by Sinan Abood, Spatial Analyst – ORISE Research Fellow, USDA Forest Service
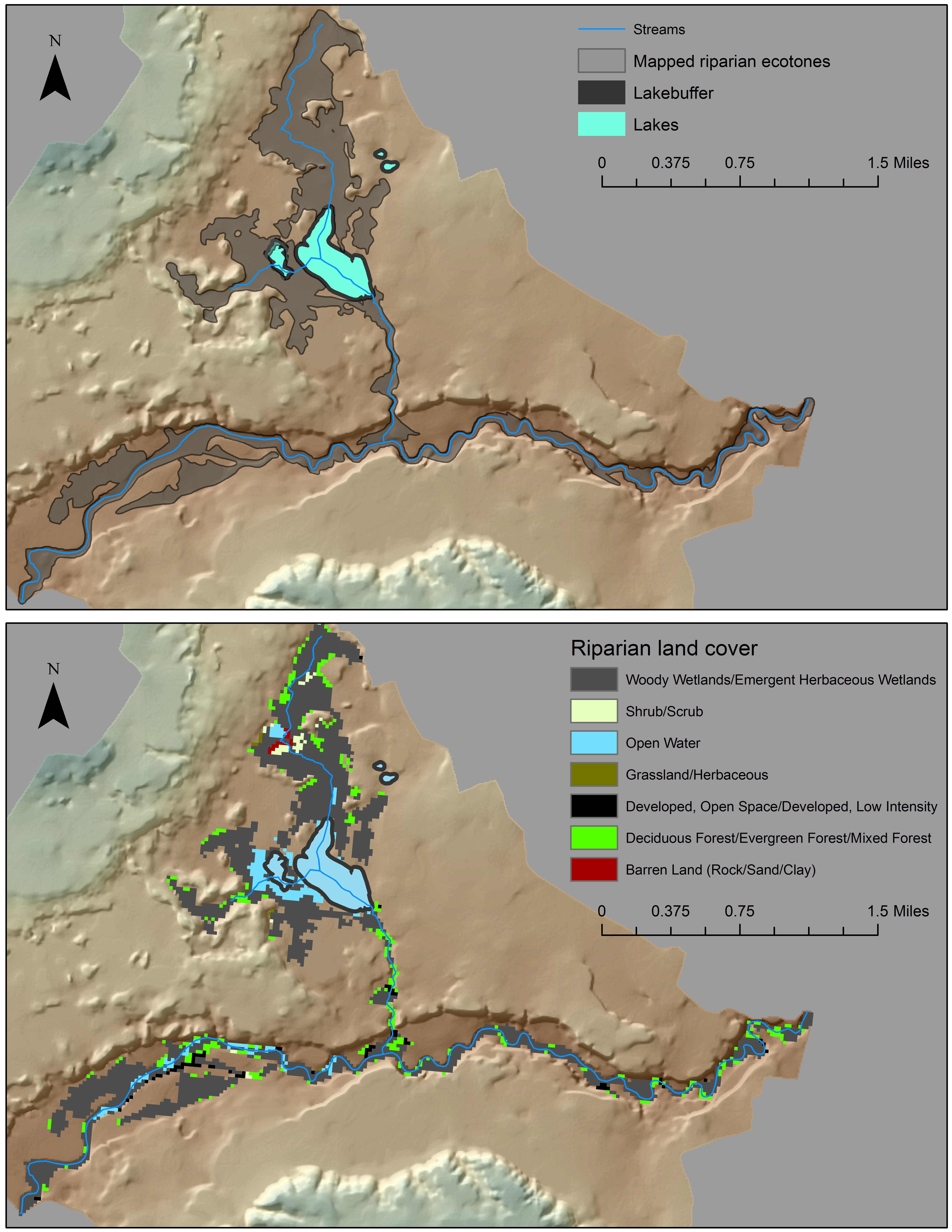
Riparian ecosystems provide many physical, ecological, and biological functions of economic and social value, serving as the zone of interaction between streams and the terrestrial ecosystems around them. It is common to use a fixed width buffer to delineate riparian zones, but this fails to account for the complex geomorphology that governs floodplains and riparian vegetation. In order to better inventory and conserve the riparian areas within our national forests, the USDA Forest Service utilizes a GIS toolbox developed by Dr. Abood (Forest Service) and Dr. Maclean (Michigan Technological University) for delineating variable-width riparian areas. This approach recognizes the dynamic and transitional nature of riparian ecotones using hydrologic, geomorphic, and vegetation datasets as inputs into the delineation process.
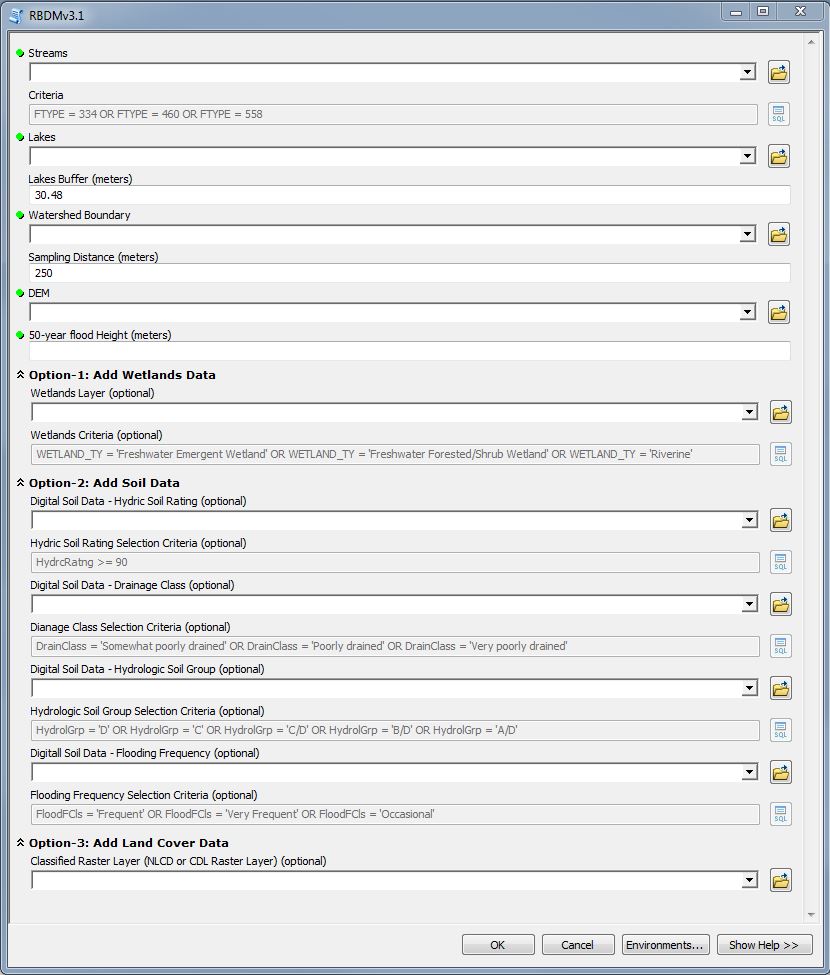
RBDM v3.1 is an ArcGIS for Desktop toolbox that efficiently delineates variable-width riparian areas. The model is independent of landform and also accounts for river/stream watercourse and its associated floodplain in the delineation process. Optional datasets provide extended riparian mapping capability based on wetlands, riparian soils, and land cover attributes.
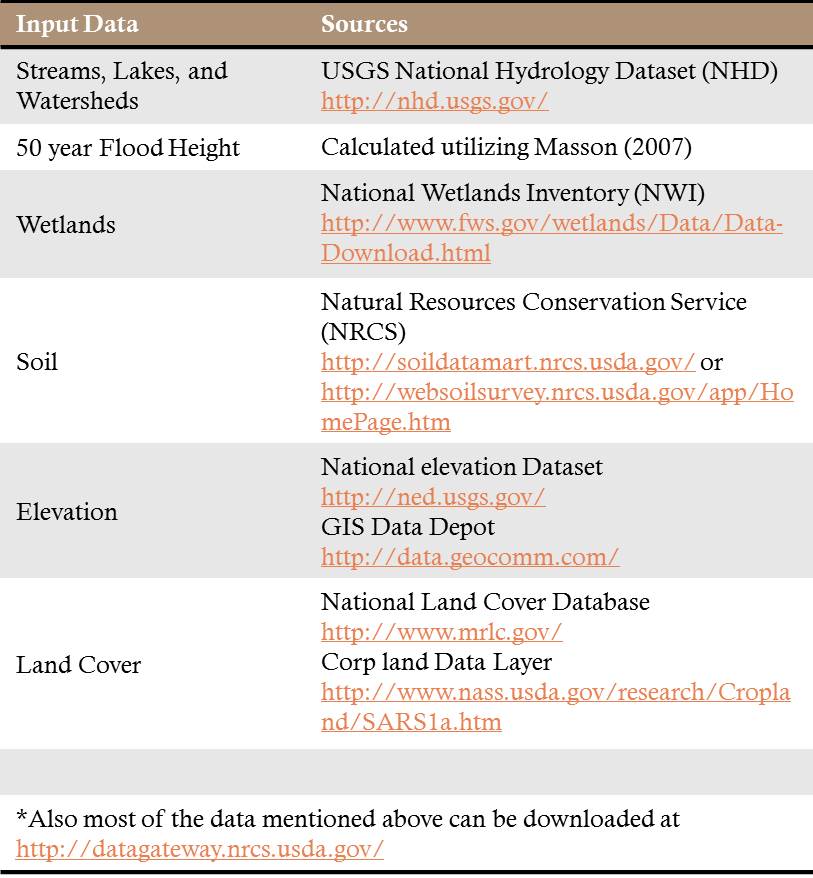
The input data can be downloaded through free and open source geospatial portals. Many of these data are also available through web services from Esri’s Living Atlas of the World. The result is a cost effective, robust, and accurate workflow to assist decision makers in mapping and managing riparian areas.
The RBDM v3.1 utilizes three national datasets as optional inputs: National Wetlands Inventory (NWI), Soil Survey Geographic Database (SSURGO), and National Land Cover Database (NLCD) or Cropland Data Layer (CDL) as land cover inputs. Incorporating NWI and SSURGO datasets improves the overall delineation process accuracy, since riparian ecotones may not be confined only to the floodplain but also can extend to other surface waters such as contiguous lakes and wetlands. Land cover information is used to develop the acres of lossgain of riparian land cover classes over a period of time.
“Criteria” helps the user to choose what types of streams (i.e. intermittent, ephemeral, or perennial) to include in the delineation process and helps optimize the model’s running time. “Sampling Distance (meters)” represents the sampling distance away from a stream segment toward uplands. The sampling distance value is specified by the user and the maximum distance is 3000m. “DEM” is the Digital Elevation model input. The model utilizes the DEM with different spatial resolutions such as 1m, 2m, 3m, 5m, and 10m. “50-year flood height” is the hydrological descriptor of variable-width riparian ecotones. Determining an appropriate 50-year flood height value is critical to achieve accurate riparian areas mapping, so Mason and Maclean (2007) developed a simple methodology to calculate the 50-year flood height utilizing the USGS Water Data for the Nation. For more information about RBDM, see here and here, or contact Sinan Abood directly at sinanayadabood@fs.fed.us.


Article Discussion: