ArcGIS Image for ArcGIS Online, an extension to ArcGIS Online, makes imagery more accessible and more easily managed. Because it is software as a service (SaaS), it eliminates the need for organizations to maintain infrastructure for imagery. Uploaded imagery and the results of analysis are saved as image services so that they can be shared and used in ArcGIS throughout an organization. This article describes how to control the display of dynamic imagery layers to optimize specific workflows.
Dynamic imagery layers give users control over the visualization of individual input images after creation to aid interpretation and visual analysis. For most imagery shared online, the visualization of those input images is set during creation.
Tile cache layers are created this way, with the visualization choices made prior to creation, indicating how to they will be displayed in the input imagery. For tiled imagery layers, there are options to alter the order of the raster bands, the stretch applied to the pixel values, and the image brightness.
Dynamic imagery layers from ArcGIS Image for ArcGIS Online have all the custom display options of the tiled imagery layers, but also provide additional control of the input images. Tiled and dynamic imagery layers have similar capabilities in terms of use in raster analysis, source pixel access, and custom visualization options. However, dynamic imagery layers have additional functionality that allows you further control over the display of the input imagery through processing templates, image display order, and filtering. Between the image display options and these additional control properties, dynamic imagery layers give you complete control over the visualization of the imagery layer.
What does a dynamic imagery layer allow you to do that a tiled imagery layer does not? The quick answer is, control over input images. Dynamic imagery layers are controlled by a set of properties that allow for many visualization options that are not available for tiled imagery layers.
.
These properties are used as instructions for the application to use to display the individual input images. This allows you to control the order in which they display, which one will appear on top if there is overlap, and whether the input images display at all. Processing templates can also be added to dynamic imagery layers to provide preset visualization options for users. The creator of the dynamic imagery layer has control over many visualization settings when creating the layer and can stipulate which of those settings can be changed by the user.
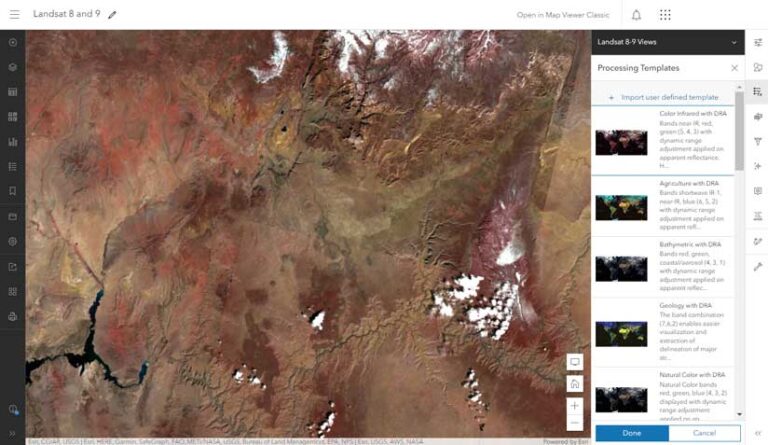
Custom Visualization Using Processing Templates
Processing templates in ArcGIS Image for ArcGIS Online allow for preset custom visualizations. An image collection, a layer configuration, lets you maintain the metadata about input images. The attribute table included with the image collection allows you to maintain the metadata, which can be used to provide additional display and filtering options.
If a mosaic dataset was used to create the dynamic imagery layer, any field that you add to the attribute table using ArcGIS Pro will appear in the attribute table. The tables can be accessed in the map to view the attributes, or they can be used to modify the display of the dynamic imagery layer.
When the dynamic imagery layer is added to Map Viewer in ArcGIS Online, or to ArcGIS Pro, or to any other ArcGIS app, the results of those instructions will be visualized. When the dynamic imagery layer is created, default instructions control how it is displayed.
These properties can be changed at the creation of the layer for a specific default visualization. Dynamic imagery layers display according to these instructions on the server and are visualized on the user’s machine. The user can modify those properties to customize the display if the creator of the imagery has allowed them to be modified.
Modifying the Image Layer
There are many options that control the display of the imagery layer. You can change them when the dynamic imagery layer is created. The first set of properties you can modify control include:
- Default resampling method
- Compression
- Default processing template
- Allowed fields (image collection)
- Allowed mosaic methods
- Allowed mensuration capabilities
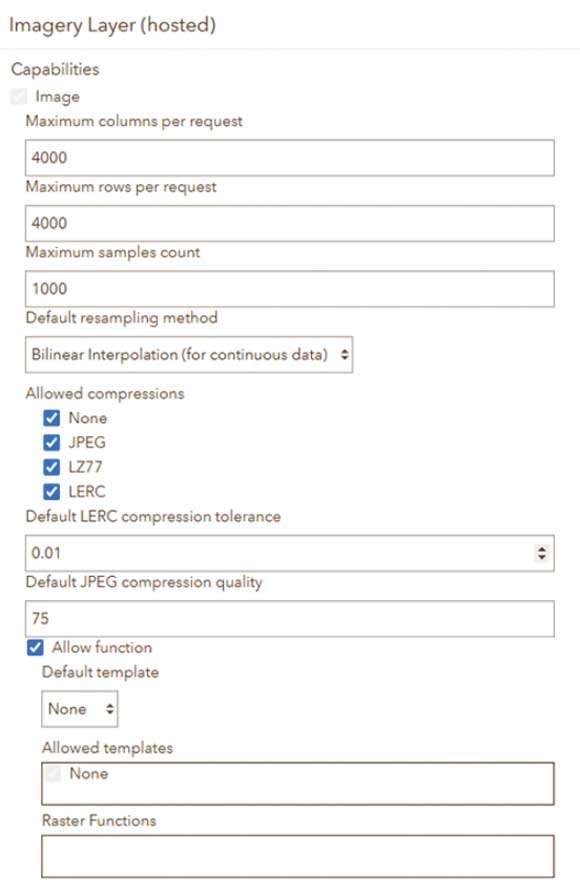
These properties are in the Item Details page for the imagery layer where you can modify aspects of the dynamic imagery layer. These properties let a creator of the dynamic imagery layer ensure that it is used as desired by end users by changing the default look of the imagery layer.
If the input imagery data is a mosaic dataset, you can even alter the default properties of the mosaic dataset to control the order of the input images, what metadata is included, or other mosaic dataset properties. Mosaic datasets can be used as input imagery in ArcGIS Pro with the Create Hosted Imagery wizard. This process also allows you to add more fields to the mosaic dataset that will appear in the dynamic imagery layer with the image collection configuration.
Dynamic imagery layers also allow you to perform image management tasks on the imagery layer. These tasks can be used to clean up the imagery layer by doing the following:
- Modifying visible areas
- Removing NoData areas
- Adding overviews to improve performance
- Correcting the color within the imagery layer
- Calculating statistics to improve the display
Controlling Display from the Map Viewer
You can control the display of a dynamic imagery layer by setting properties when the layer is created, from within its item details page, and also when the layer is displayed in Map Viewer. When the dynamic imagery layer is added to Map Viewer in ArcGIS Online, there are additional properties that can be modified. The properties available in Map Viewer can control the band combination, which processing template is chosen, or even which input image shows up on top.
When the dynamic imagery layer is selected, a few buttons will appear on the right side of Map Viewer. Visualization properties are controlled through four primary tabs located on the right side of Map Viewer: Styles, Processing Templates, Image Display Order, and Filter.

Styles
With this property, you can control the band combination, stretch type, and style. These capabilities are also enabled for tiled imagery layers. Processing templates based on raster function templates (RFTs) can be added as symbology options.
Processing Templates
This property allows adding RFTs to the dynamic imagery layer. For Map Viewer Classic, the Image Display property allows you to add RFTs, which can be used to change the visualization and create derived imagery layers from different analytical tools.
Image Display Order
Control the order of the input images with this property. For overlapping input images such as drone-collected images, you can set which image will appear on top as you pan and zoom within the map. If your input images share the same spatial extent but were collected over different time periods, you can set the order in which they display by default.
Filter
This property allows you to control which images are visible by creating a query that limits the images displayed to those that meet the criteria. You can use any property in the attribute table or in the metadata to control the display.
Workflows Enhanced by Dynamic Imagery Layer
Some workflows are enhanced by using dynamic imagery layers, rather than tiled imagery layers.
Review of Drone Imagery
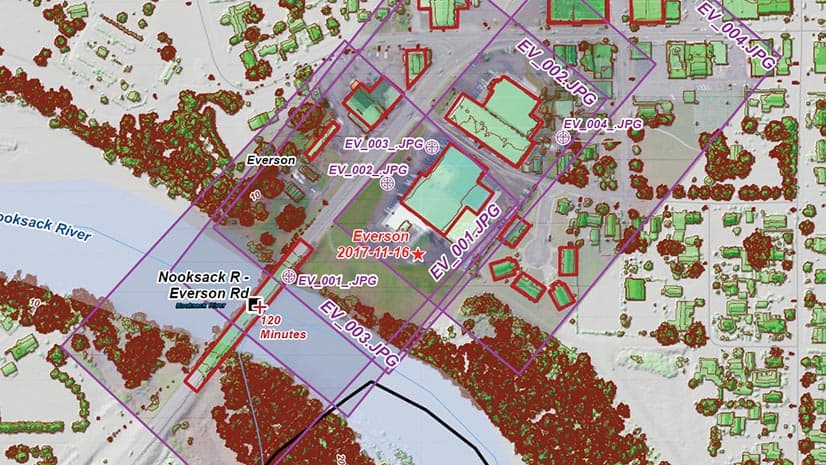
You can preserve the input imagery in a dynamic imagery layer and use the different dynamic display options such as Closest to center, By attribute display, or Closest to nadir. By viewing drone data in different ways, you can recognize features or look around overhanging features. Both ArcGIS Drone2Map and SiteScan for ArcGIS can be used to publish to ArcGIS Image for ArcGIS Online. For ArcGIS Drone2Map, there is also a mosaic dataset that can be published outside of the application as a dynamic imagery layer with the image collection layer configuration from ArcGIS Pro.
Time Series Analysis
You can review a specific area over a specific time period by adding input images that represent the same location from different capture dates into a dynamic image collection and adding a field in the attribute table or modifying a field in the attribute table. By filtering the imagery layer, changes over time can be visualized in the map.
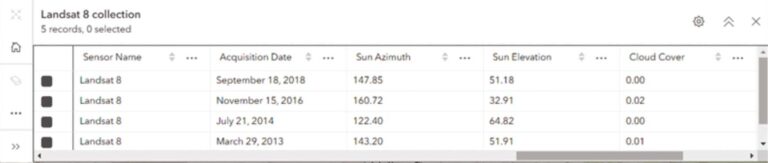
Filtering Satellite Sensor Data
Creating a dynamic imagery layer (image collection) with satellite sensor data and choosing the raster type for that imagery layer allows the metadata for that input imagery to be added to the attribute table. Most satellite sensor data includes additional information about that input image. For example, Landsat 8 images, additional fields for cloud cover, and sun azimuth are added to the attribute table. Using the filter, you can dynamically remove images that have cloud cover over a certain threshold or images that were captured at a particular sun azimuth.
Conclusion
Both tiled imagery and dynamic imagery layers from ArcGIS Image Online have a lot of capabilities that you can use to enhance the use of imagery in your organization. Dynamic imagery layers give users control over the visualization of individual input images to create the desired visualization. Depending on the application of imagery, each type of imagery layer can be useful by providing context for a map, supplying input for analysis, or displaying the same imagery in multiple ways. These are just some of the uses for dynamic imagery layers. The visualization controls allow you to use the input imagery in any manner you desire.