ArcGIS Image Analyst is the ArcGIS Pro extension that provides tools for advanced image visualization, exploitation, and geospatial analysis. The latest release features change detection, expanded deep learning capabilities, enhanced support for multidimensional data, improved motion imagery capabilities, and much more.
Below, take a tour of all the new imagery and remote sensing-related features we’ve added in the ArcGIS Pro 2.7 (December) release to help expand and streamline your workflows.
Change detection
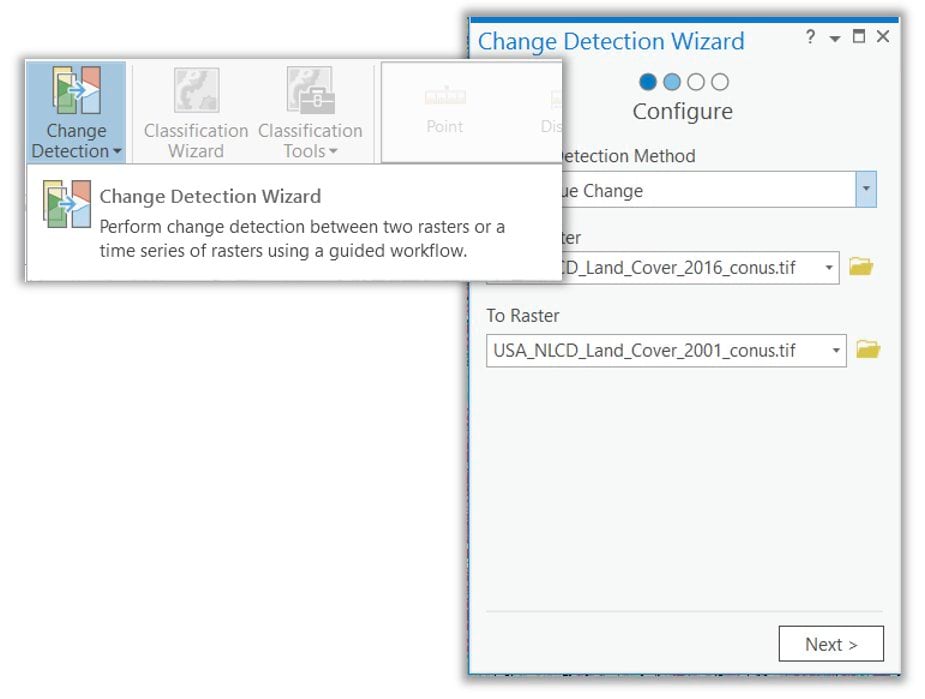
Creating change maps using imagery is one of the most fundamental applications in imagery and remote sensing. Identify changes due to human activity, abrupt natural disturbances, or long-term climatological or environmental trends.
Use change detection tools to determine the type, magnitude, and location of change by comparing two raster datasets or by analyzing a time series image cube containing data collected for one area at different times.
The new Change Detection Wizard provides guided workflows for categorical change detection, timeseries change detection, and pixel value change detection.
Deep learning
Deep learning is transforming the speed at which you can gain intelligence from imagery. This release adds new model types, multispectral support for training, multilabel classification, and better accuracy reporting for object detection.
New model types
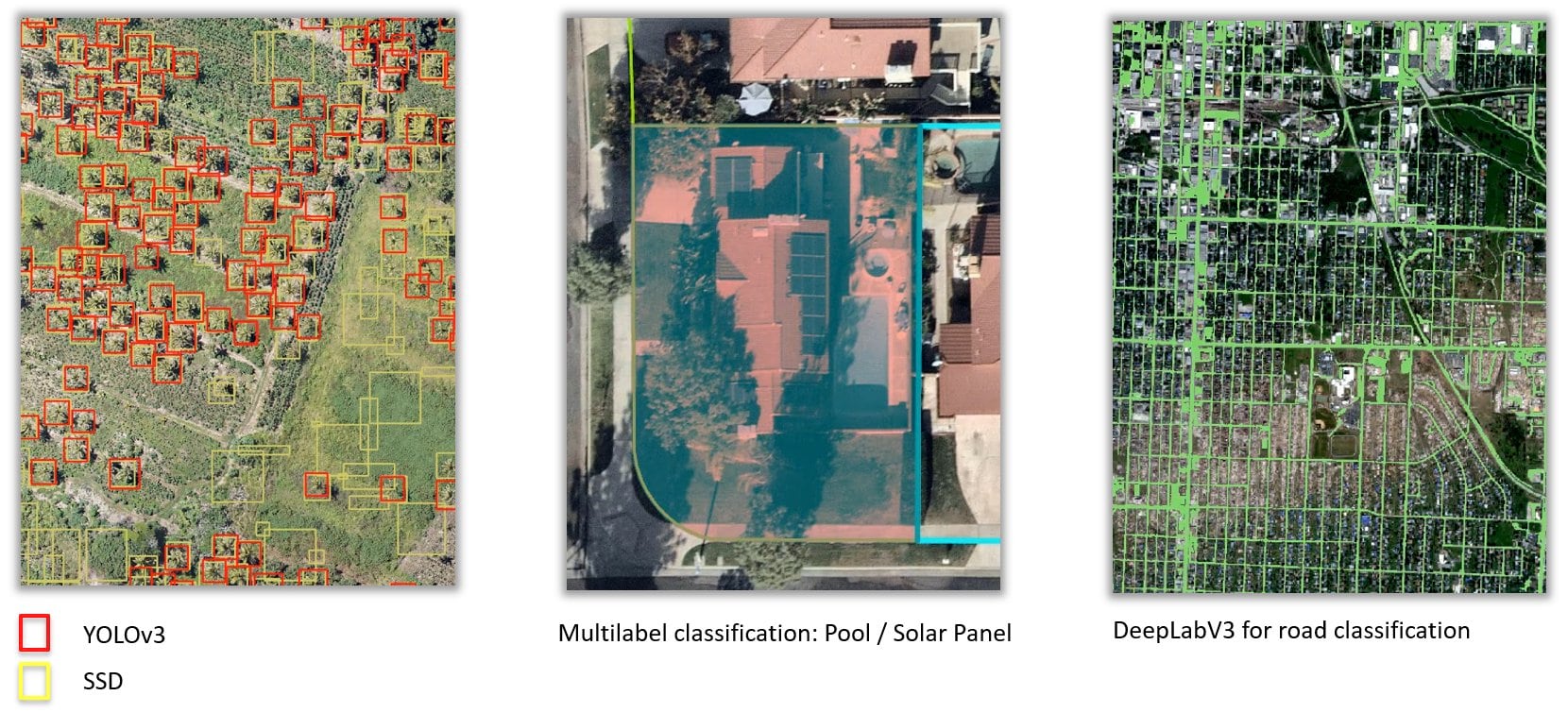
In addition to the models previously supported in ArcGIS Pro 2.6, we’ve added support for new model types to train AI models, including YOLOv3, FasterRCNN, and DeepLab.
YOLOv3 and FasterRCNN both support object detection workflows. FasterRCNN is slower than models like SSD, but it can provide results with higher accuracy. YOLOv3 is a one-stage detector, so it’s fast.
DeepLab supports pixel classification models. It is found to be better than UNet on all benchmarks. It also takes into account the same amount of context with fewer filters than UNet, so it can achieve higher accuracy. It performs best when there are classes that are drastically different in dimensions (grasslands versus fields, for example).
Multispectral support for training
Most earth observation sensors provide multiple bands to leverage. With this release, the restrictions on working with a three-band image are eliminated. All bands in a multispectral image can be used for feature extraction.
Training multispectral data with sparse training samples (another enhancement) eliminates the need for classifying every pixel in a training sample image for land-cover classification (as an example). This leads to significant productivity improvements. Additionally, pixels that are not classified will be ignored during the training process. The support for multispectral imagery enables users to leverage the spectral responses of bands outside the visible range.
Multilabel classification
Now you can easily extract multiple types of features without having to train a model multiple times. For example, in one pass, the system can classify houses, houses with pools, and houses with pools and solar panels—no need to train multiple models and then perform additional analysis to join common features into a single GIS dataset.
Better accuracy reporting for object detection
The new accuracy reporting tool calculates the accuracy of a deep learning model by comparing the detected objects from the Detect Objects Using Deep Learning tool to ground truth data.

Multidimensional management, processing, and analysis
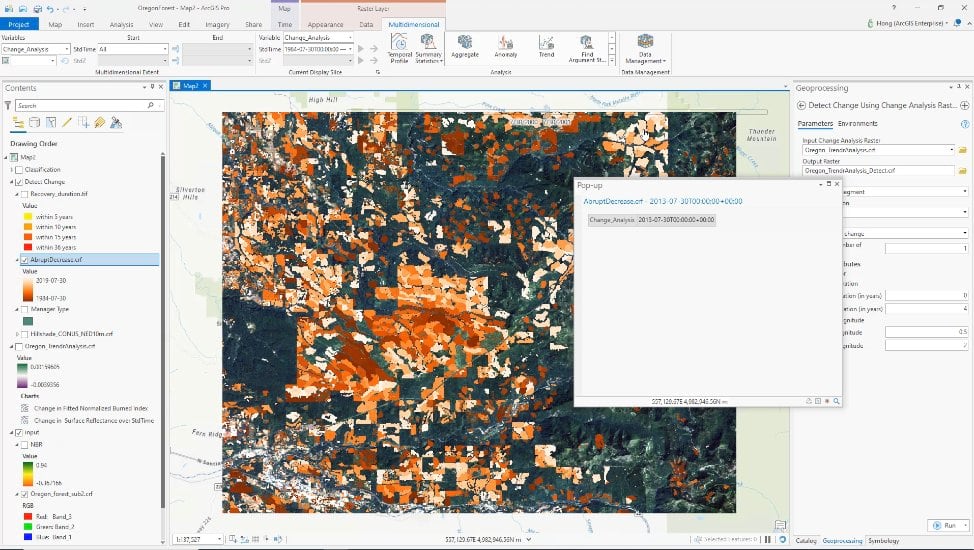
For multidimensional analysis, you can now identify trends in your data using new statistical methods, merge and summarize categorical data in a time series of rasters and attach processing templates directly to raster datasets—including multidimensional datasets.
These are all the new and enhanced multidimensional tools and functions:
- Summarize Categorical Raster—Generate a table containing the pixel count for each class, in each slice of an input categorical raster.
- Generate Trend Raster—Includes new options to evaluate presence and absence of trends.
- Detect Change Using Change Analysis Raster—Now supports LandTrendr model results.
- Aggregate Multidimensional Raster—Create a multidimensional raster layer by combining existing multidimensional raster variable data along a dimension.
Raster functions
Raster functions are operations that apply processing directly to the pixels of imagery and raster datasets (as opposed to geoprocessing tools, which write out a new raster to disk).
As with every release, we added new raster functions to support additional workflows. With the 2.7 release, we’ve added six new band indices and two new multidimensional functions, and we’ve enhanced some of our existing functions. These can be helpful when analyzing and mapping wildfires, delineating content changes in surface water, identifying snow cover, monitoring droughts, and emphasizing human-made built-up areas.
Two additional functions have been added to support multidimensional workflows:
- The LandTrendr Analysis raster function evaluates changes in pixel values over time using the Landsat-based detection of trends in disturbance and recovery (LandTrendr) method.
- The Aggregate Multidimensional Raster function creates a multidimensional raster layer by combining existing multidimensional raster variable data along a dimension.
Other existing raster functions have also been enhanced:
- Compute Change has a new Filter Method parameter that filters classes generated for categorical change detection.
- Generate Trend now includes Mann-Kendall and Seasonal-Kendall trend analysis methods.
- Kernel Density has a new Input Barriers parameter that alters the influence of a feature when calculating density (requires ArcGIS Spatial Analyst).
- Merge Rasters now supports merging multidimensional raster datasets spatially or across variables and dimensions.
- Statistics now includes additional statistics fill methods, including Majority and Minority.
- Zonal Statistics now includes Median and Percentile statistics types for floating-point value rasters.
Motion imagery
Exploiting motion imagery in ArcGIS Pro is now even more user-friendly, with timeline indicators for products that have been generated, customizable video player controls, and improvements for choppy playback.
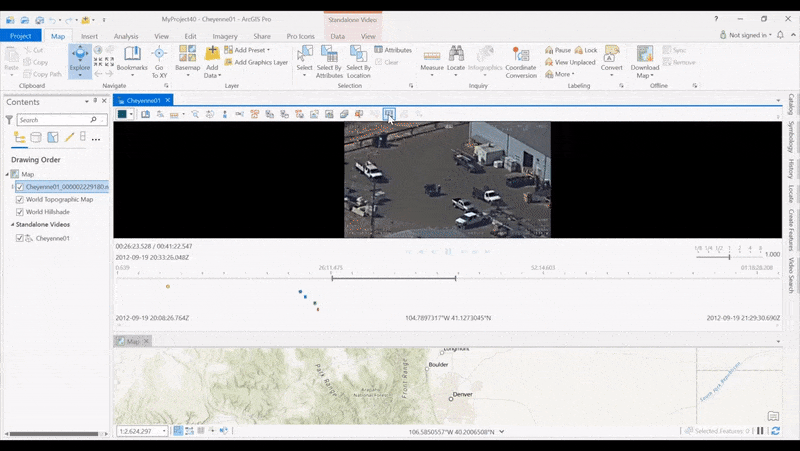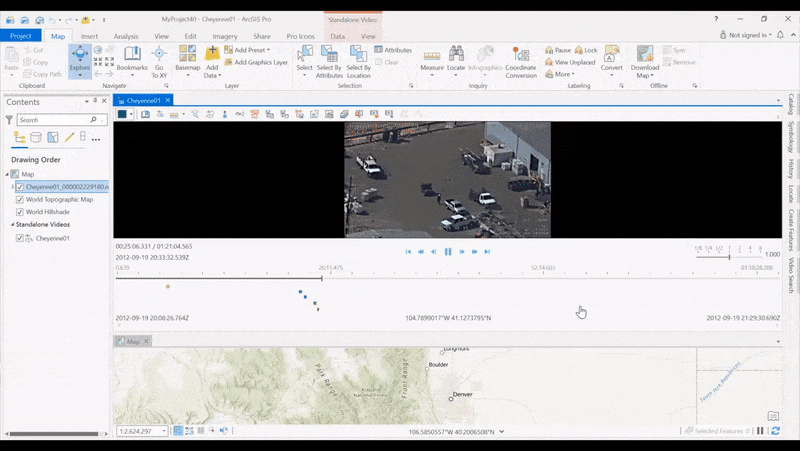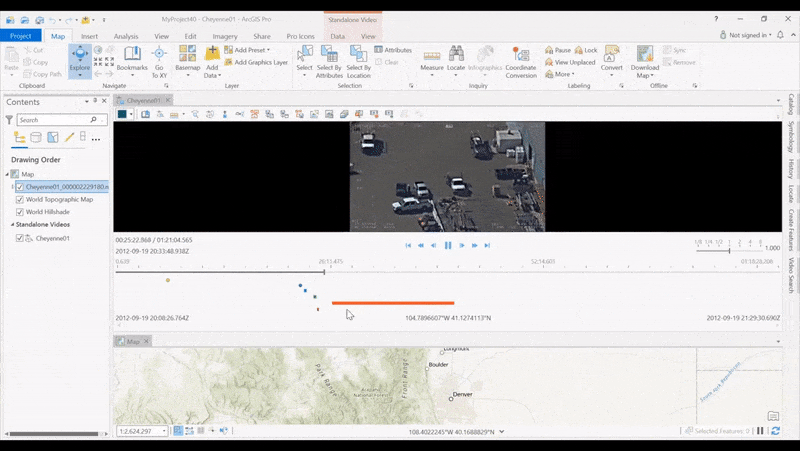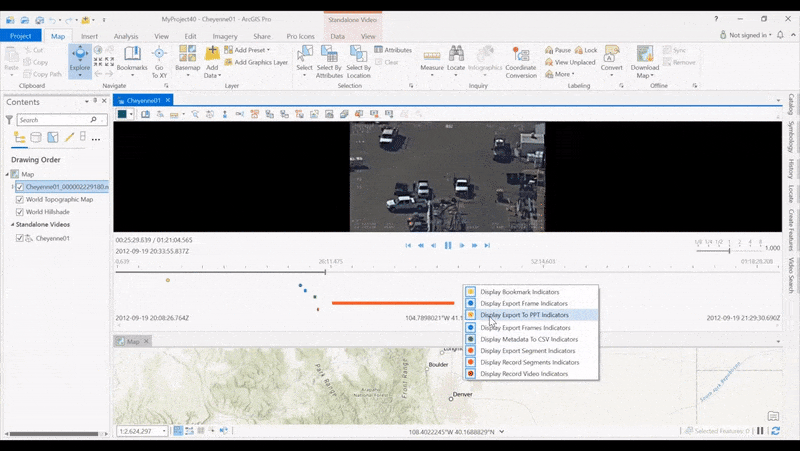
Create Indicators on the Timeline allows analysts to see where products have been created along a video’s timeline, and then click video segments to quickly retrieve the location. With new timeline indicators, you can create and display indicators for activities launched from the Quick Launch toolbar, including Bookmark, Export Frame, Export PPT, Export Frames, Metadata to CSV, Export Segment, Record Segment, and Record Video.
The increasing capabilities of the video player in ArcGIS Pro have also increased the number of controls for interacting with the video and map. Not all buttons are used by all analysts, so now you can configure the video player buttons to customize your instance of ArcGIS Pro.
Some videos have malformed metadata in them, which can cause choppy behavior due to a lag in the processing time of certain video frames. To improve this experience, the Enable Frame Dropping option decodes a video stream’s image before the next image comes and then drops the current frame to continue playback and reduce the choppiness.
Stereo
We’ve made a few key bug fixes for stereo users and added some enhancements to improve the user experience.
In response to one of the most popular feature requests from users, ArcGIS Pro now allows you to choose the way stereo models are oriented when displayed in the stereo map. You can orient stereo models so that north is Up or Right; Up or Left; Down or Right; or Down or Left.
Users are now prompted to choose only stereo models within a single flight line, thereby minimizing stereo map rotation when switching between models.






Article Discussion: