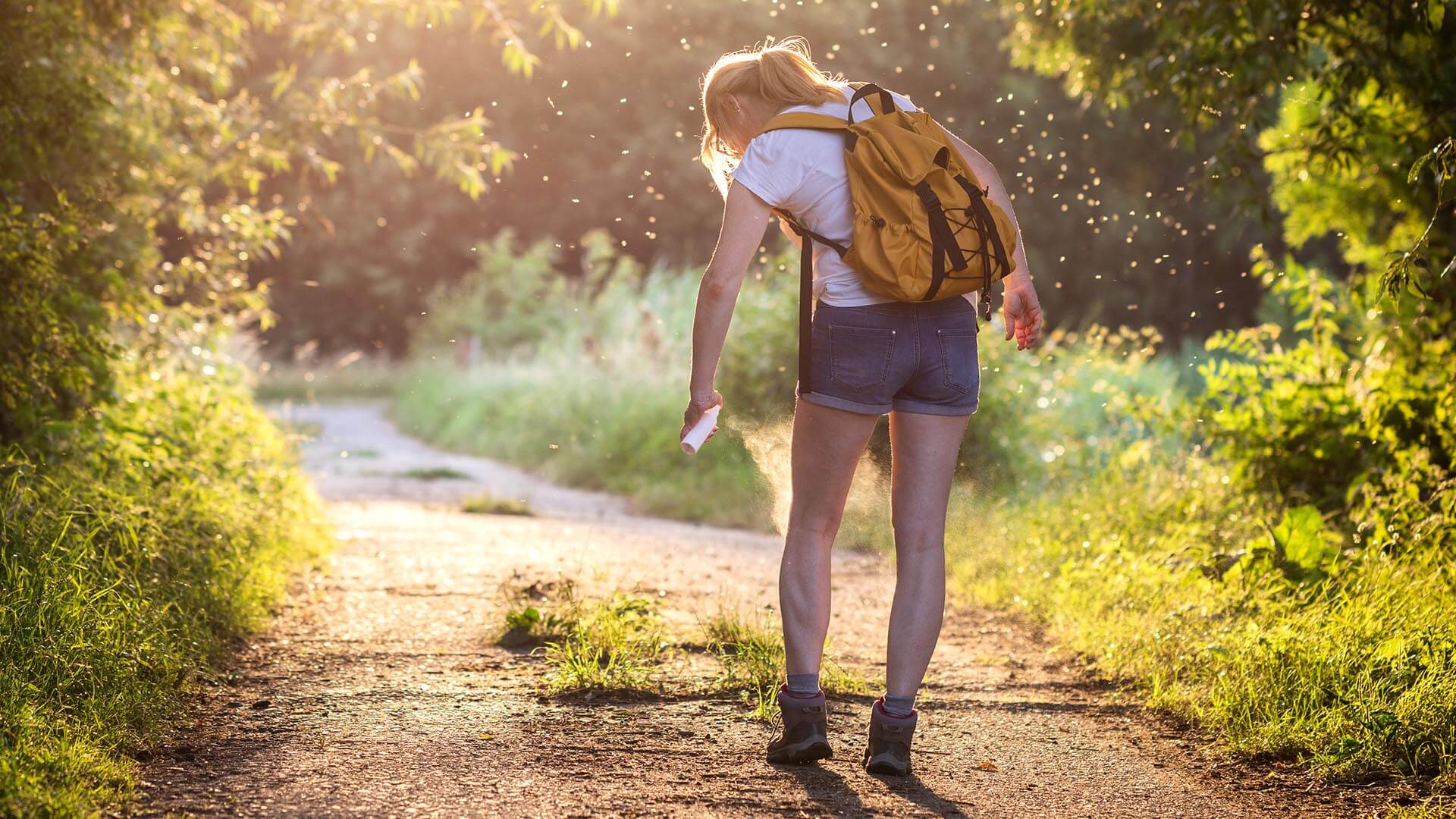
Off the coast of Massachusetts, a tiny pest is plaguing a popular vacation destination, forcing visitors and residents to rethink what they eat and buy. For business executives, it’s another reminder of how important it is to spot a trend early, analyze its origin, and adjust accordingly.
That’s what happened on Martha’s Vineyard. One bite from the lone star tick, multiplying there and elsewhere in the United States, causes its victim several months of severe allergic reactions to meat or dairy, turning charcuterie boards into gastrointestinal torture. As restaurants and markets became aware of what was happening, they deftly adapted menus and shelves to suit newly lactose- and meat-intolerant customers, reported The New York Times.
For a grocery store, a restaurant, or most any B2C operation, there’s a lesson hiding between the lines. Spotting, analyzing, and adjusting to what’s happening where—whether it’s the spread of a food-related illness, a social trend, or broad changes in consumer tastes—separates the smart businesses from the irrelevant.
Spotting and Analyzing Trends as They Emerge
Businesses spot trends by looking for unusual patterns in their sales data. The key is understanding why these patterns happen and where they’re happening.
Analyzing root causes might mean sifting through social media feeds and online chatter to connect the geographic dots—a form of location intelligence. A business school dean shared one example of the process in a WhereNext article:
Analysts at one of the world’s biggest investment firms recently used the power of location intelligence to guide an investment strategy. In researching a luxury handbag maker, the company sifted through online searches for questions such as, “Where can I buy [the company’s] handbag?” By using spatial analysis to correlate those searches to the locations of those conducting the searches, the company was able to pinpoint hot spots of demand.
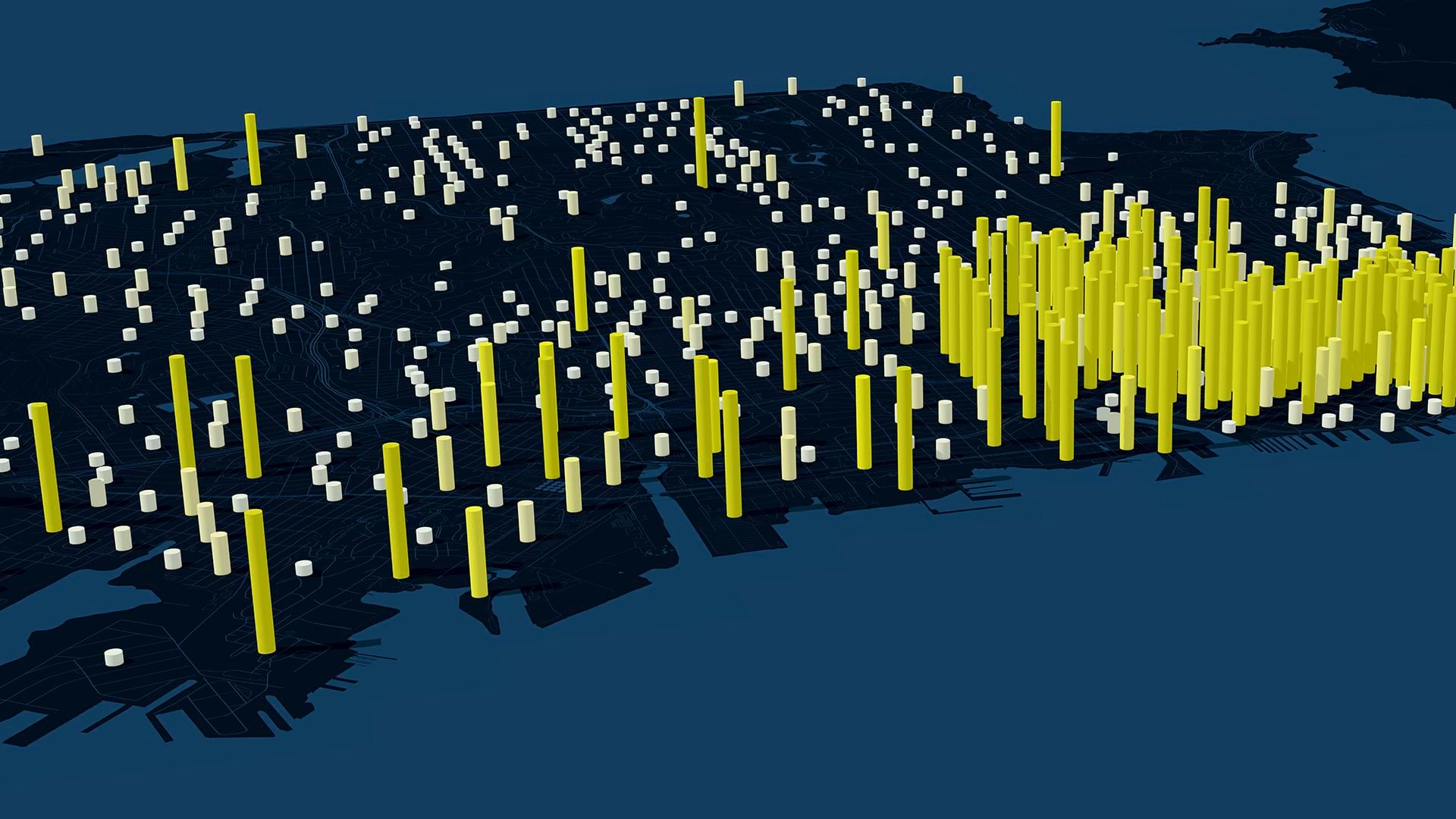
Sales and marketing experts have long used geographic information system (GIS) technology to gauge what existing or prospective customers are interested in, in which locations. GIS analysis produces maps that turn sales spreadsheets into intuitive visuals.
Adjusting to Business Performance Anomalies
While it’s a skill to spot a trend, companies also need to react to it.
A mattress maker discovered this when managers noticed that one of their plush fabric models sold better in northern US cities than in southern ones, despite sporting a universally attractive price. When they dug into the location data, the answer was obvious: customers in colder climates wanted that extra warmth and comfort. The manufacturer didn’t understand where their products worked best until analysts dove into the data.
With location intelligence like this, a company can adjust everything from where raw materials are sourced to how inventory is managed across a distribution network. For the mattress maker, understanding customer preferences in certain geographies changed how the organization marketed its products.
“We have a budget for ads, but you’ve got to know where to spend it,” the analytics director told WhereNext. Location-based insights helped executives see areas where e-commerce is expected to grow, allowing the company to adjust its supply chain accordingly.
Business leaders also use location intelligence to anticipate consumer needs rather than merely react to them. Geospatial analysis combined with artificial intelligence, known as geospatial AI, can help companies visualize when and where demand will spike next.
For manufacturers, restaurants, grocery stores, and retailers of every stripe, location intelligence can be key to spotting, analyzing, and adjusting to trends before they bite into sales.
The Esri Brief
Trending insights from WhereNext and other leading publicationsTrending articles
December 5, 2024 |

January 6, 2026 |
November 18, 2025 |

November 24, 2025 | Multiple Authors |

September 23, 2025 |
July 25, 2023 |