
The vision for the modern workplace centers on collaboration, data-driven insights, and empowering every employee with innovative tools. ArcGIS for Microsoft extends this vision by embedding location intelligence into the applications organizations use every day to create a spatially-enabled modern workplace. By bringing maps, spatial analytics, and geospatial data into Microsoft 365, the Power Platform, and Fabric, ArcGIS for Microsoft enables a location-aware, connected, and informed workplace.
Seamless Integration of Location Intelligence into Daily Workflows
A modern workplace is one where all people have access to their critical tools and data in one place. ArcGIS for Microsoft fulfills this by bringing geospatial capabilities into the Microsoft platforms employees already use. This enables everyone to access location information and it becomes a natural extension of daily work rather than a separate, siloed task.
Perhaps the most impactful integration is ArcGIS for Teams, which brings authoritative apps and maps directly into the communication and collaboration hub of the modern workplace. Users can share interactive maps and location data right in a meeting, chat, or channel conversation, just as easily as sharing a document. Workflows can be extended with automated processes that can post the latest incident map to the team’s channel, and everyone can pan, zoom, and explore the map without leaving Teams.
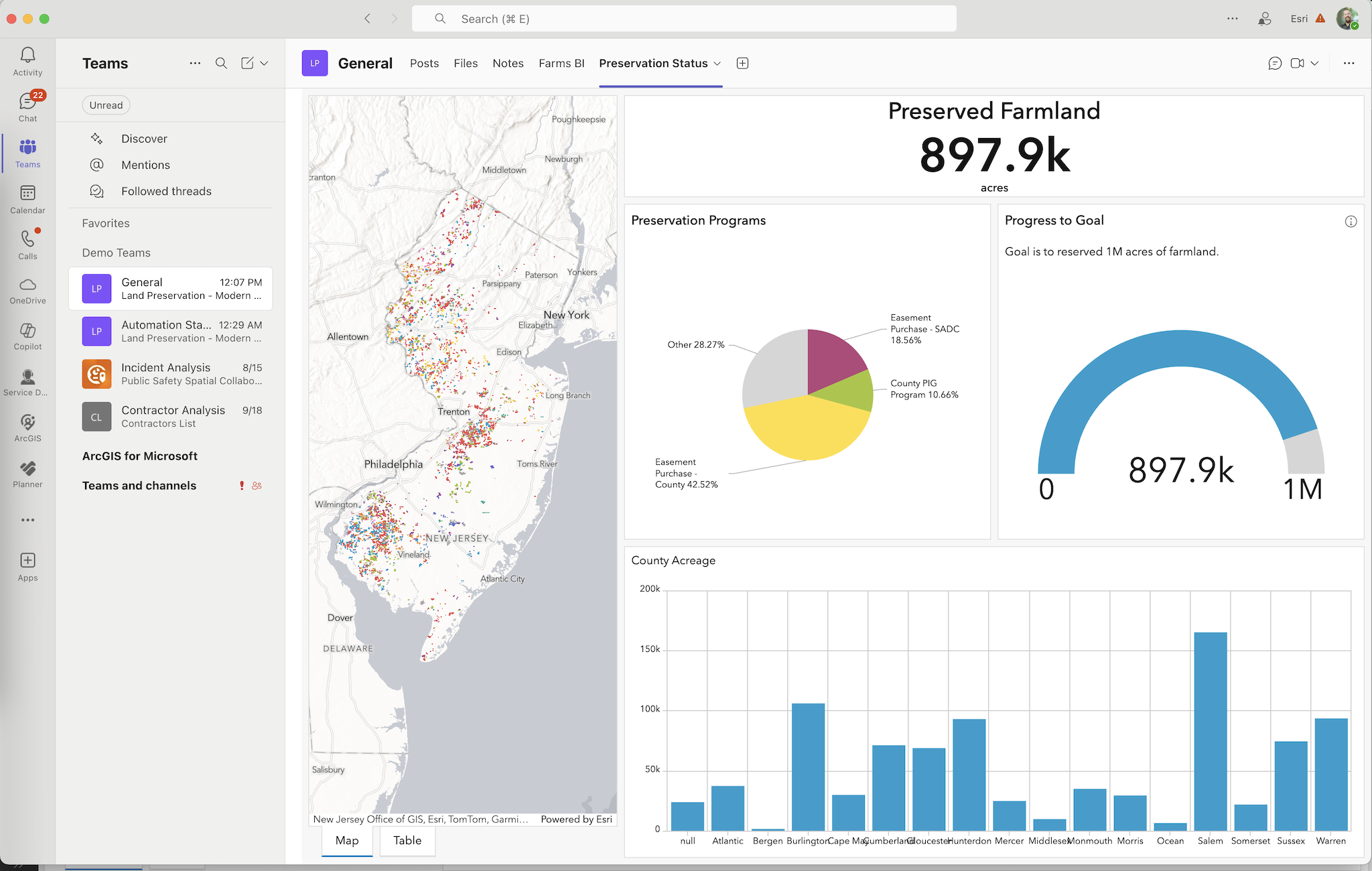
Colleagues can discuss insights on the map in real time, tag locations, and collaboratively make decisions. In the past, such collaboration might require sending static map screenshots via email or going to URLs in a browser; now it happens fluidly in the same space where chat and meetings occur. The pattern is reducing cross-platform switching and keeping spatial data in the flow of work, which ultimately boosts productivity and understanding. This tight integration ensures that working with location data is no longer a niche activity for GIS professionals, but a routine part of analysis and decision-making for any employee.
Democratizing Spatial Insights for Everyone
In the past, working with Geographic Information Systems (GIS) often required specialized software and expertise. This meant only trained analysts or GIS professionals would tap into the organization’s geospatial data. However, a modern workplace ethos is about empowering everyone with the information and tools they need. ArcGIS for Microsoft supports this by democratizing access to maps and spatial analytics, making these capabilities available to anyone using familiar Microsoft apps.
