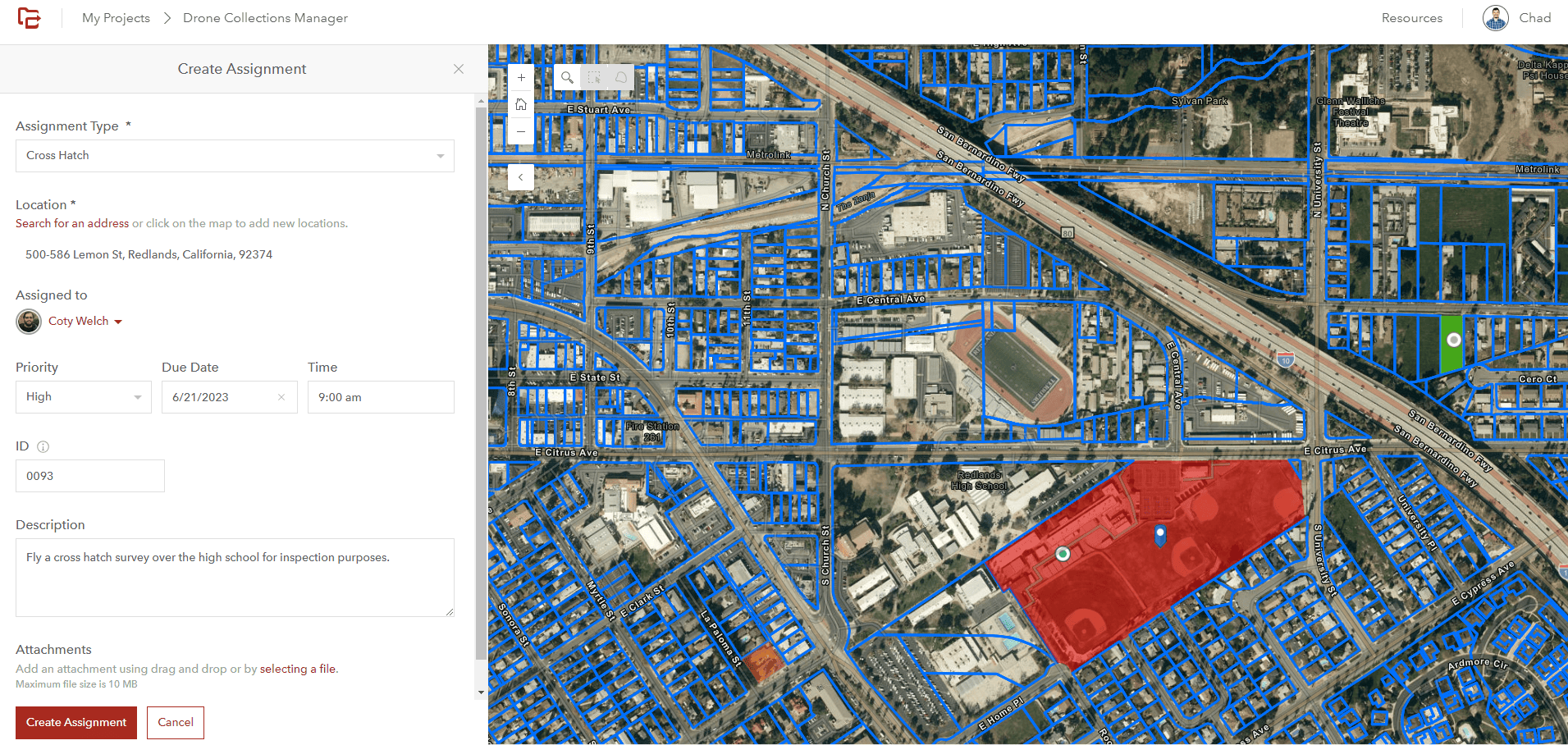
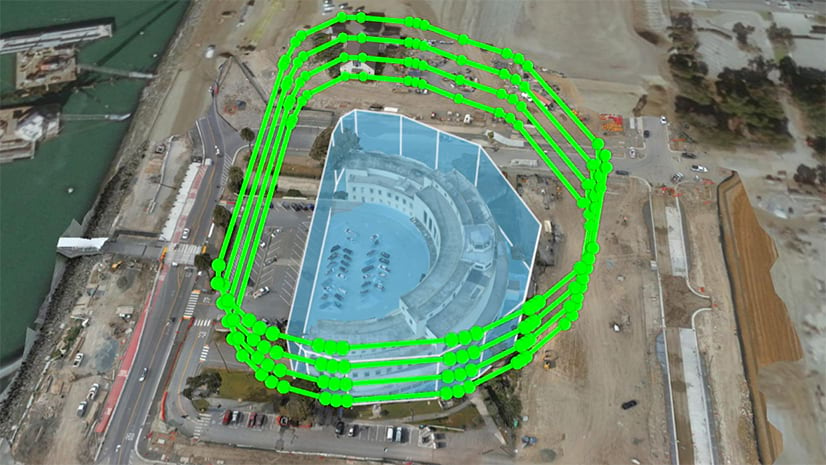
Workforce works very well for assigning missions to pilots however, leveraging features from Workforce for creating actionable flight plans can also be a very impactful workflow. ArcGIS Flight can import features from ArcGIS Online or ArcGIS Enterprise to be used in flight planning. Once a flight has been assigned a pilot can select the polygon representing the flight area to begin a flight plan. This feature is important because it uses existing data to make sure that the entire required area for the mission is being flown. You can learn more about ArcGIS Flight here. We also wrote another article about using ArcGIS data to plan flights here.
Using drones with ArcGIS Field Maps
Ground Control Points
An essential part of gathering geographically accurate imagery is gathering ground control points. ArcGIS Field Maps is an effective tool for GCP (Ground Control Points) collection. Field Maps can utilize high-accuracy GNSS devices to gather points to be input in ArcGIS. Not all projects require a high level of Geographic accuracy, but ArcGIS makes it easy to collect accurate data. In a future article, we will cover best practices for GCP collection but for now, it is important to know that ArcGIS Field Maps is a key component in collecting accurate GCPs for reality mapping missions.

Mobile Basemaps
Field Maps also works well for validating observations derived from drone data or to work as a timely basemap in the field. As seen in this example a team member can make an actionable observation in Map Viewer and assign it to a mobile worker in ArcGIS Workforce.
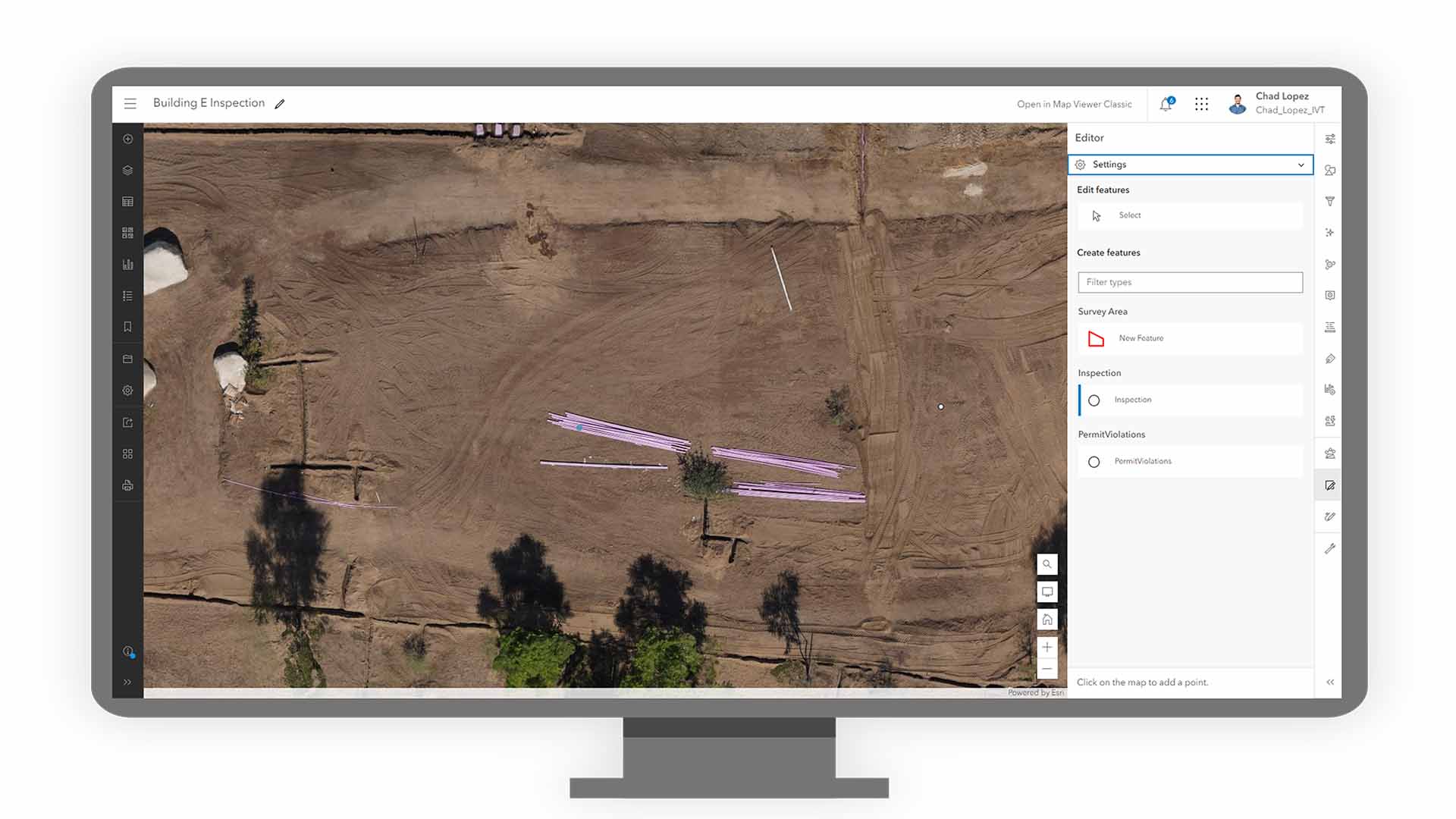
In the field, workers can navigate to the observation site and take precise action, viewing the imagery as observed. In this case, the worker knows exactly which pipes to move because they can see it in the drone-derived orthomosaic opened in Field Maps.

We walked through a few examples of how ArcGIS Field apps support coordinating drone operations. ArcGIS apps and drones complement each other very well. You can swiftly and easily answer any operational question that may arise when working with a UAS fleet. Using ArcGIS for your drone operations allows you to take advantage of the breadth of the entire ArcGIS suite of tools. ArcGIS has proved itself to be a dependable, user-friendly, and versatile solution for mobile workers. Using ArcGIS apps for coordinating drone operations also keeps your entire team, stakeholders, dispatchers, and pilots connected and on the same page. It is a natural fit to extend those capabilities to your drone pilots.





Article Discussion: