We’re excited to announce the availability of 4 new field types that revolutionize the way we work with date, time, and numeric data in ArcGIS Online. In this article, we’ll introduce the new field types, explore use cases to highlight the practical applications of each, and offer tips to help you seamlessly view, store, and edit data using the new field types. These new field types are:
Whether you’re managing temporal data, numerical values, or intricate time zone conversions, these field types can offer an improved mapping and data management experience.
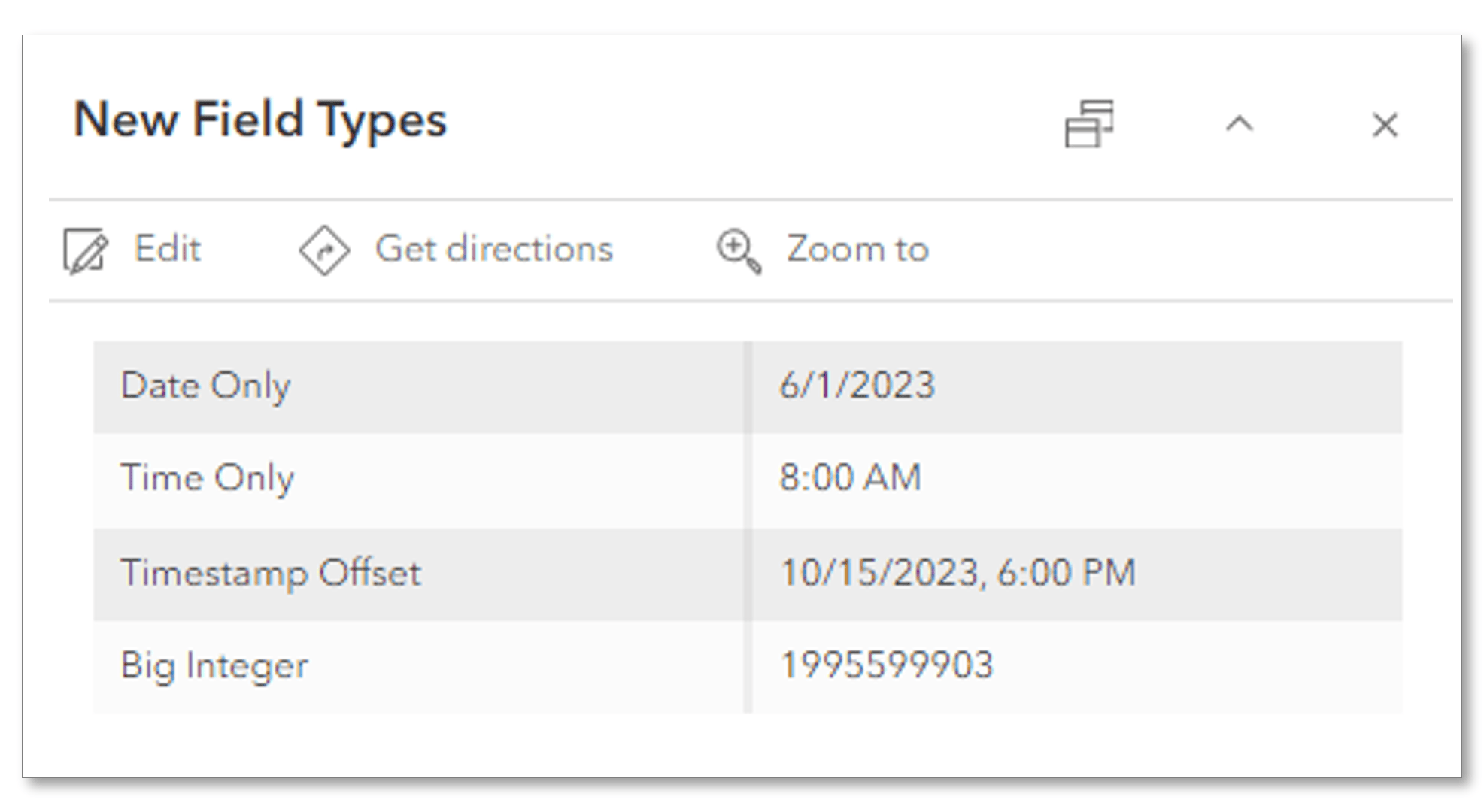
New Field Types
Date and Time
Many feature layers store date and time information. This data could represent a point in time when a feature was mapped, or last inspected. Previously, ArcGIS Online only provided the Date field type, which combined both date and time values; each date value has an associated time value, and vice versa.
The new field types allow you to store date values, time values, or both separately, depending on your requirements. The Date only, Time only and Timestamp offset field types offer you more options and flexibility for managing your date and time data.
Big Integer
That’s not all, we also added a new field type for big integers. The Big integer field is designed to handle integer values that exceed the capacity of the Integer field type. With it, you can store values ranging from -9,007,199,254,740,991 to 9,007,199,254,740,991. This gives you more flexibility for working with large numerical data in your projects.
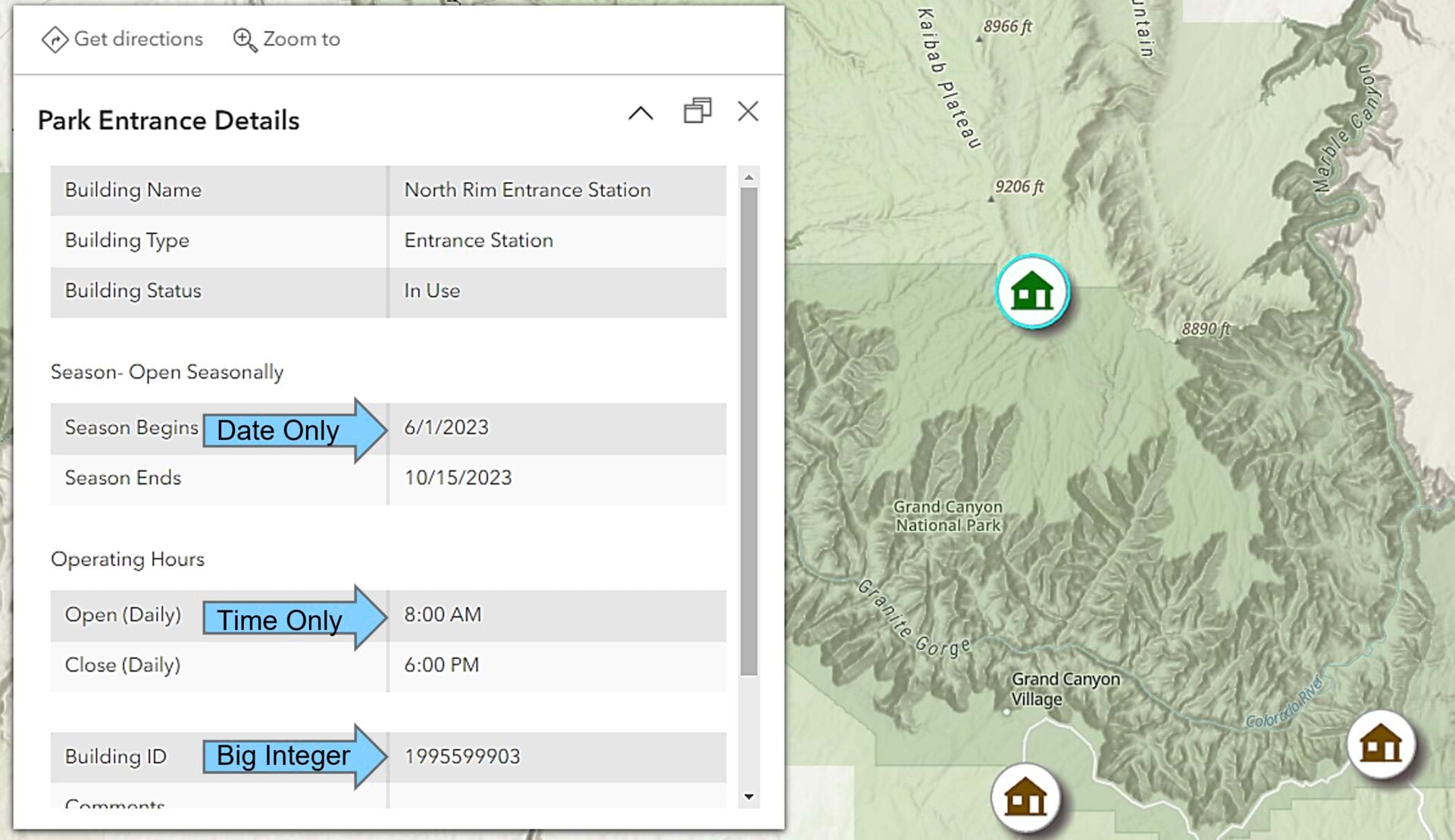
Let’s have a look at some other new features that can be used to help with managing temporal data.
Timestamp Offset
The Timestamp offset field type stores the date and time along with the time zone the data was collected in. This is great for mapping phenomenon that occur across multiple time zones. From earthquakes to car accidents, recording the time zone along with the date and time allows us to learn more about how events are distributed throughout the day across different time zones.
Time zones are displayed as offsets representing the difference (in hours and minutes) between UTC and the local time. The Timestamp offset field stores the overall date and time in one long string with the offset at the end. For example,
- Pacific Time is 8 hours behind Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), or GMT-8, which is displayed as -08:00
- October 10, 2023 at 3:00 pm GMT-8, is stored as 2023-10-10T15:00:00.000-08:00
Web Map Time Zone
In the past, the date and time values were always displayed in the device time zone. Now you can set the time zone on web maps in Map Viewer, to gain more control over the way time zone aware fields (like date and timestamp offset fields) are displayed. To learn more, check out this article on Working with Time Zones in Map Viewer.
Pro Tip: Time Zone Aware Fields
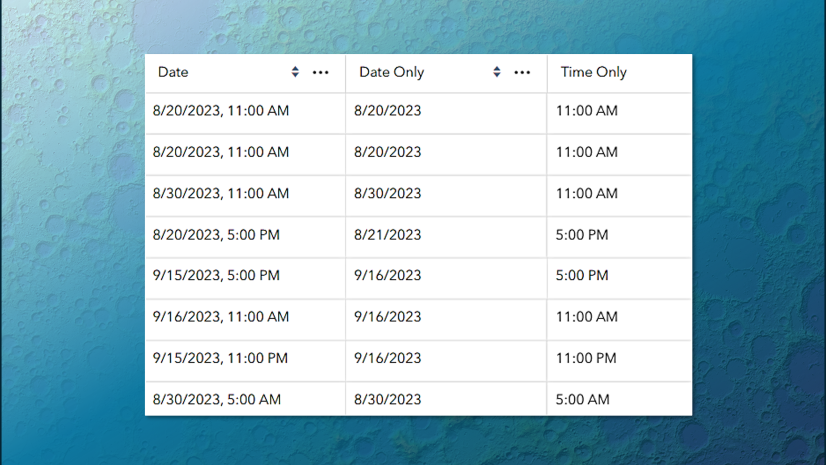
ArcGIS Online adjusts time zone aware fields based on the time zone of the device. For example:
- the value 10/01/2023 8:00 am Pacific Time (GMT-8)
- displays as 10/01/2023 10:00 am when viewed from Central Time (GMT-6)
The new Date only and Time only field types are not time zone aware. The values in these fields remain as-is regardless of where in the world the map is being viewed. Check out the ArcGIS Online help for more info on how date and time fields are displayed in ArcGIS Online.
Example: Hurricane Activity across Multiple Time Zones
We’ll explore a map of tropical storm locations across the globe that leverages the new field types and the web map time zone to display data that spans across time zones.
To view the map:
- Open the Hurricane Activity Map
- Click on a point to open the pop-up
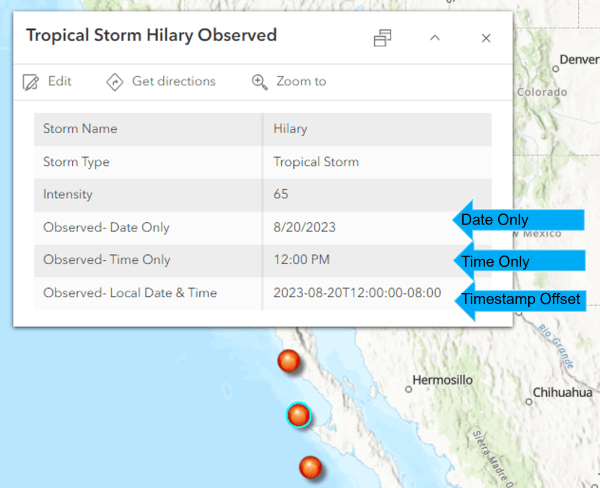
- Note the new field types: Date Only, Time Only, and Timestamp offset.
- The Date Only field displays the date the storm was observed.
- The Time Only field displays the time the storm was observed
- The Timestamp offset field displays the origin date, time, and time zone where the storm was observed.
Another thing to note about this map is that the web map time zone is set to Data’s time zone. Setting the web map time zone gives you more control over the display of time zone aware values. In this case, it means that the timestamp offset field isn’t affected by device time, and values display as-is.
Edit Data with New Field Types
Forms make editing new fields easy with the use of date and time pickers, and a drop-down menu for selecting the time zone offset. For more information on how to get started creating your own forms, see this article on using Smart Forms in Map Viewer.
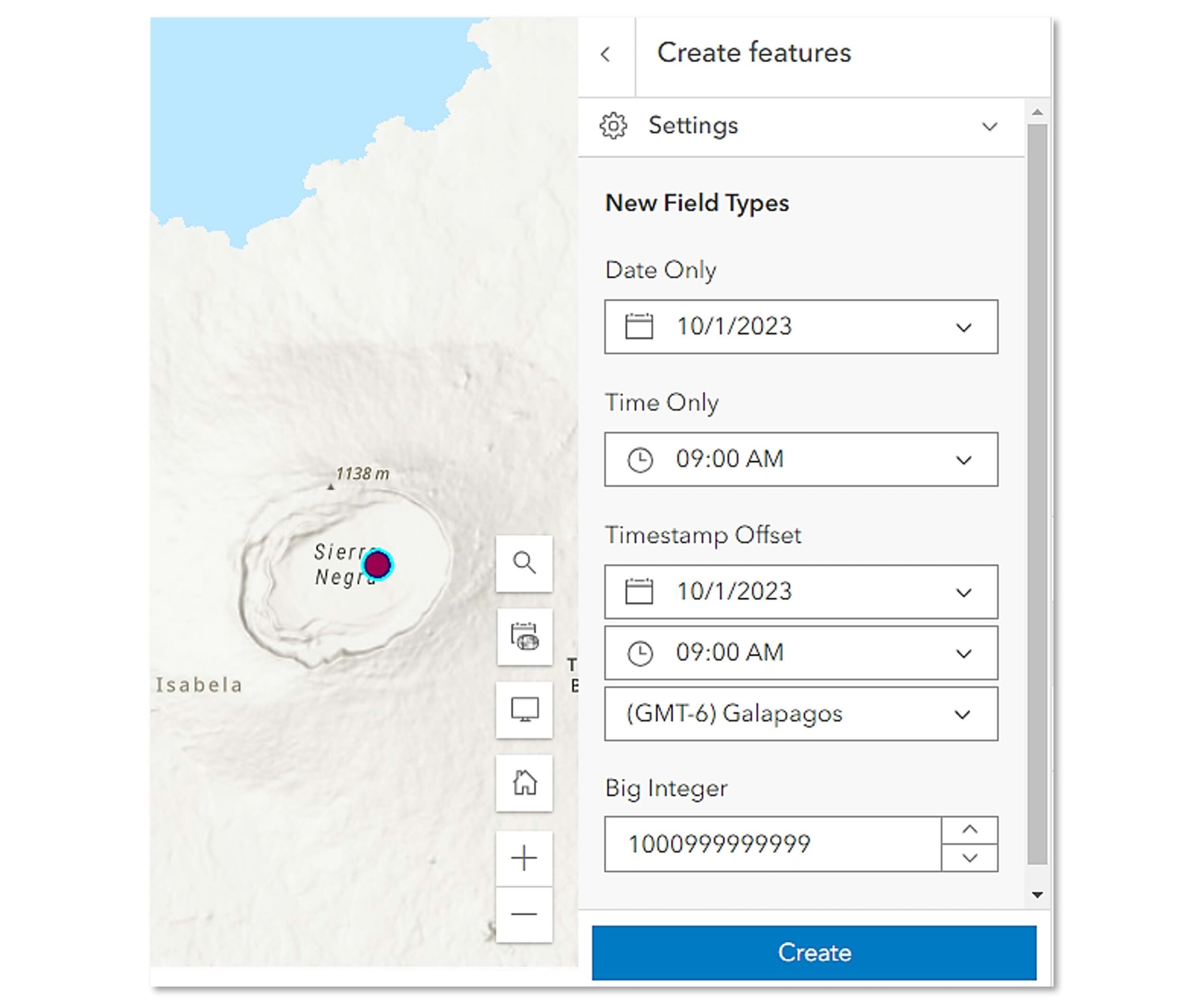
Where to Find New Field Types
- Map Viewer- Map Viewer and the new field types are built using the 4.x API platform, aka ArcGIS Maps SDK for JavaScript.
- ArcGIS Online– New field types are supported in Map Viewer and other apps built on the 4.x API including Story Maps and Instant Apps. However, older applications like Map Viewer Classic and Web App Builder do not support new field types.
- ArcGIS Pro 3.2 – New field types are supported at ArcGIS Pro 3.2. Check out this article to learn more about what’s new in ArcGIS Pro 3.2.
We plan to add broader support for new field types including smart mapping, filtering, generating charts, and working offline. Keep an eye out for more updates in upcoming releases.
Summary
We’re excited to introduce this improved experience for viewing, storing, and editing data using these new field types. This marks the initial phase of our plans to simplify the management of date, time, and big integer data throughout the ArcGIS ecosystem. Take some time to get acquainted with these new field types. Visit ArcGIS Online Help for more information on how to use them to maximize the potential of your own data. Stay tuned for more updates and resources and be sure to join the conversation on Esri Community to let us know your thoughts.




Commenting is not enabled for this article.