In practice, this means everyone in an organization – even with no GIS background – can incorporate maps into their work. They might use ArcGIS for Excel functions to turn a spreadsheet of farm market addresses into an interactive market analysis map. Organizations that spatially-enable the SharePoint document management system with ArcGIS for SharePoint, the geotagged documents are extended to ArcGIS applications. The interfaces in these integrations are common to users across the enterprise. By lowering the technical barrier, spatial thinking can become a part of everyday problem-solving across roles.

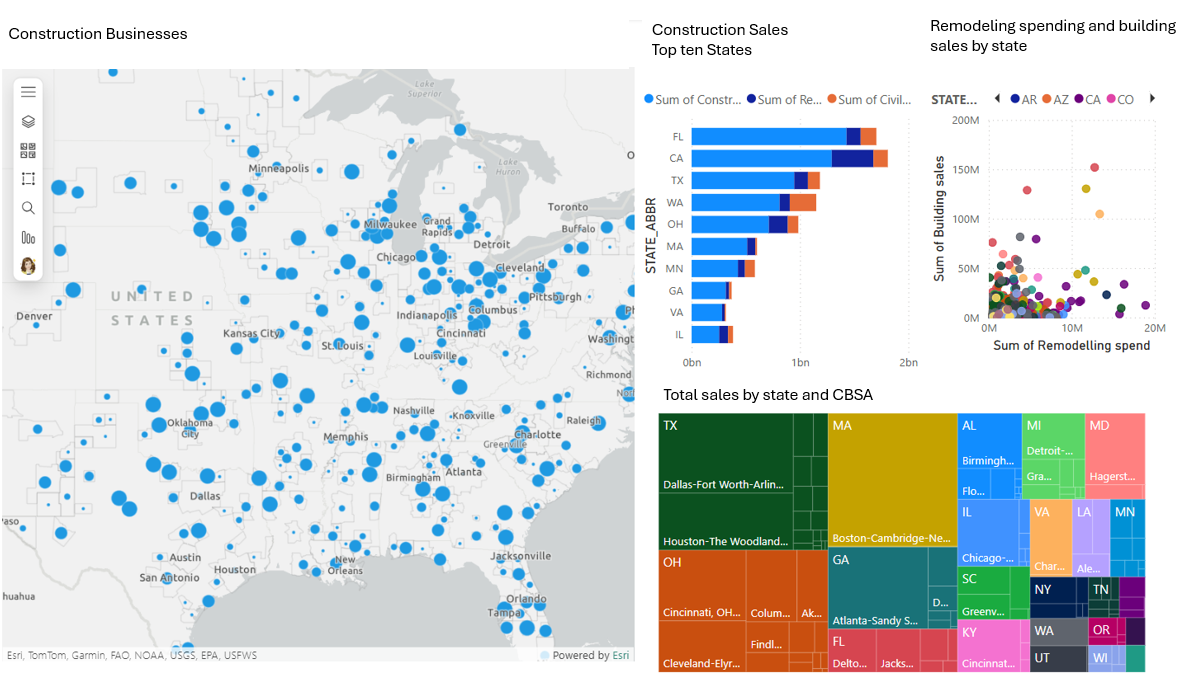
Another example of democratization is how ArcGIS for Power BI integrates mapping into business intelligence workflows. Power BI is widely used by non-technical business users to create dashboards and reports. With the ArcGIS for Power BI visualization, anyone building a dashboard or report can add an interactive map with just a few clicks. They can plot data points, use smart map styles, and even enrich their data with demographics. The report builder doesn’t need to learn a new mapping software – the mapping capabilities are provided following common Power BI use patterns. And the report consumers, like managers, stakeholders, and constituents, can interact with the map and report just like they would with any other Power BI report.
Extended with Copilot and AI Assistants
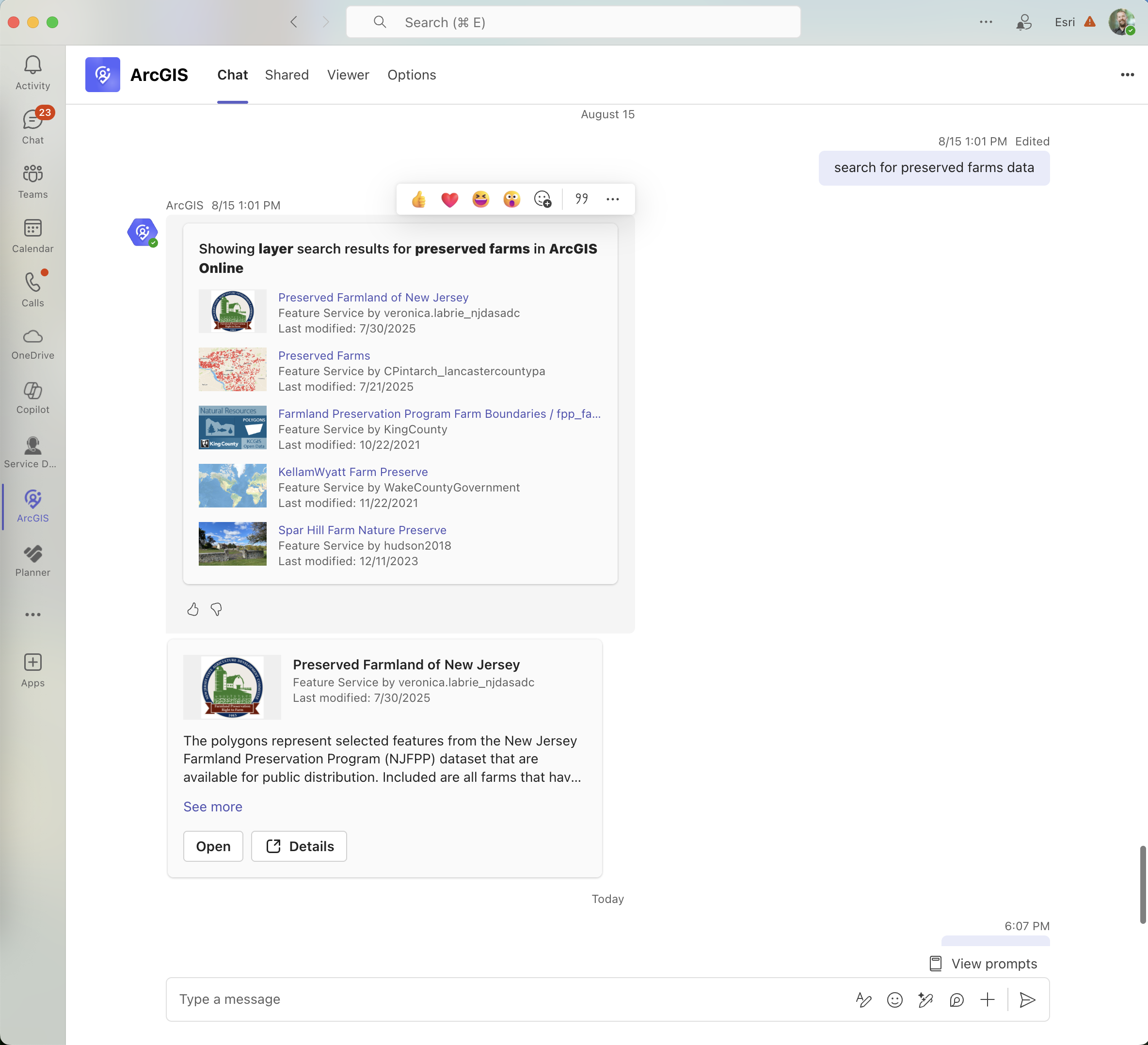
This vision is extended with features like ArcGIS for Teams’ conversational interface: users can search for maps or data within Teams using natural language via an AI-powered assistant. This enables users to ask a question in plain English – such as “search for preserved farm data” – and the relevant ArcGIS items are returned inside the Copilot interface removing barriers and empowering more people.
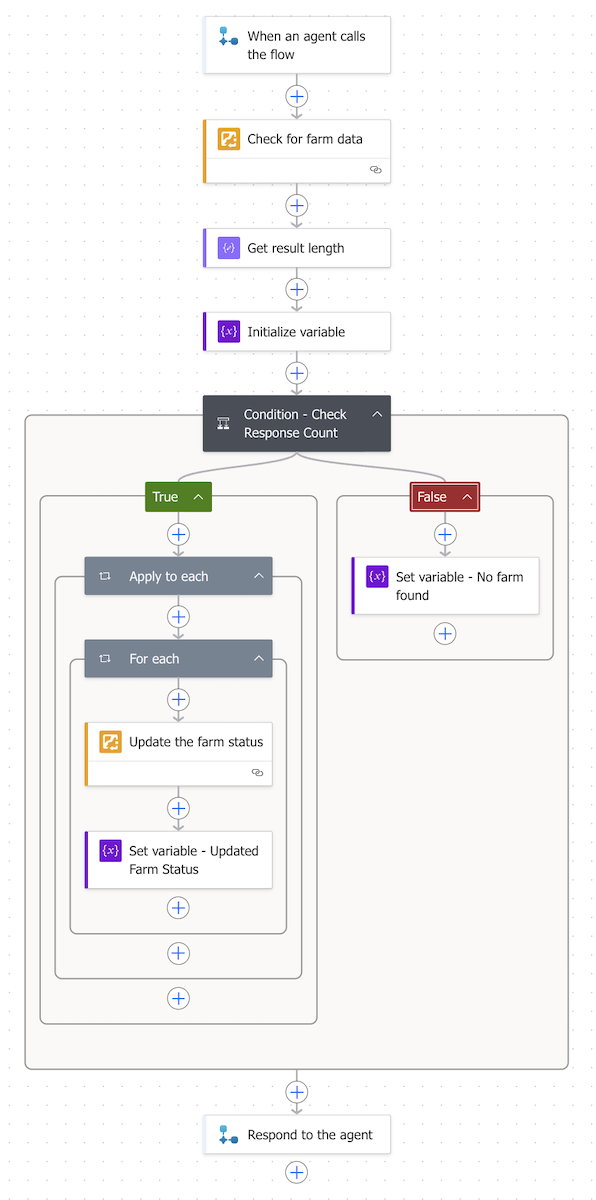
Copilot workflows become even more powerful as organizations build and tune Agents. Power Automate can be used to build Tools and the ArcGIS Connectors for Power Automate bring spatial capabilities to those Tools. Organizations can have an Agent that can query an authoritative feature layer. Or it can take a generative approach to create a PDF Report that was configured in Survey123 and automate the file management and sharing aspects.
Enhancing Collaboration and Decision-Making with Spatial Context
Modern business decisions are increasingly data-driven, and Microsoft’s workplace tools aim to centralize data so teams can make decisions together based on a single source of truth. By allowing teams to see “the where” behind data, it helps them discover patterns and relationships that would otherwise remain hidden in spreadsheets and charts. This richer context leads to more informed and confident decisions, often more quickly than before.
Collaborative decision-making also improves when teams have shared, interactive visuals to discuss. ArcGIS for Microsoft enables users to “share data-rich maps to collaborate and guide action.” In a Teams meeting, for example, colleagues might pull up a live ArcGIS Dashboard that shows key metrics on a map. This shared visual becomes a focal point for discussion and collective analysis.
The net effect is a cultural shift: location intelligence becomes part of the organizational DNA. Employees start thinking about “where” questions as readily as “what” or “when” questions because the tools to answer those “where” questions are at their fingertips. This widespread use of spatial thinking and tools is precisely how ArcGIS for Microsoft extends a modern workplace vision – by ensuring technology empowers everyone to work smarter, not just a select few. In a modern workplace, a good idea no longer gets stalled waiting for the “GIS guy” – anyone with the idea can run with it, using location intelligence to bolster their case.
Driving Innovation and Efficiency with Low-Code Automation and App Builders
Another pillar of a modern workplace is encouraging innovation from all corners of the organization, not just the IT department. No code/low code application and process builders enable citizen developers to create apps and automated workflows. ArcGIS for Microsoft amplifies this innovative spirit by bringing location-aware capabilities into these low-code platforms to configure automations that support holistic workflows. The result is that employees can easily configure solutions that leverage location data and automate geospatial processes, streamlining operations and sparking new ideas.
Enterprise-Ready Solutions
Many organizations choose to deploy ArcGIS environments on Microsoft Azure, or take advantage of built in ArcGIS technology in managed environments like Microsoft Fabric. For any technology to become part of the core modern workplace, it must meet enterprise requirements like security, scalability, and manageability.
Security and Performance
Many organizations choose to deploy ArcGIS environments on Microsoft Azure to take advantage of the cloud’s scalability and reliability. Doing so allows them to architect an environment that can handle large volumes of geospatial data and heavy processing loads without worrying about on-premises server limitations.
ArcGIS GeoAnalytics for Fabric brings over 180 spatial analysis tools into Fabric Spark Notebooks to perform spatial analysis at any scale. This means even large datasets can be engineered or analyzed to find patterns and the results can feed directly into tools like ArcGIS for Power BI or the soon to be released ArcGIS Maps for Fabric workload for consumption.
The ability to scale GIS workloads in the cloud aligns with the modern workplace trend of cloud-first IT strategy – employees get fast, responsive tools, and IT can securely accommodate growth or spikes in usage.
Summary
A modern workplace is about breaking down silos, fostering collaboration, and equipping people with intelligence at their fingertips. By treating location data as another shared asset in the Microsoft environment, ArcGIS for Microsoft follows the same logic: it turns geographic information into a common resource for brainstorming, analysis, and innovation, rather than a specialized domain.
ArcGIS for Microsoft helps organizations to embody the spatially-enabled modern workplace principles by integrating one of the most important dimensions of data – the “where” – into the Microsoft tools people use. Maps and location analytics become as commonplace in the work environment as documents and spreadsheets, enriching the context for every decision. As a result, organizations today can operate with greater situational awareness, agility, and innovative capacity. They can see the literal bigger picture.

Article Discussion: