In today’s rapidly changing world, sustainability and climate action have become critical priorities for individuals, organizations, and governments alike. To effectively address these challenges, innovative technologies are playing a pivotal role. One such technology is Geographic Information System (GIS), which offers powerful tools for understanding, analyzing, and managing spatial data. In this blog, we will explore the various ways GIS is being leveraged to drive sustainability efforts and take climate action.

GIS in Sustainability:
Throughout the world Geographic Information Systems are playing a central role in sustainability efforts by providing a comprehensive ecosystem for integrating and visualizing diverse environmental data. It enables stakeholders to make informed decisions by mapping and analyzing various sustainability factors. With GIS, information on land use, biodiversity, water resources, and energy consumption can be overlayed on infrastructure assets and analyzed to identify patterns, relationships, and areas for improvement.
One of the key applications of GIS in sustainability is the analysis of land cover data. By utilizing GIS, areas suitable for conservation or restoration efforts can be identified. This helps organizations in preserving and restoring ecosystems, promoting biodiversity, and protecting natural resources while planning and operating their networks. GIS also aids in the monitoring and management of protected areas, ensuring their long-term sustainability. By integrating data on protected areas, land use, and ecological factors, GIS enables effective planning and decision-making to maintain the integrity of these areas.
Overall, GIS provides a powerful tool for understanding and managing sustainability factors. By leveraging its capabilities, stakeholders can gain valuable insights, identify opportunities for improvement, and make informed decisions to promote a more sustainable future.
Leveraging Location Intelligence for Climate Action:
Location intelligence, a critical component of GIS, plays a pivotal role in climate action initiatives. By leveraging GIS, decision-makers can identify vulnerable areas susceptible to climate change impacts, such as rising sea levels, extreme weather events, or heatwaves. Through the analysis of spatial data, targeted strategies can be developed to mitigate risks, adapt infrastructure, and protect communities.
GIS enables the mapping of flood-prone areas, allowing for the development of risk management plans and the implementation of measures to minimize the impact of potential flooding. Additionally, GIS can identify suitable locations for the installation of renewable energy infrastructure based on solar or wind potential. By analyzing solar radiation or wind patterns, decision-makers can optimize the placement of solar panels or wind turbines, promoting the generation of clean and sustainable energy for use throughout their networks and infrastructure. Furthermore, GIS facilitates the monitoring and tracking of greenhouse gas emissions, a crucial aspect of climate action. By integrating data from various sources, GIS aids in the development and evaluation of climate action plans. It enables decision-makers to assess the effectiveness of emission reduction strategies, identify areas for improvement, and track progress towards climate goals.
In summary, GIS and location intelligence are invaluable tools in climate action. They enable decision-makers to identify vulnerable areas, develop targeted strategies, and monitor progress towards climate goals. By harnessing the power of GIS, we can make informed decisions and take effective action to address the challenges of climate change.
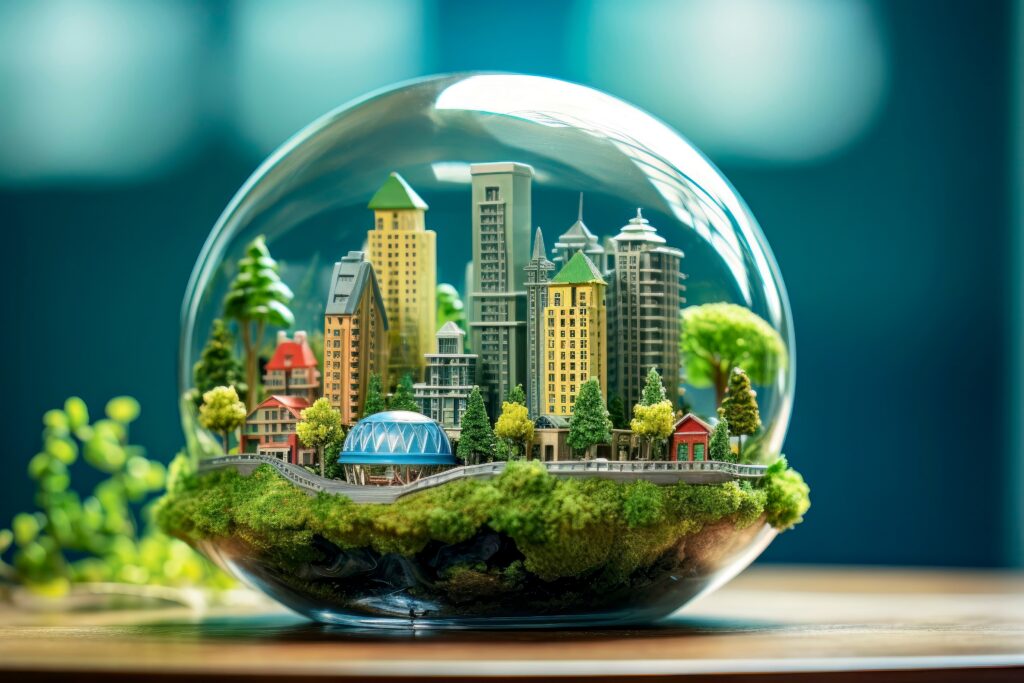
Reducing Environmental Impact:
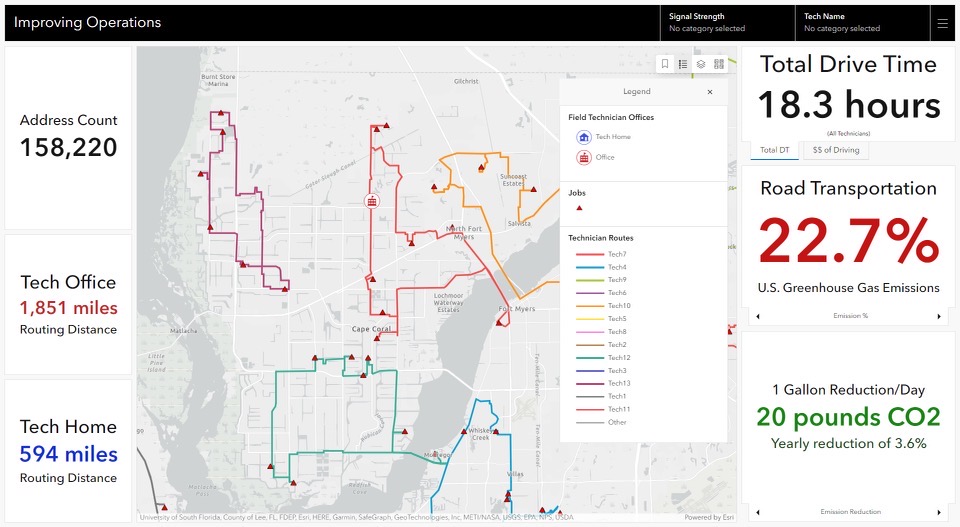
Geographic Information Systems play a crucial role in reducing environmental impact, particularly in infrastructure planning and operations. One area where GIS is instrumental is in optimizing vehicle operations to minimize congestion and emissions. By analyzing workflows, driving patterns, and population density, GIS can identify optimized routing options that reduce carbon impact while improving the experience for employees and customers, helping organizations achieve more sustainable and efficient operations.
GIS also contributes to the identification of suitable locations for renewable energy installations, such as vehicle charging stations. By analyzing factors like solar radiation, wind patterns, and land availability, GIS can help identify optimal sites for solar farms or wind turbines. This maximizes energy generation while minimizing ecological disruption, promoting the transition to clean and sustainable energy sources. Furthermore, GIS supports sustainable practices in various sectors.
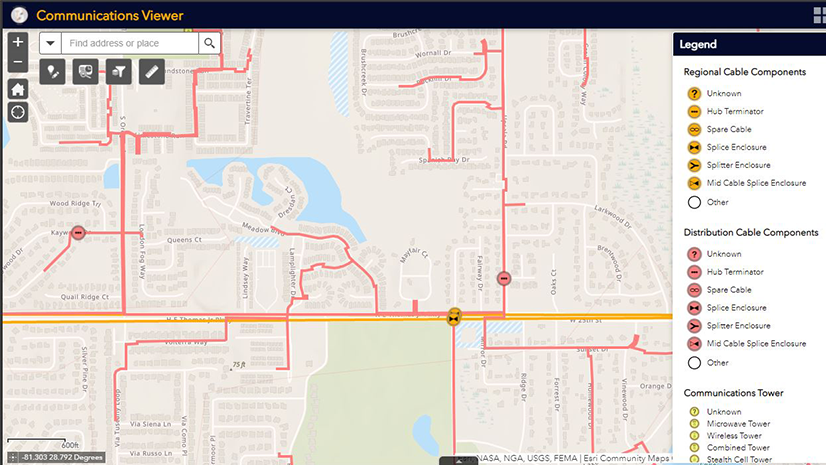
For example, in telecommunications, GIS can optimize network planning, reducing needs for field walkouts or overbuilt networks. By analyzing the built and natural environment and climate data, GIS provides valuable insights to network operators, enabling them to optimize site selection, project schedules, and network management practices. This promotes more efficient and sustainable telecommunications practices, reducing waste and minimizing environmental impacts.
In summary, GIS is a powerful tool for reducing environmental impact, particularly in infrastructure planning and operations. By optimizing vehicle operations, network maintenance and operations, identifying suitable locations for renewable energy installations, and supporting sustainable practices in infrastructure, GIS enables organizations to make informed decisions that contribute to a more sustainable future.
Using GIS to Sustainably Deliver Products and Services:
Geographic Information Systems play a critical role in ensuring the sustainable delivery of products and services. One area where GIS is instrumental is supply chain management. By utilizing GIS, organizations can optimize their supply chains to minimize transportation distances, reduce carbon emissions, and enhance overall efficiency. Through the analysis of transportation routes, GIS can identify the most efficient paths for delivering goods, reducing fuel consumption and emissions. This not only helps organizations reduce their environmental impact but also improves cost-effectiveness.
GIS also contributes to sustainable waste management practices. By analyzing population density, waste generation rates, and transportation networks, GIS can identify optimal locations for recycling centers and waste treatment facilities. This enables organizations to optimize waste collection routes, reducing fuel consumption and improving overall efficiency in waste management processes. By minimizing the distance traveled and maximizing resource utilization, GIS helps organizations reduce their environmental footprint.
Additionally, GIS supports sustainable forestry practices. By monitoring deforestation, managing forest resources, and promoting reforestation efforts, GIS aids in the preservation and sustainable management of forests. Through the analysis of satellite imagery and forest inventory data, GIS can identify areas at risk of deforestation and support sustainable logging practices. This helps organizations balance economic needs with environmental conservation, ensuring the long-term sustainability of forest resources.
In summary, GIS is a valuable tool for promoting sustainable delivery of products and services. By optimizing supply chains, improving asset management practices, and supporting sustainable operations, GIS enables organizations to reduce their environmental impact and contribute to a more sustainable future.

Building a Better Future:
A Geographic Information System is a powerful tool for driving sustainability and climate action. By leveraging location intelligence, GIS enables stakeholders to make informed decisions, develop targeted strategies, and monitor progress towards sustainability goals. From reducing environmental impact to optimizing supply chains and delivering products and services sustainably, GIS plays a vital role in creating a more sustainable and resilient future. As we continue to face the challenges of climate change, harnessing the power of GIS will be crucial in shaping a sustainable world for generations to come.
By embracing GIS technology and integrating it into sustainability efforts, we can pave the way for a greener, more sustainable future. Let us harness the power of GIS to drive positive change and take meaningful action towards a more sustainable and resilient planet.
Learn more about how GIS is transforming and supporting the telecommunications industry here: https://www.esri.com/telecom