ArcGIS Hub has improved the way organizations disseminate important information to communities. But what if there was a way to help your site’s visitors quickly and easily navigate the data on your Hub site?
We are excited to introduce the Hub assistant (beta), a new beta feature available for ArcGIS Hub Premium. You can now provide your site’s users with tailored support in answering their questions pertaining to all available public datasets on your Hub site.
Based on simple prompts entered in natural language, the Hub assistant (beta) uses artificial intelligence (AI) to search your site catalog and respond to the user queries.

The Hub assistant (beta) is available with workspaces, the new experience in Hub. Workspaces provide a more consistent editing experience for items across Hub. Learn more in the ArcGIS Blog article: Workspaces is the new site management experience in ArcGIS Hub.
The Hub assistant (beta) facilitates access to geospatial data, so that your organization’s data are more visible and usable for everyone. The Hub assistant (beta) adds value to your site in a variety of ways, for example:
- Simplifies data discovery: By posing a question in natural language, users can find and explore relevant datasets without needing to navigate through catalogs or understand complex metadata.
- Accelerates insights: Quick answers to common questions are available without requiring GIS expertise or specialized tools. More experienced Hub users can use the Hub assistant (beta) to make established workflows more efficient.
- Improves accessibility: Makes geospatial data more accessible to non-technical users, policy makers, and the general public.
- Enhances decision support: Provides actionable information that can directly inform decision-making processes across various domains.
Let’s walk through a sample user query. With the Hub assistant (beta) enabled, configured, and tested as detailed below, a signed in site visitor could:
1. Start out by discovering which datasets are available from their Hub site of interest.
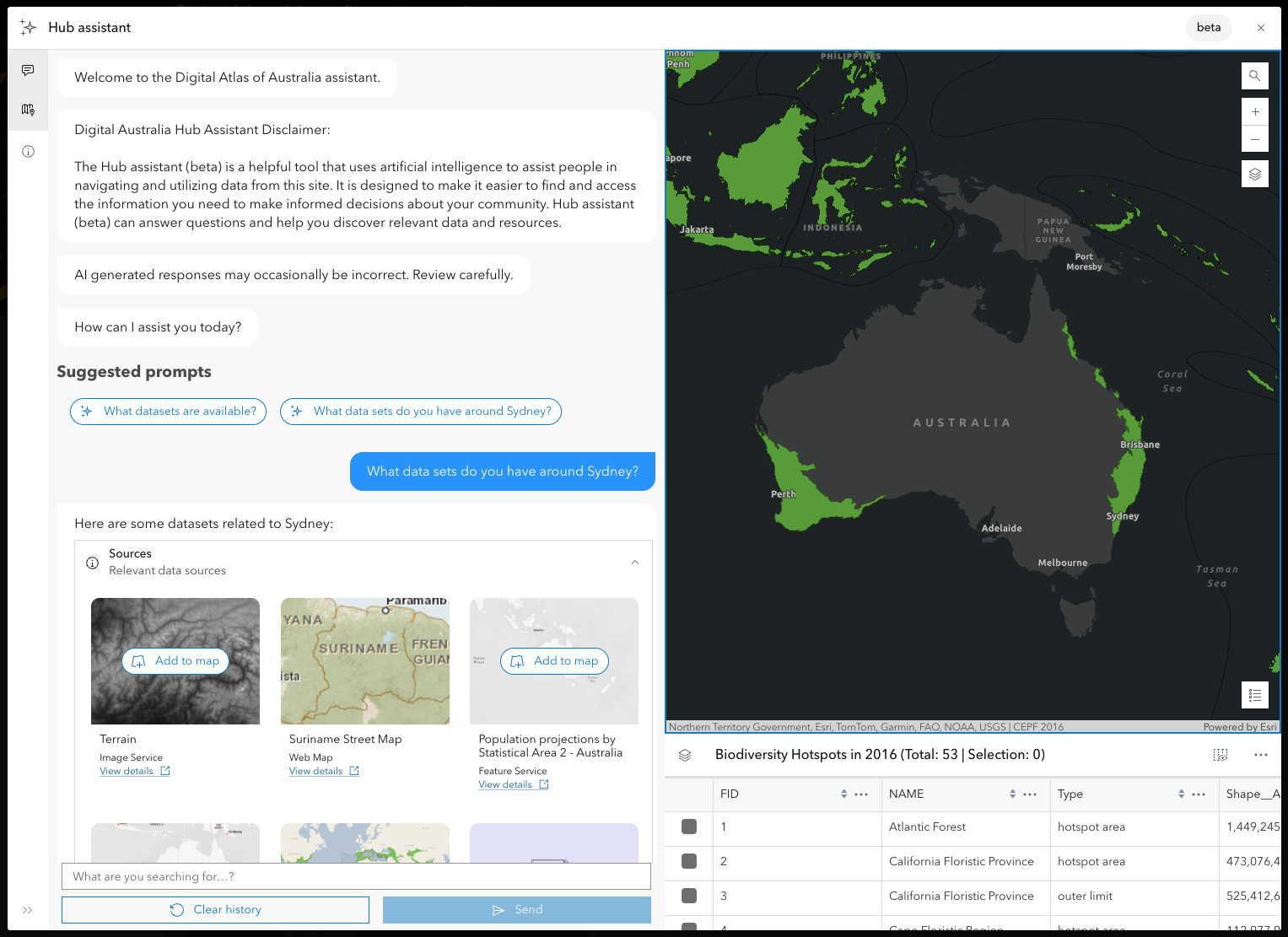
2. Begin exploring and learning about the range of datasets provided.
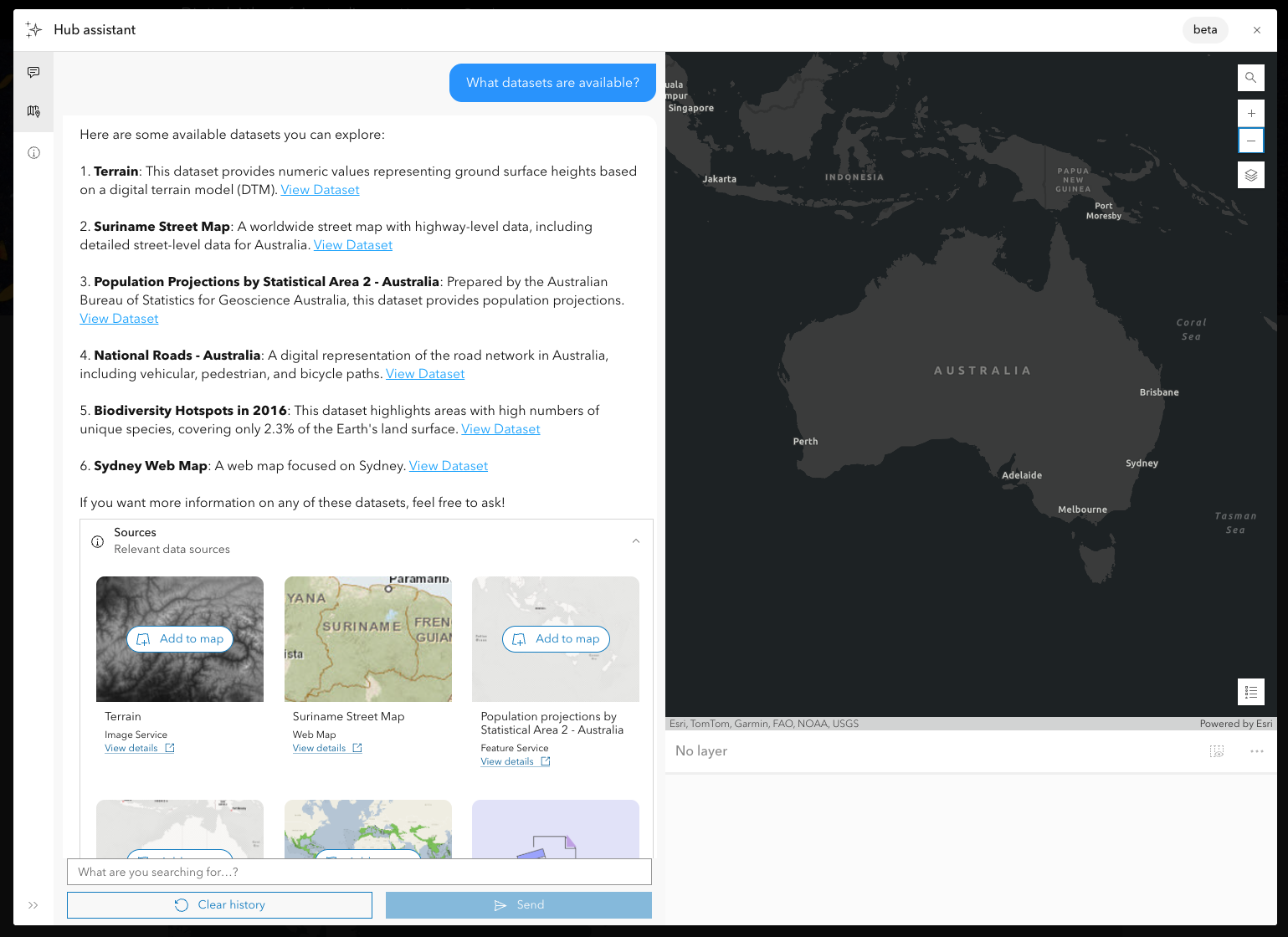
3. Narrow the area of geographic interest to focus on datasets for a particular city.
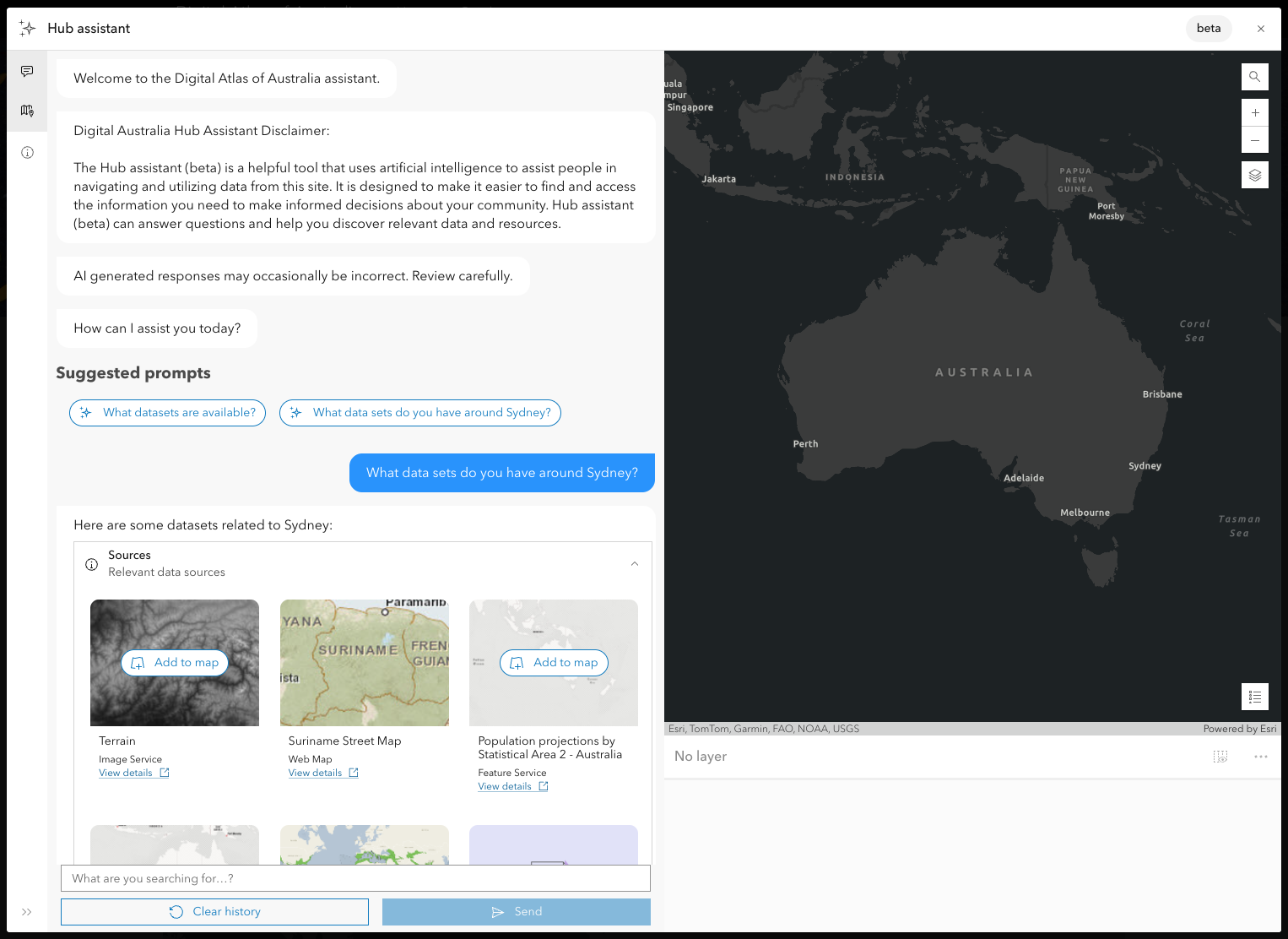
Enable the Hub assistant (beta) for your site
To use the Hub assistant (beta), the following conditions must be true:
- You or your organization must have a Hub Premium subscription.
- You must sign in with an ArcGIS Online organizational account.
- AI assistants must be enabled in your ArcGIS Online organization.
- Your ArcGIS Online administrator must turn off the “Block Esri apps and capabilities while they are in beta” setting.
Learn more about configuring ArcGIS assistants here.
Once these requirements are met, you can configure the Hub assistant (beta) in your site workspace. Site visitors can access the Hub assistant (beta) by selecting the associated icon at the bottom corner of any page.

Configure the Hub assistant (beta) on your site
Before deploying the Hub assistant (beta) on your site, it is important that you configure the settings for the assistant. You can adjust a variety of settings, allowing you to choose the intended audience, facilitate usage of the assistant, and reflect your location and the purpose of your Hub site.
Keep in mind that the Hub assistant (beta) relies on the data and metadata available on your site. So, it is crucial to create and maintain data and metadata that are relevant, complete, accurate, and current.
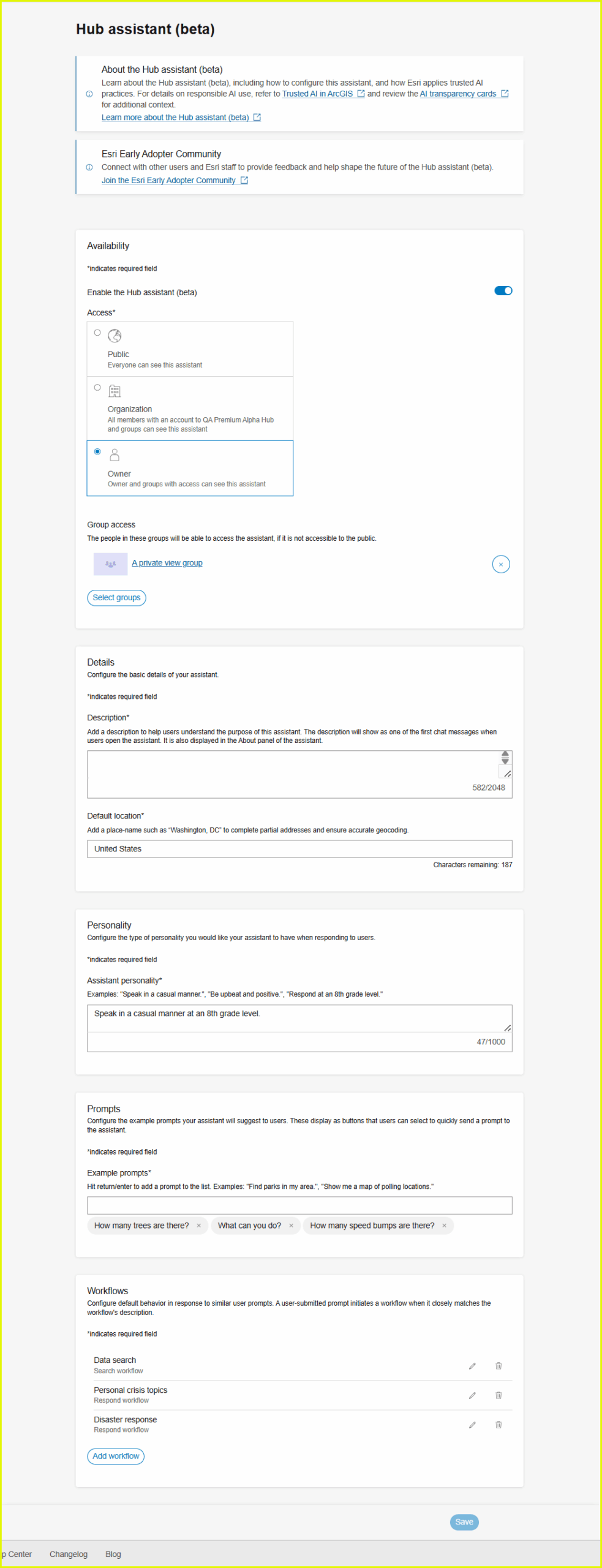
From a live view of your site, select the Manage site button to open the site workspace. Select the Settings > Hub assistant (beta) pane. Here, you can enable the Hub assistant (beta) and customize settings to meet the needs of your site.
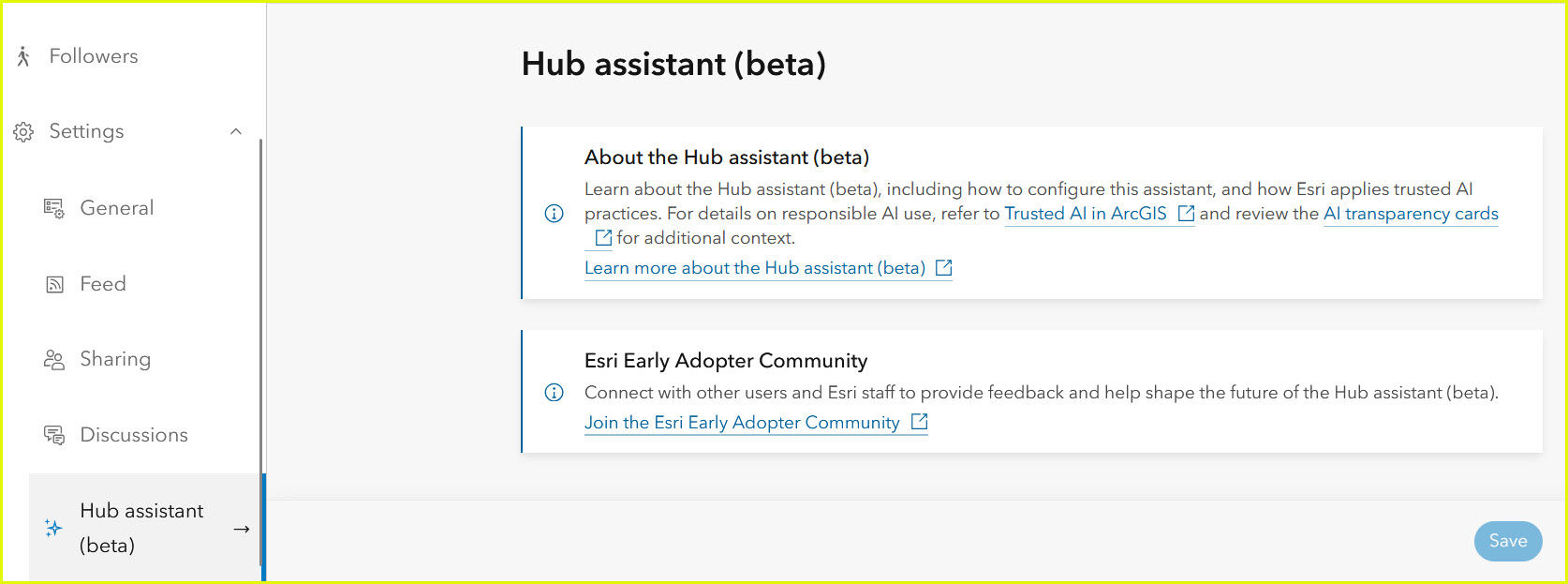
Adjust access
Access settings allow you to restrict access to the Hub assistant (beta) to the site owner or to your organization. Or when ready, you can open it to the public for visitors who sign in to your site. You also have the flexibility to limit access to specific groups of people.
Note: You may want to test the Hub assistant (beta) internally using a specified testing group before deploying it on your site. (Find more information below.)
Provide details
Configure the description and location settings to add detail and customize the assistant for your Hub site.
Add a description
The description for your Hub assistant (beta) allows you to introduce your site’s assistant and provide important information to users. This information displays at the top of the Chat window when a user initiates the assistant. It also appears on the About tab of this user- facing window.

Customize the description to include the following information:
- Introduction and purpose
- Technical description
- Data collection, usage, and protection practices
- Guidelines for use
- Limitations and restrictions
- Disclaimer statement
For example, a description might read:
“[name of assistant] is a helpful tool that uses artificial intelligence to assist people in discovering and using data from [name of site or organization]. It is designed to facilitate access to and understanding of data that is relevant to you and your community. [name of assistant] can answer questions, provide guidance on using the tool, and help you discover data. [name of assistant] is powered by Esri’s ArcGIS Hub assistant (beta) and uses natural language processing to interpret and respond to user inquiries. It is built to interact with questions and commands in everyday language.”
“[name of assistant] is a useful tool for exploring and understanding data, but it is critical to recognize that it is not a substitute for human expertise. Use the [name of assistant] as a place to start in research or decision-making, and seek additional information from experienced professionals, as needed. All output from the [name of assistant] is based on the data available within the [name of site] catalog. Consider any and all limitations or biases in the data provided.”
Set the default location
Configure a default location for the assistant based on your geographic location or the location that your site represents. With this location set, when a user enters prompts with incomplete address information, such as “123 Main St.”, the assistant infers the default city to complete the address.
Use the following resources to learn more:
Customize the personality
Configure the personality of the Hub assistant (beta) on your site by providing a description of the tone you’d like to achieve. Use a natural language prompt, such as “Speak in a casual manner.” You may want to include instructions such as “Speak at an 8th grade level.” to ensure that the assistant simplifies complex information and uses language that is easy to understand.
Creating example prompts
Write example prompts so that your site visitors can try out the assistant even if they don’t have a specific question or if they don’t know how to craft a prompt themselves. These example prompts appear as selections when the Hub assistant is initiated.
Some pointers for writing effective prompts include:
- Use clear and simple language
- Be specific
- Describe the desired format of the response
- Specify the audience
- Iterate prompts to refine results
Be sure to test the example prompts for your site internally before deploying the Hub assistant (beta) publicly on your site. (Find more information below.)
Check out this blog article for tips on how to write prompts for AI assistants.
Set up workflows and create guardrails
Hub provides three default workflows as a place for you to start. This includes a search workflow: Data search and two response workflows: Personal crisis topics and Disaster response. The Hub assistant (beta) initiates a workflow when the workflow’s description closely matches a user-submitted prompt.
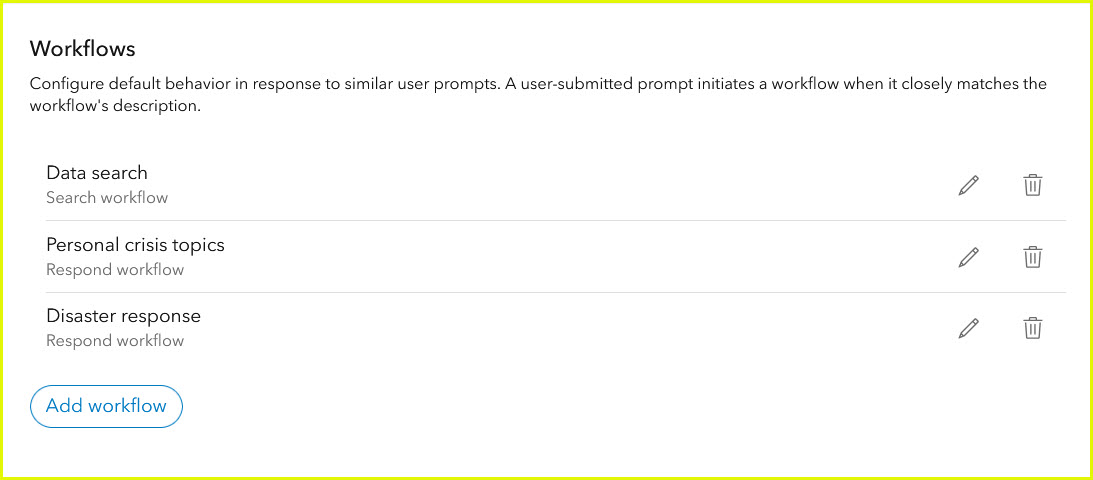
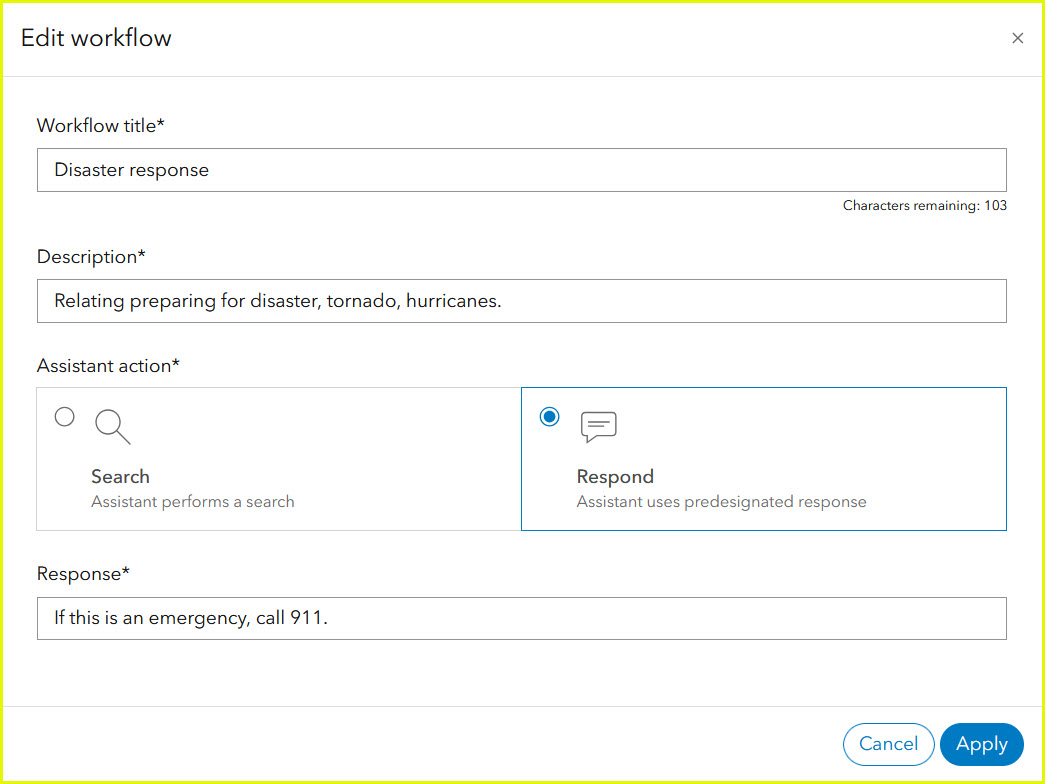
It is essential to view and modify the default response workflows to reflect the correct emergency response number, resources, and other pertinent information for your area. Select the edit pencil to edit any of these default workflows.
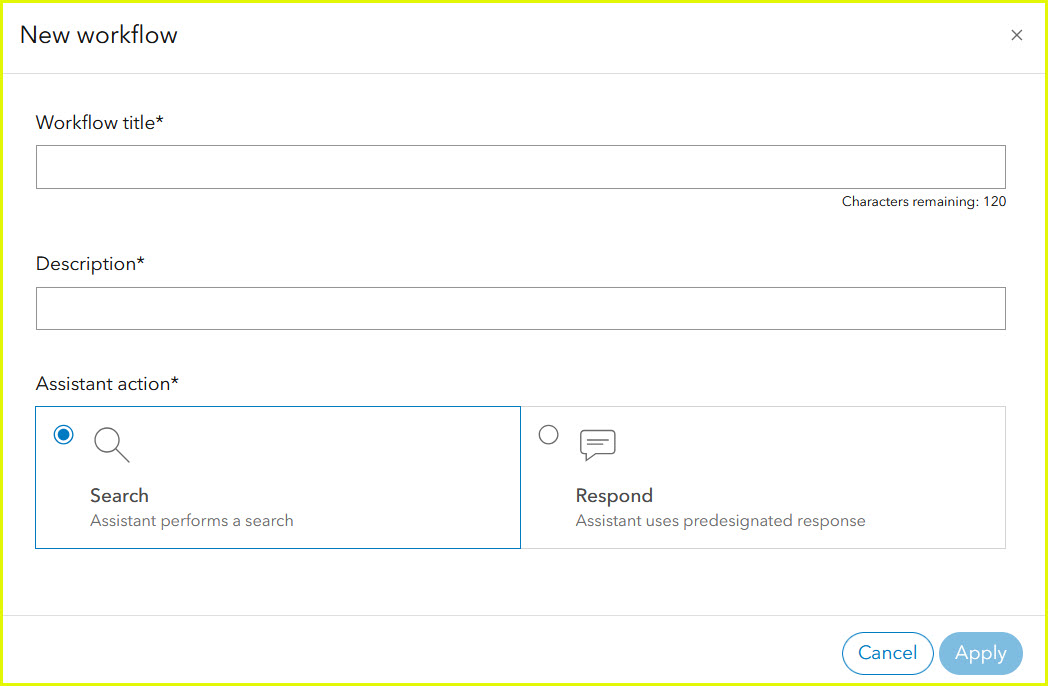
To add additional workflows, select the Add workflow button. Enter a title and description and choose a search or respond action.
Be sure to test the guardrails you’ve set for the Hub assistant (beta) internally before deploying it publicly on your site. (Find more information below.)
Learn more about setting up the Hub assistant (beta) on your site.
Test the Hub assistant (beta) internally
As with any feature on your Hub site, it’s important to test the Hub assistant (beta) within your organization before deploying it on your public-facing site. Create a testing group of organization members and restrict access to only that group. As described above, you can control access in the site workspace on the Settings > Hub assistant (beta) pane under Availability.
For a comprehensive test of the Hub assistant (beta), the testing group members can submit some of their own prompts in addition to the sample prompts you’ve generated, including questions about local information. They should also test the guardrail workflows to ensure that the emergency information provided is accurate and relevant to your site.
Ensure that group members have a chance to report any testing issues and provide their impressions and recommendations to adjust the configuration of the Hub assistant (beta). If you make changes, perform additional testing and solicit feedback until the group is satisfied with the functionality of the assistant on your site.
After testing internally, you may want to deploy it to a group of external site users for additional testing before finally opening it to the public or your specific intended audience.
Limitations and bias
Consider carefully that artificial intelligence can generate suggestions that are misleading or inaccurate. Apply human judgment in interpreting and acting upon the assistant’s outputs to avoid the possibility of reinforcing any unintentional biases in the AI models used by Hub assistant (beta). Report any security or privacy concerns to the ArcGIS Trust Center.
More ways to learn
- Participate in the Esri Early Adopter Community to ask questions and submit ideas during the beta period.
- Dig into the ArcGIS Hub assistant (beta)
- Sign up for the ArcGIS Hub e-newsletter.
- Showcase your sites by submitting them to the ArcGIS Hub Gallery.
- Register and attend Hub webinars.




Article Discussion: