Many organizations are increasingly dedicated to collecting imagery of their assets, leveraging this data to document both existing conditions and changes over time. However, this type of analysis presents several challenges, such as cataloging the data, preparing it for analysis, and ensuring accessibility for various analyses, including change detection, feature extraction, and trend estimation. How can a a single imagery layer be used in all these workflows?
When dealing with imagery that spans multiple dates, ArcGIS offers a robust end-to-end suite of tools designed for the effective management, analysis, and visualization of large datasets. One compelling solution to consider is the use of multidimensional imagery layers in ArcGIS Online in a unique way.
Multidimensional imagery layers are capable of handling multiple variables across many dimensions efficiently. You may be familiar with multidimensional imagery layers when they are used with NetCDF data or other scientific datasets. However, these imagery layers can also be used to display just one variable and still take advantage of its ability to visualize imagery over different time periods. These layers not only facilitate sharing imagery across your organization but also extend access to selected external groups or the public.
Imagery layers can be created through various methods, but for this specific solution, we will focus on utilizing a mosaic dataset to create our multidimensional imagery layer. This blog will explore how and why multidimensional imagery layers can significantly enhance your organization’s management, utilization, and accessibility of multi-date remotely sensed content, showcasing a unique use case that streamlines workflows and improves analytical capabilities.
Mosaic datasets and time
As you learned in a previous blog, mosaic datasets are a great way to catalog your imagery assets and prepare them for sharing and analysis. A primary capability of the mosaic dataset model is that it can provide the framework and backbone critical to the administration of imagery data over time. Mosaic datasets can manage an existing or growing stack of data or even other mosaic datasets as input, which allows users to create a single dataset for a particular area covering a span of time. Datasets that contain a collection of content like this can be time enabled and then navigated with the time slider in ArcGIS Pro. Once the mosaic dataset is created and time enabled, it can also be shared as an imagery layer in ArcGIS Online, and visualized with the time slider in Map Viewer.
Another option to manage time in your mosaic dataset is to make it a multidimensional mosaic dataset. This lets you easily explore and analyze imagery over time and space with the multidimensional tools. Although traditionally used for datasets containing scientific or other similar types of datasets, multidimensional mosaic datasets can store multiple images covering a particular area for multiple time periods. This is best applied to remotely sensed content like reality mapping products such as orthomosaics and surface models, individual multispectral satellite scenes, and aggregated images such as cloud free satellite composites. When the mosaic dataset is made dimensionally aware and shared online, Map Viewer can be used to engage with the imagery layer and visualize change over time through configuring the multidimensional properties.

Multidimensional imagery layers
The multidimensional imagery layers that are described in this blog are imagery layers that contain data with more than one time period represented for a particular area. These imagery layers are described as being multitemporal and can also be referred to as archival imagery layers, living imagery layers or time series imagery layers as well. In ArcGIS Online, when a multidimensional imagery layer is added to the Map Viewer, the other time periods can be visualized by manipulating the time slider or multidimensional slider. These tools use the time data within the imagery layer to show points of interest or ranges in time. You can even animate the map to see it change over time, or use Multidimensional Filter raster functions or the Image Collection Explorer for image collection imagery layers.
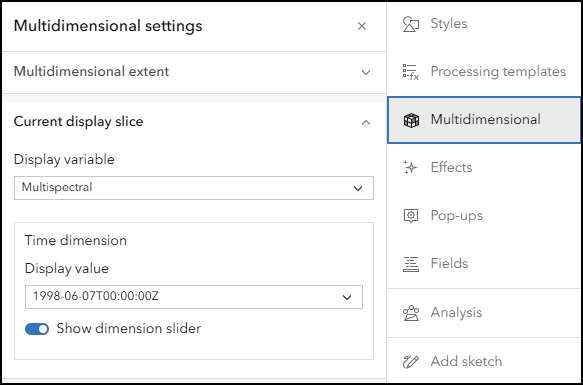
Uses for multidimensional imagery layers
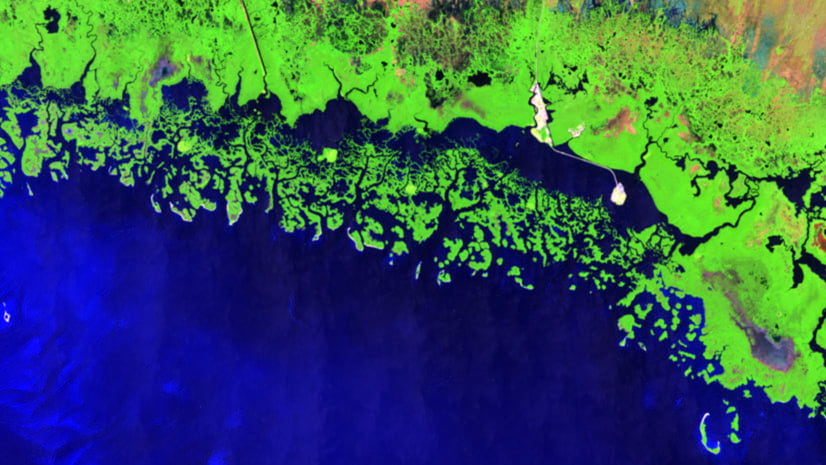
Multidimensional imagery layers can provide a lot of opportunities for analysis and visualization for your organization. Visualizing change in a particular area, analyzing what has changed, and measuring the change with remote sensing sometimes requires multiple datasets. With multidimensional imagery layers, you can manage, analyze and visualize change with one imagery layer. In addition to the analysis, you can also provide an easier way for users in your organization to access large collections of related data. Here are two common uses for multidimensional imagery layers:
- Over the years – you can add one imagery layer that provides access to multiple time periods. So, municipalities that collect imagery of their assets every year can create a multidimensional imagery layer that allows users to access all this imagery in one layer..
- Before, during, and after – when events occur, many can be seen remotely from satellite to drone imagery. With multidimensional imagery, you can access and leverage the information of before, during and then after events of interest. For natural disasters, these views can aid and inform the recovery effort during the event or provide a way to forecast what may happen in the future unless steps are taken.
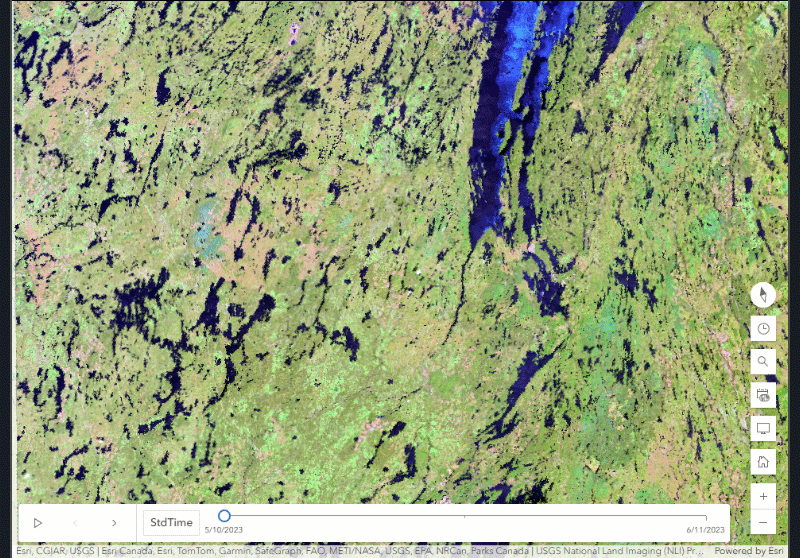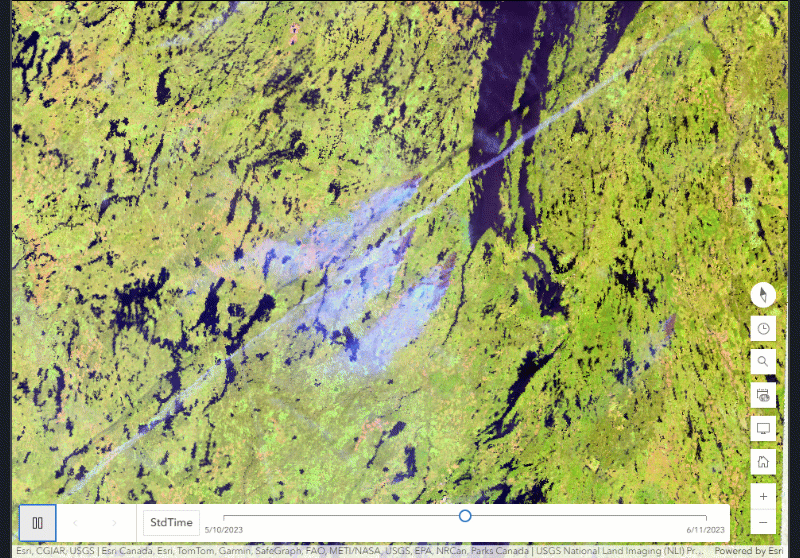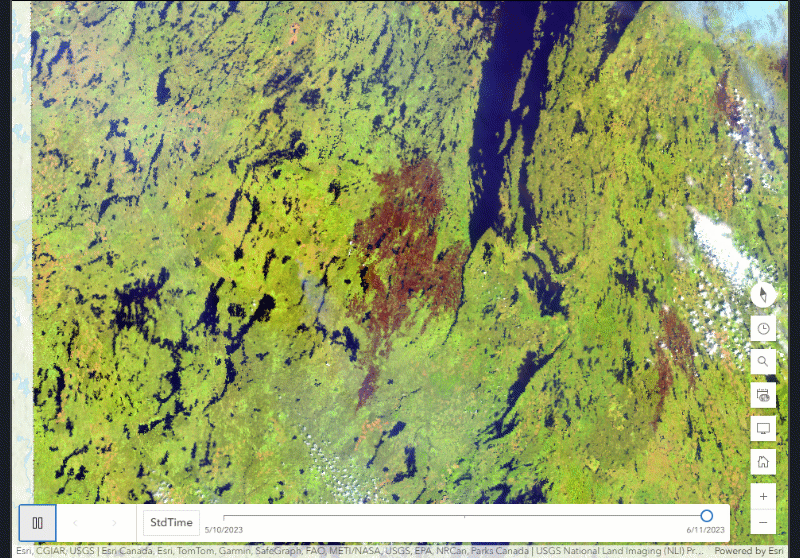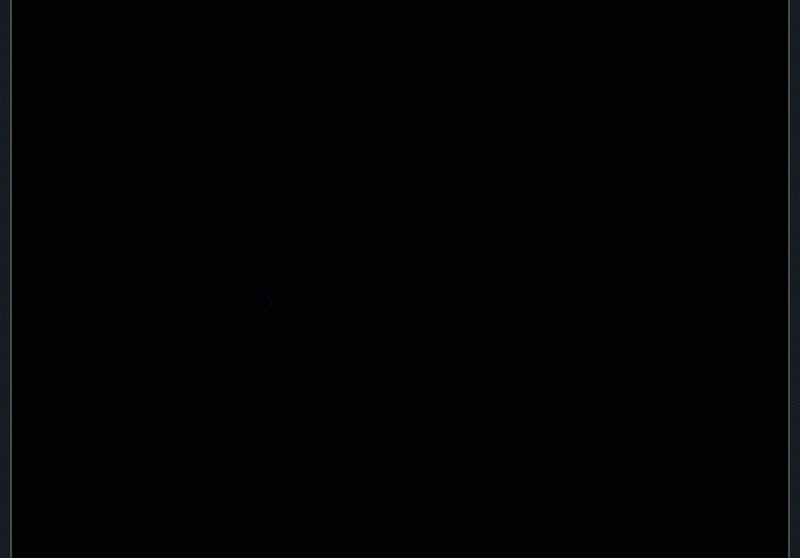
Conclusion
Multidimensional imagery layers can provide a lot of functionality in regard to maintaining your imagery assets in your organization. Investments in imagery can often be witnessed by providing an accurate view of what is currently present and a retrospective view of what used to be. How multidimensional imagery is used depends on the organization or the research being conducted. We look forward to hearing about how you use multidimensional imagery in your organization.
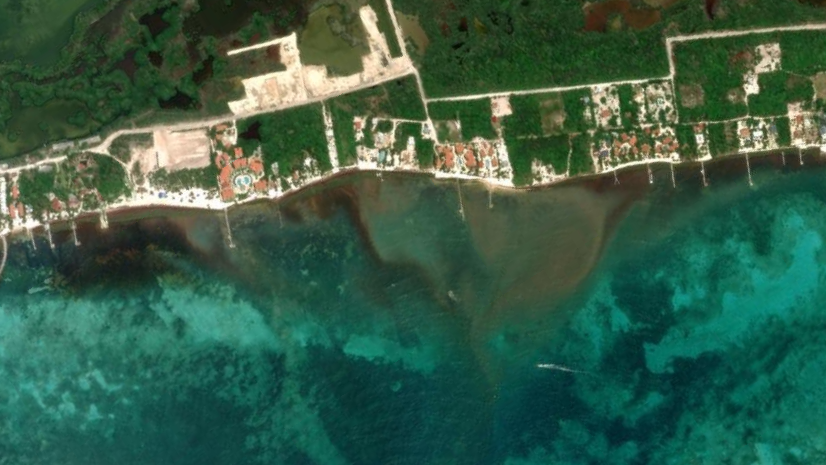



Article Discussion: