Digitizing old records is essential for organizations to preserve historical data, improve accessibility, and enhance record-keeping practices. This process involves converting physical documents into digital formats, which helps in understanding historical shifts and ensures information is available for future generations. The challenge lies in creating an automated solution that can handle the diverse nature of documents that require digitization.
In this blog post, we’ll provide a high-level summary of a workflow that leverages recent advancements in deep learning and traditional raster-to-vector conversion tools available in ArcGIS Pro. This approach is designed to save time and can be adapted to different kinds of maps, though it does require some human intervention. For those interested in step-by-step instructions, please refer to this comprehensive story map.
Some of the tools and steps we have used here will be familiar to users who have previously attempted scanned map digitization using geoprocessing tools in ArcGIS. However, the key breakthrough that has helped improve the results is the availability of several pre-trained AI models in ArcGIS Living Atlas of the World. In the next section, we will focus on these pre-trained models.
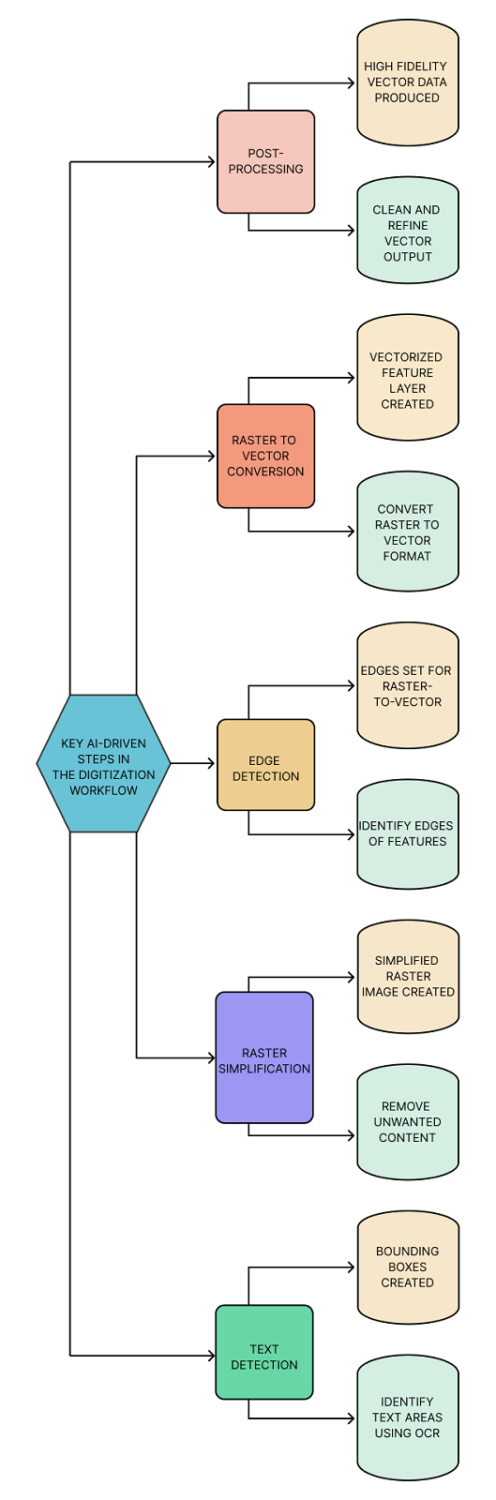
Key AI-driven Steps in the Digitization Workflow
- Text Detection:
- Objective: Identify text areas within the scanned map.
- Model: Optical Character Recognition (OCR) model in the Living Atlas.
- Tool: Detect Object using Deep Learning tool.
- Output: Bounding boxes around text areas, creating a feature layer with polygon features containing the extracted text.
- Raster Simplification:
- Objective: Clean the scanned map image by removing unwanted content such as symbology, noise, and color fills.
- Model: Map Simplification model in the Living Atlas
- Tool: Classify Pixels Using Deep Learning tool.
- Output: A simplified raster image.
- Edge Detection:
- Objective: Identify the edges of features to be extracted.
- Model: Edge Detection model in the Living Atlas.
- Tool: Classify Pixels Using Deep Learning tool.
- Output: Edges of features, setting the base for raster-to-vector conversion.
In addition to these new AI models, we use several geoprocessing tools to convert the raster to vector and apply post-processing to clean up the results.
- Raster to Vector Conversion:
- Objective: Convert raster images to vector format.
- Tool: Raster to Polygon tool in ArcGIS Pro.
- Output: A vectorized feature layer.
- Post-Processing:
- Objective: Clean and refine the vector output.
- Tools: Pairwise Erase, Smooth Polygon, Collapse Hydro Polygon, Pairwise Buffer, Pairwise Dissolve, Simplify Line, and Trim Line tools.
- Output: Cleaned and simplified vector data with high fidelity.
The digitization workflow can thus be represented as follows:
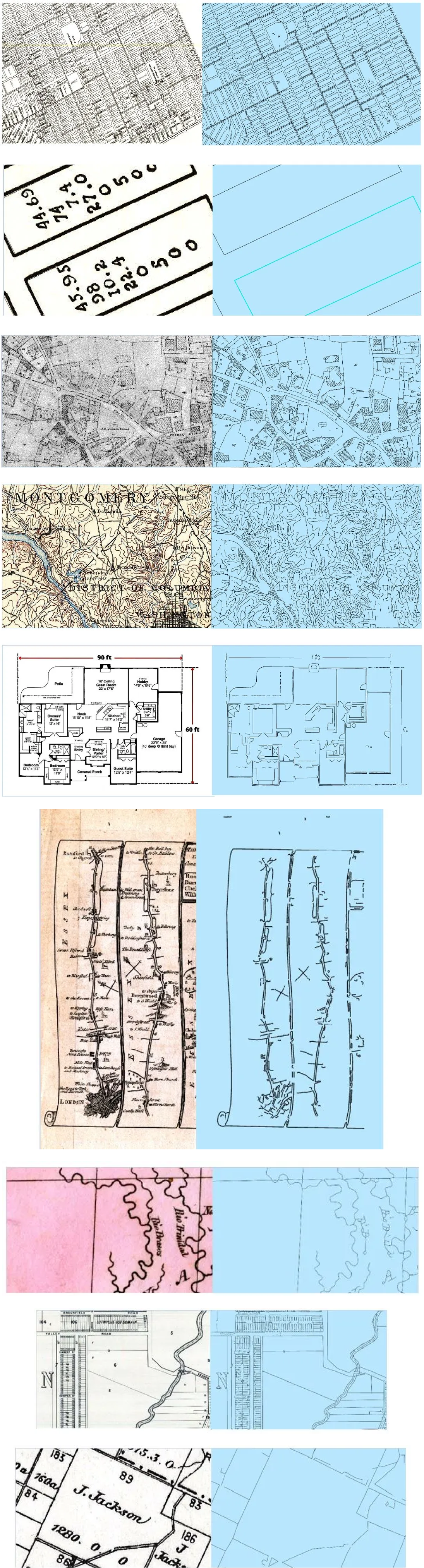
Here are some examples of how digitized outputs look on different types of maps.
This overview provided a glimpse of digitization using ArcGIS Pro, which drastically simplifies the process and ensures the accuracy and preservation of historical data. See our comprehensive story map for a detailed guide with step-by-step instructions and additional examples.
Commenting is not enabled for this article.