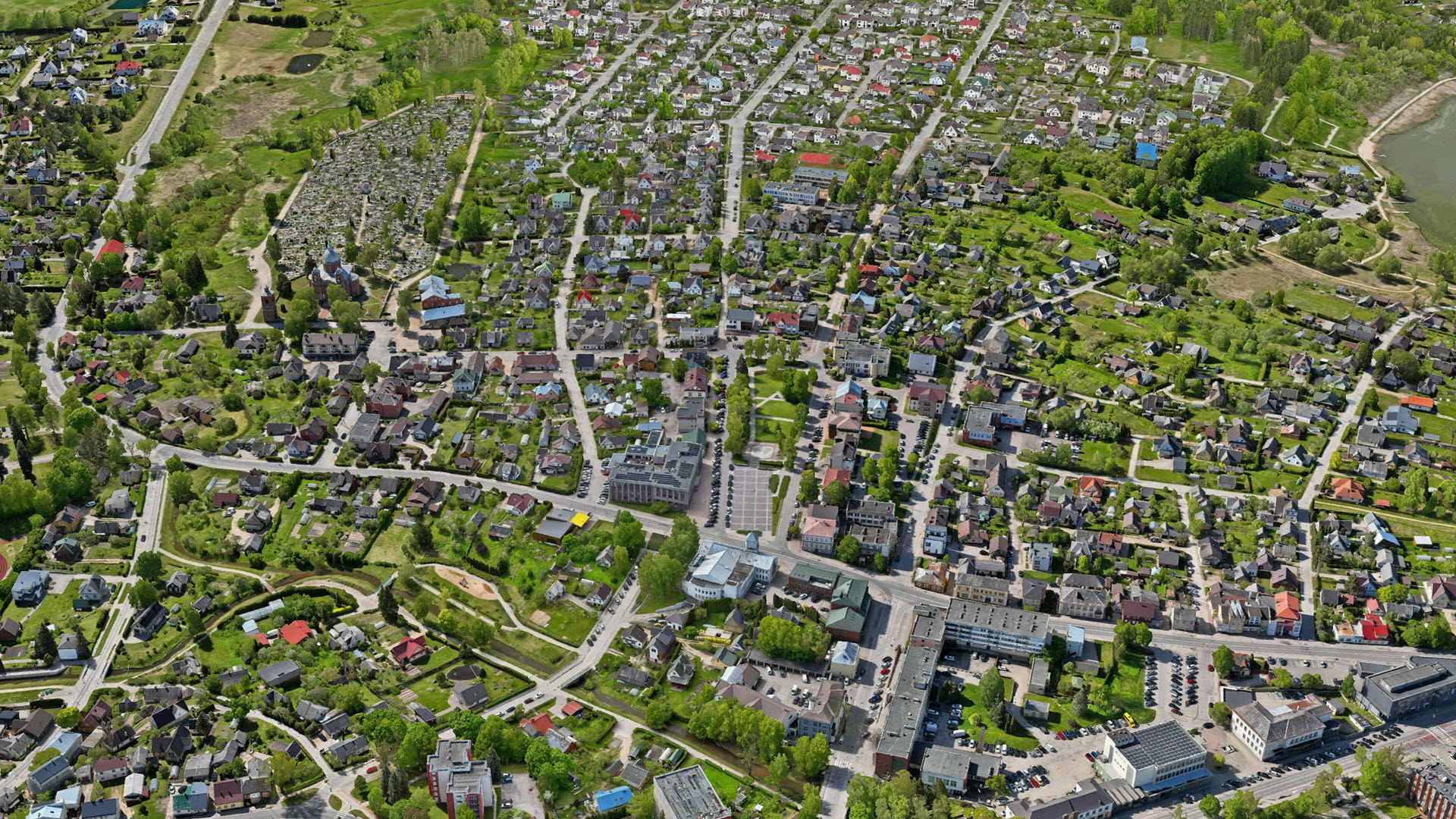
3D mesh of the city of Utena, Lithuania. Data courtesy: Utena District Municipality & HNIT Baltic
Mapping entire cities or even countries is a complex challenge that requires capturing vast geographic areas. Traditionally, this involves expensive aerial surveys and specialized equipment to achieve high-quality data on a large scale. But what if you could achieve the same using flexible and cost-effective drones?
Using drones is attractive because they have low purchase costs and can often be operated easily without extensive flight permissions. At the same time, they require more flights and generate a larger number of images, which presents challenges for managing and processing such large datasets.
The latest release of ArcGIS Reality Studio introduces a range of new features that automatically adapt to these drone data characteristics, allowing for handling large-area mapping projects executed with drones. In combination with already existing features for managing multiple flights and distributed processing, Reality Studio enables you to execute even the largest projects effortlessly. As with aerial data, it only takes three simple steps to process your data. All three steps have been improved to work with drone data.
Would you like to achieve this as well? Let’s get into the details below.
Import drone imagery
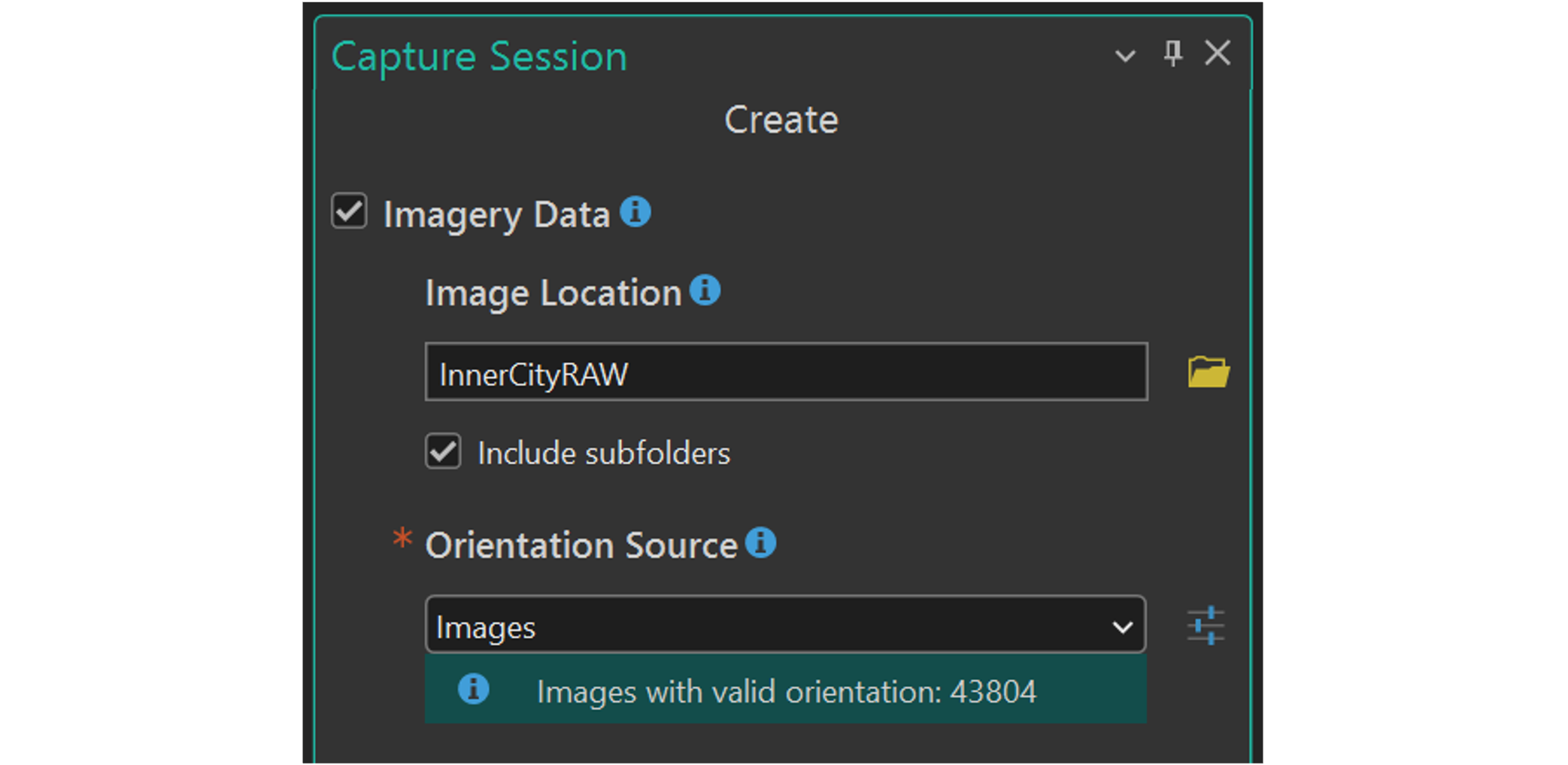
Import of images and orientations in one go
Importing drone imagery into Reality Studio can simply be done by selecting your image directory during capture session creation. Reality Studio reads the image header and automatically extracts the position and rotation of the camera during image capture. This information is recorded during the flight with GNSS and inertial sensors and is stored in the header of the image. Furthermore, Reality Studio extracts the intrinsic camera parameters such as image format, pixel size and focal length from the image header .
Match other reference systems
Drone-captured imagery often comes in a default GNSS -based system such as WGS 84, which may not align with the coordinate system used in your project. By selecting a target reference system during import of capture sessions, you can seamlessly integrate the imagery with other geospatial datasets. This allows you, for instance, to use ground control points in a local projected system.
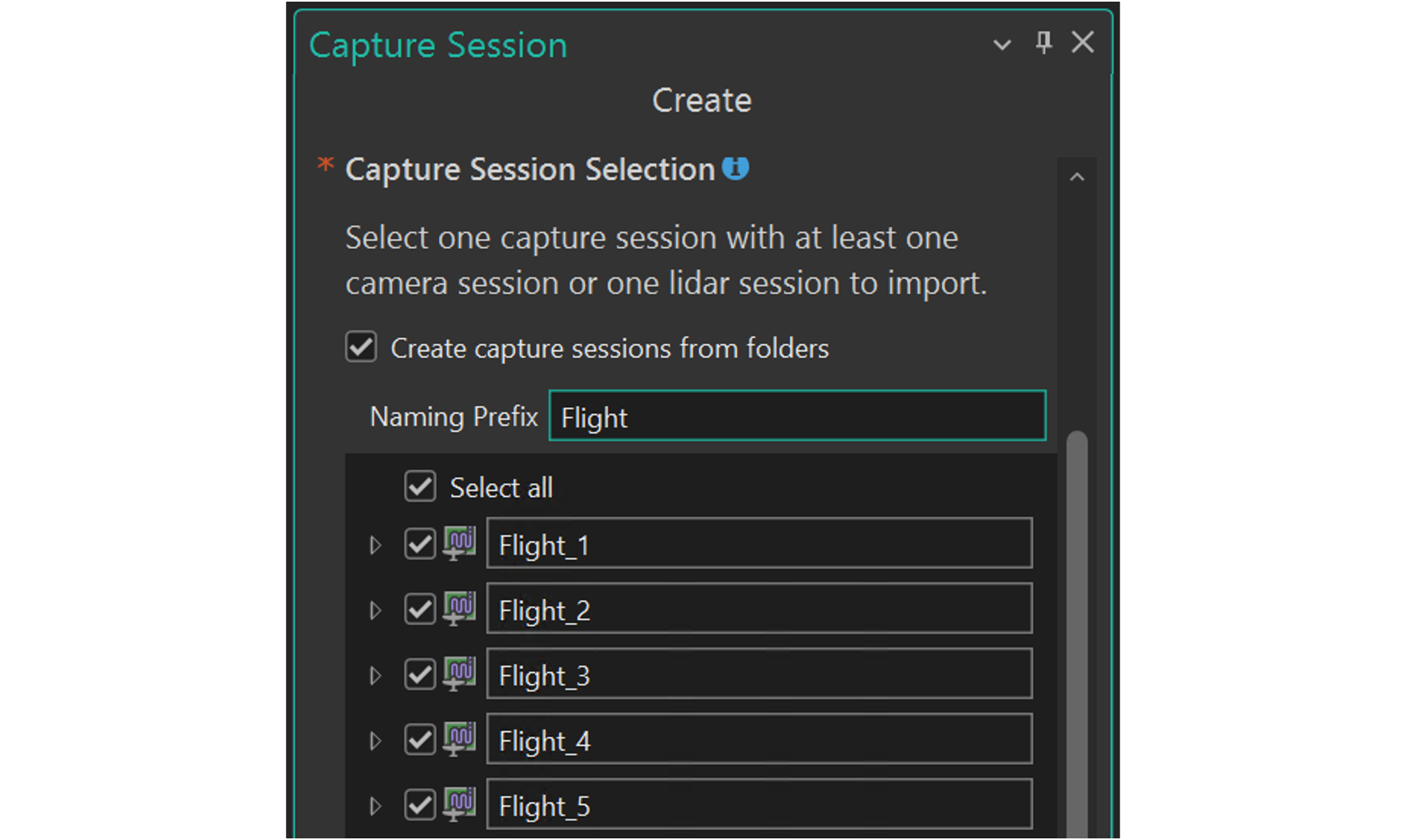
Import multiple capture sessions at once
Reality Studio organizes all data from a single flight into its own capture session. This enables high accuracy, as each flight can have the best possible camera calibration.
Capturing large areas with a drone typically requires multiple flights, resulting in several capture sessions . Since these sessions are all part of one larger mapping project, joint processing is essential to produce a seamless dataset.
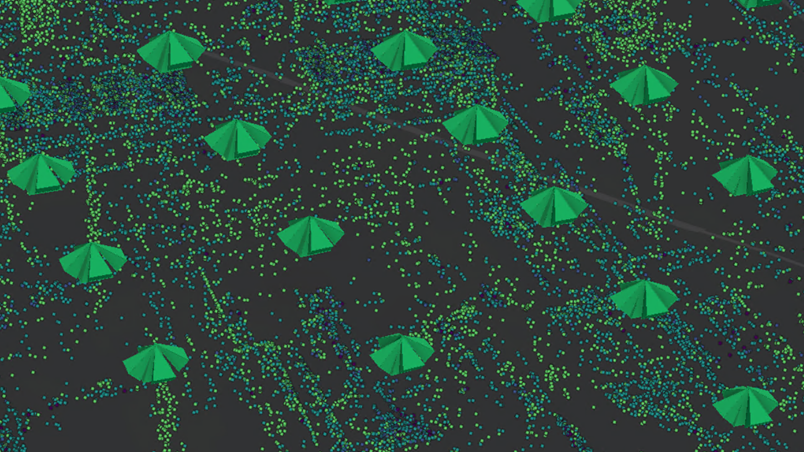
Perform an alignment to optimize your orientations
Once a capture session is created from the images, users can improve the provided input position, rotations and intrinsic camera parameters with an alignment.
The goal of the alignment is to optimize the orientation of the input images with respect to each other and, optionally, to ensure accurate georeferencing if ground control points are provided. This is achieved by first detecting identical points in the input images, so that with given image orientations, these points can be reconstructed in 3D object space. Subsequently, the image positions, rotations and camera intrinsics are adjusted to minimize the discrepancy between the originally detected point and the reprojected 3D point in image space.
Finally, we know for each image exactly where it was captured and how the camera was rotated. The alignment algorithm behaves adaptively to the drone case to maintain fast processing while guaranteeing high accuracy at the same time.
To make the workflow for setting up an alignment as smooth as possible, Reality Studio allows you to select the estimation of specific intrinsic camera parameters for multiple capture sessions at once.
Create a reconstruction
Dedicated optimization of reconstructions from drone data
Reality Studio now features new capabilities designed for large-area reconstruction from drone datasets. With the newly introduced dedicated Drone scenario, you can process large drone datasets to produce geospatial products from your aligned data. To efficiently process the large number of images in drone datasets, the Drone scenario is tuned to deliver results with high performance. Using this scenario, you can derive both 2D products, such as True Orthophotos or DSMs, and 3D products like Meshes, Point Clouds, or Gaussian Splats, from your images.

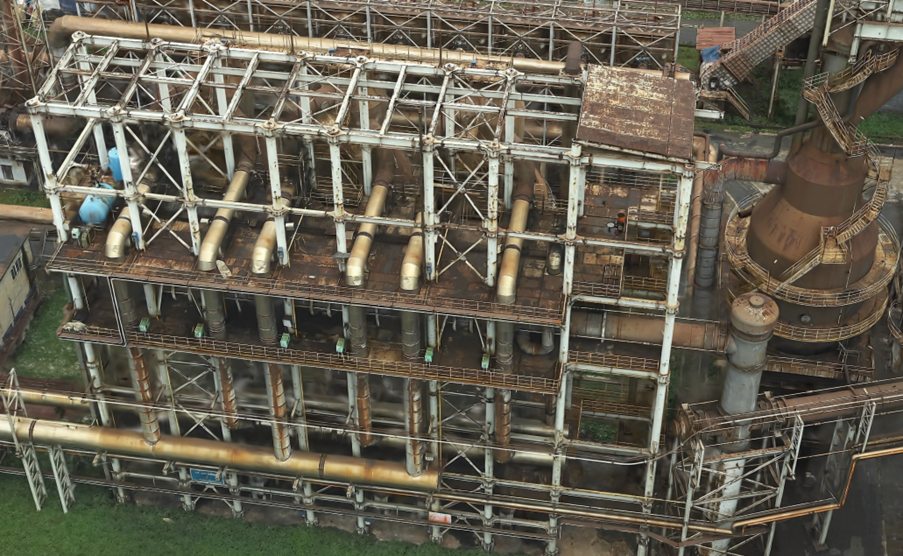
A new output format to make your drone data shine
Drone imagery can suffer from less stable capture conditions, which can make the reconstruction of fine structures challenging. Reality Studio addresses this with a newly added Gaussian Splat layer. This advanced visualization technique offers an efficient way to represent and render complex 3D scenes, enabling the reconstruction of fine details and transparent surfaces. With Gaussian Splats, you can achieve rich, detailed, and accurate reality mapping even from challenging drone datasets.

Summary
With its latest features, Reality Studio empowers users to efficiently process drone data and produce stunning results in just a few steps. A streamlined import of data, optimization of the alignment and dedicated reconstruction tools in combination with a new output format enable powerful workflows with drone data. Leveraging these features, you can generate accurate products with high performance at scale.
Whether you’re working on urban planning, environmental monitoring, or infrastructure projects, these tools will help you unlock the full potential of drone-based mapping.
Get in touch with your local Esri distributor to request an evaluation of Reality Studio to discover how these innovations can transform your workflow.
Want to learn more about Reality Studio?
Check out the documentation or join the Esri Community.



Article Discussion: