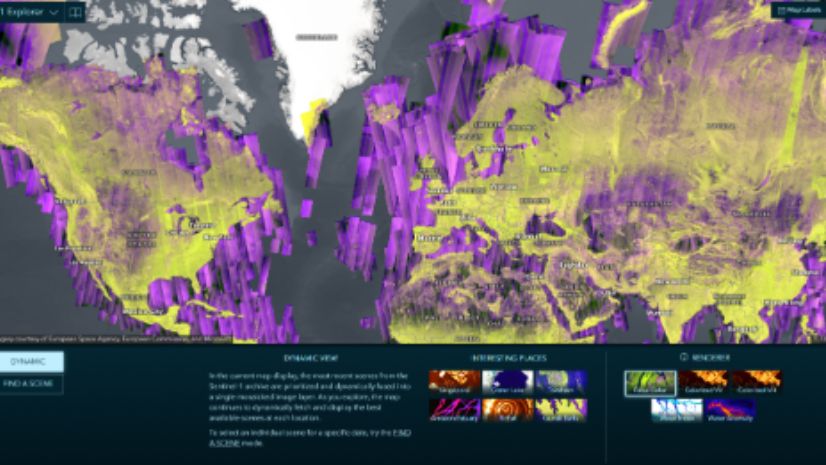
NISAR: A New Lens on Earth’s Rhythms
In the ever-evolving symphony of Earth’s processes—where glaciers shift, forests breathe, and the crust subtly flexes—NISAR (NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar) emerges as a revolutionary observer. Launched on July 30, 2025, this joint mission between NASA and the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) is not just another satellite—it’s a sentinel of change, equipped with dual-frequency synthetic aperture radar (SAR) that listens to Earth’s whispers with astonishing sensitivity. With the ability to detect surface movements as small as a centimeter, NISAR offers a rhythmic pulse of the planet every 6 to 12 days, piercing through clouds, darkness, and weather to reveal the unseen.

A Lifeline from Above: Illuminating Earth’s Shifts to Empower Humanity
This isn’t just a technological marvel—it’s a lifeline. NISAR’s data illuminates the subtle shifts that shape our world: the slow collapse of ice sheets, the creeping loss of wetlands, the silent depletion of groundwater. It brings clarity to the chaos of natural hazards and offers foresight to those who need it most. For scientists, it’s a treasure trove of insight into climate change and Earth’s crustal dynamics. For professionals in agriculture, infrastructure, and emergency response, it’s a tool for resilience. And for the public, it’s an opportunity for empowerment—a chance to see, understand, and act.
First Light: NISAR’s Vision Comes into Focus
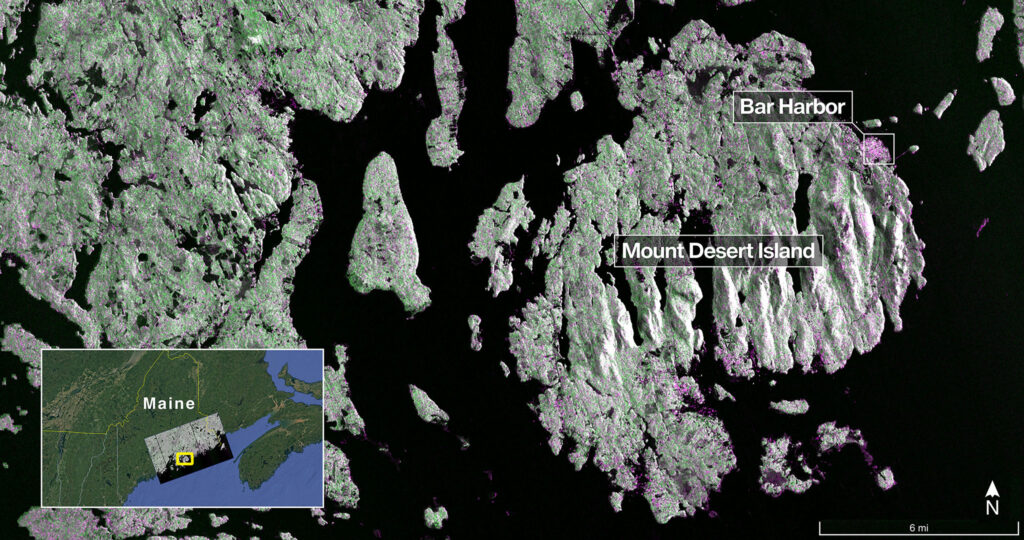
As NISAR settles into orbit, its eyes begin to open. On August 21, 2025, the satellite captured its inaugural radar image—Mount Desert Island, etched in stunning detail by its L-band synthetic aperture radar. Forest canopies, urban textures, and shimmering water bodies emerged with striking clarity, revealing the power of radar to see what the eye cannot. Now in its final calibration phase, NISAR is nearly ready to begin its full mission, with both its NASA-built L-band and ISRO-built S-band radar systems performing flawlessly. Within days, this sentinel will begin its rhythmic scan of Earth’s surface, offering a new dimension of insight into the planet’s dynamic story.
Getting Started with NISAR in GIS
As NISAR prepares to begin its full mission, users can already start exploring its potential through sample datasets and guided tutorials. The Alaska Satellite Facility (ASF) offers helpful resources for working with NISAR data in ArcGIS Pro, including NISAR in GIS: Working with NISAR Data in ArcGIS Pro and Spatial Subsetting for NISAR Data: Methods for Reducing the Spatial Extent of NISAR Products. These tutorials provide practical steps for accessing, visualizing, and analyzing radar data—empowering users to begin building workflows that will scale with the mission’s long-term data stream. Whether you’re a scientist, analyst, or educator, these tools offer a hands-on introduction to integrating NISAR into your GIS (geographic information system) practice.
When Earth Speaks, GIS Listens: Unleashing the Power of NISAR
True magic unfolds when GIS enters the story. Through platforms like ArcGIS, NISAR’s radar signals transform into living narratives—interactive maps, dashboards, and models that make sense of complexity. Imagine emergency managers visualizing subtle ground shifts before a landslide, overlaying population data to prioritize response. Picture conservationists tracking deforestation trends over time, sharing findings through narrative maps that inspire action. Envision farmers monitoring soil moisture and crop health, even in cloudy conditions, to optimize irrigation and support food security. Engineers, planners, scientists—all empowered by the fusion of SAR and GIS.
Guardians of a Changing Earth: NISAR and GIS in Action
As Earth quietly shifts beneath our feet, NISAR listens —not to the clamor of immediate events, but to the subtle rhythms of change unfolding over time. Its radar captures the gradual tremors before a landslide, the creeping swell of flood-prone regions, and the imperceptible strain building beneath tectonic plates. While not designed for real-time alerts, NISAR’s consistent observations offer a powerful lens for understanding patterns, assessing risk, and informing preparedness. Through ArcGIS, these signals become spatial narratives—maps and models that help emergency managers visualize long-term ground deformation, overlaying it with population and infrastructure data to guide strategic planning and resilience efforts.
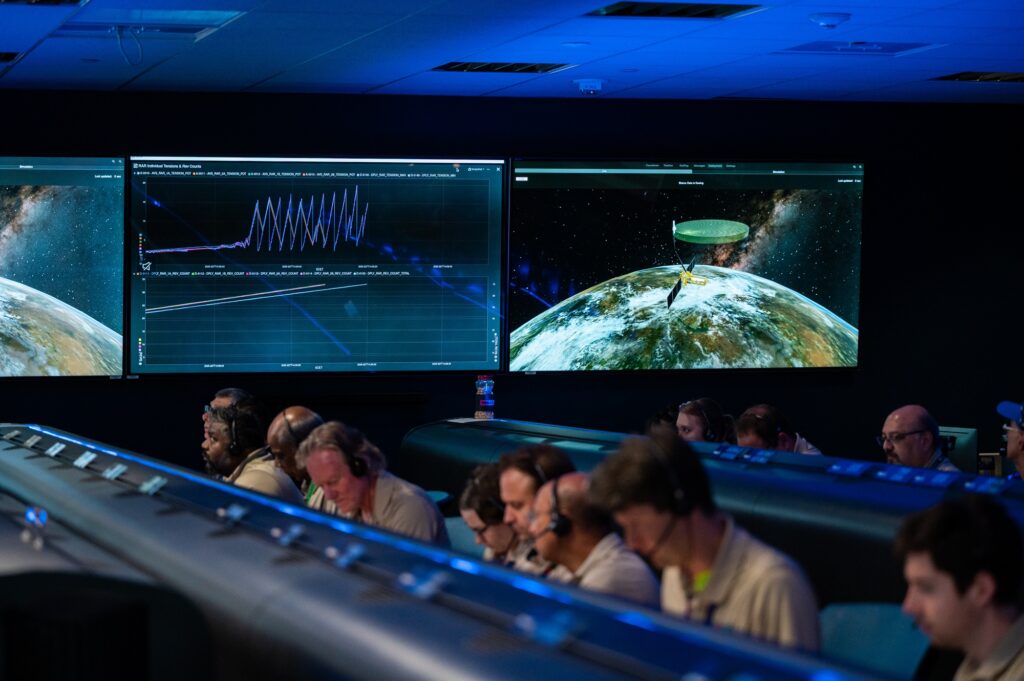

In forests and wetlands, NISAR sees what the eye cannot. It tracks the slow unraveling of ecosystems—deforestation, wetland loss, and climate-driven change—regardless of cloud cover or darkness. With ArcGIS, scientists can analyze these patterns over time, quantify degradation, and share their findings through interactive maps and narrative maps. These insights fuel conservation strategies, inform climate adaptation, and guide policy decisions that shape our collective future.
Across fields and farms, NISAR’s radar pierces through rain and haze to monitor soil moisture, crop structure, and seasonal shifts. For agricultural professionals, this is more than data—it’s a safeguard for food security. ArcGIS integrates this information with field boundaries, yield data, and weather forecasts, helping farmers optimize irrigation, assess crop health, and plan with confidence.
And beneath our cities and infrastructure, NISAR detects millimeter-scale ground deformation—signals of gradual strain that may precede structural challenges. With ArcGIS, engineers and planners can visualize these risks spatially, prioritize inspections, and communicate findings to stakeholders. It’s not about reacting in the moment—it’s about seeing the future unfold and preparing wisely.
A Beacon for the Future
Together, NISAR and ArcGIS are more than technological achievements—they are instruments of hope and guardians of resilience. This dynamic alliance transforms Earth’s quiet signals into bold, actionable insights. From tectonic shifts to ecosystem change, NISAR’s data lays the foundation for global resilience—supporting disaster response, environmental stewardship, and climate adaptation. By democratizing access to advanced Earth observation, they empower scientists, decision-makers, and communities to anticipate, adapt, and protect. In this new era, we are no longer passive witnesses to change—we are informed stewards, equipped with the tools to respond faster, plan smarter, and understand deeper. In a world shaped by accelerating environmental shifts, this partnership stands as a beacon—illuminating the path to a more informed, responsive, and sustainable future.