Esri’s curated library of pretrained deep learning models accessible through ArcGIS Living Atlas of the World has an exciting new addition—the Vision Language Context-Based Classification model. What sets vision-language models apart from traditional deep learning models is their ability to understand and process not only images but also interpret and generate human-like text.
At this year’s Developer and Technology Summit plenary, Rohit Singh puts the Vision Language Context-Based Classification model to the test by using it to identify buildings damaged in the Palisades fire that recently swept through western Los Angeles County.
In his ArcGIS Pro project, Rohit has an imagery layer showing the fire’s perimeter and a layer showing the footprints of 13,000 buildings within it.
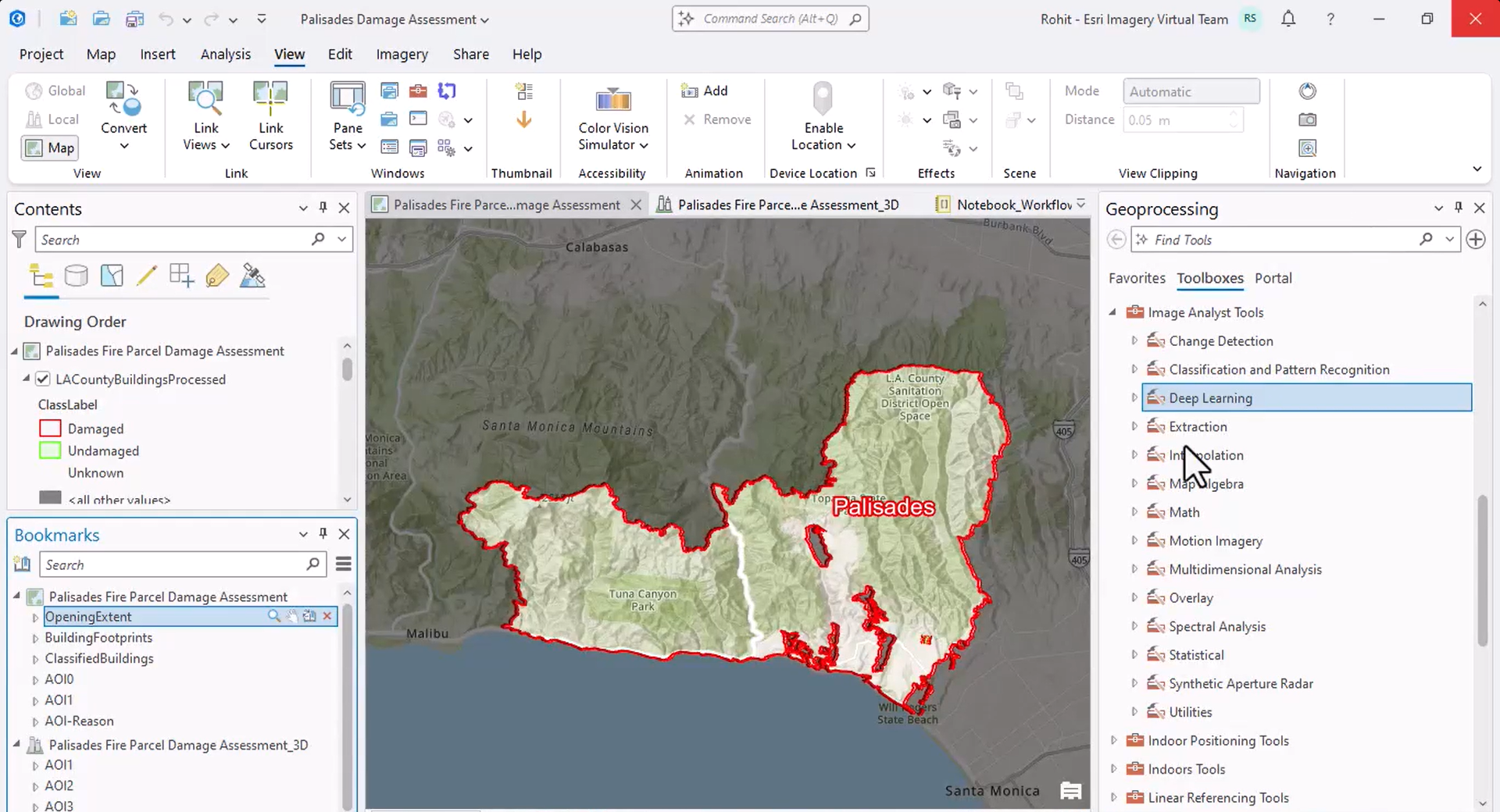
To classify the buildings, he uses the Classify Objects Using Deep Learning tool, which runs a deep learning model on an input raster and a feature class to assign a class or category label to each input feature.
For the classification model, he selects the Vision Language Context-Based Classification model. The model leverages OpenAI’s GPT 4o model and takes prompts in natural language for additional context on the input imagery and the desired way of classifying objects; so, Rohit provides it with appropriate context and specifies the custom class labels—damaged and undamaged—he wants the model to employ to describe each identified building.
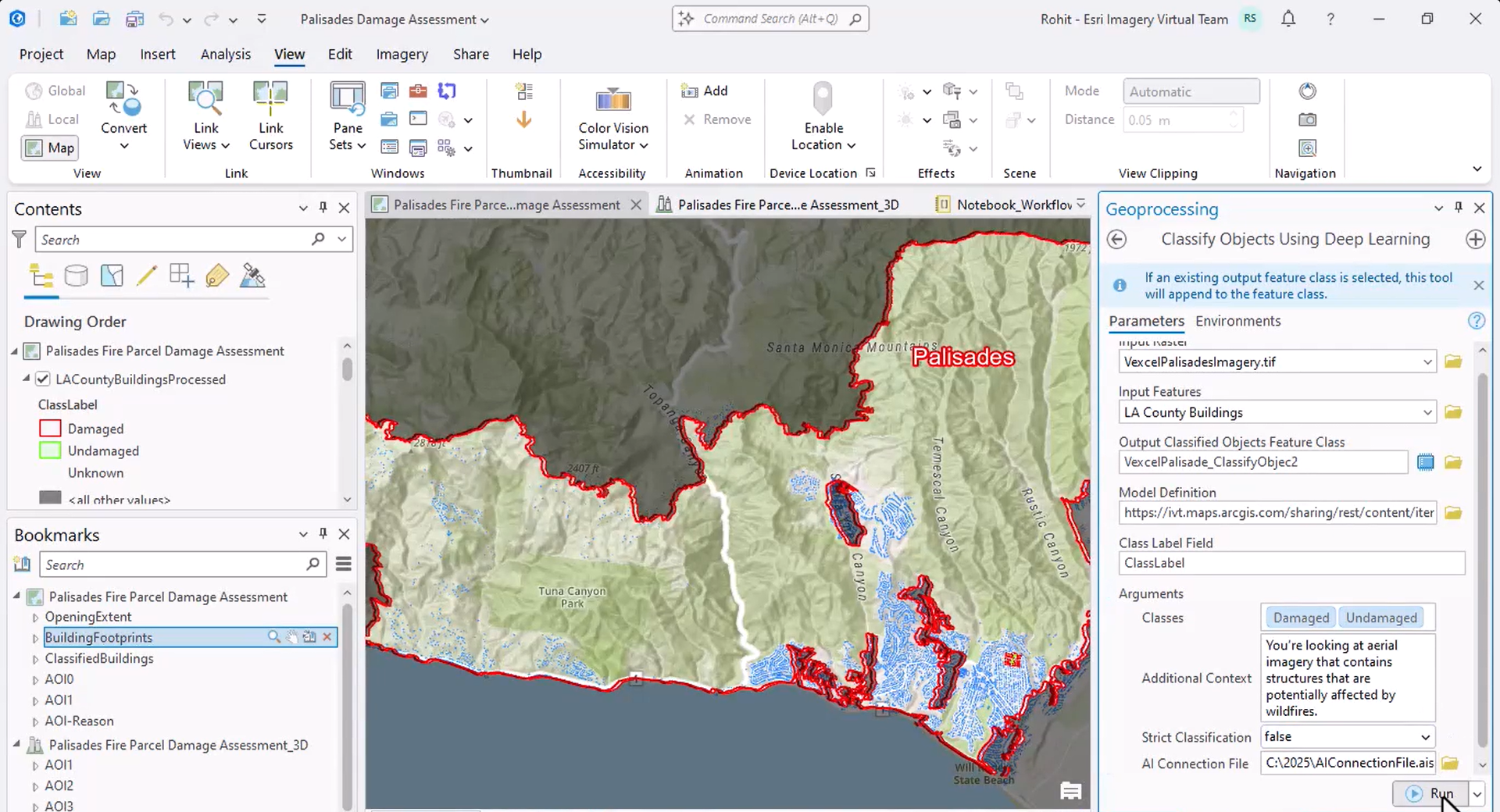
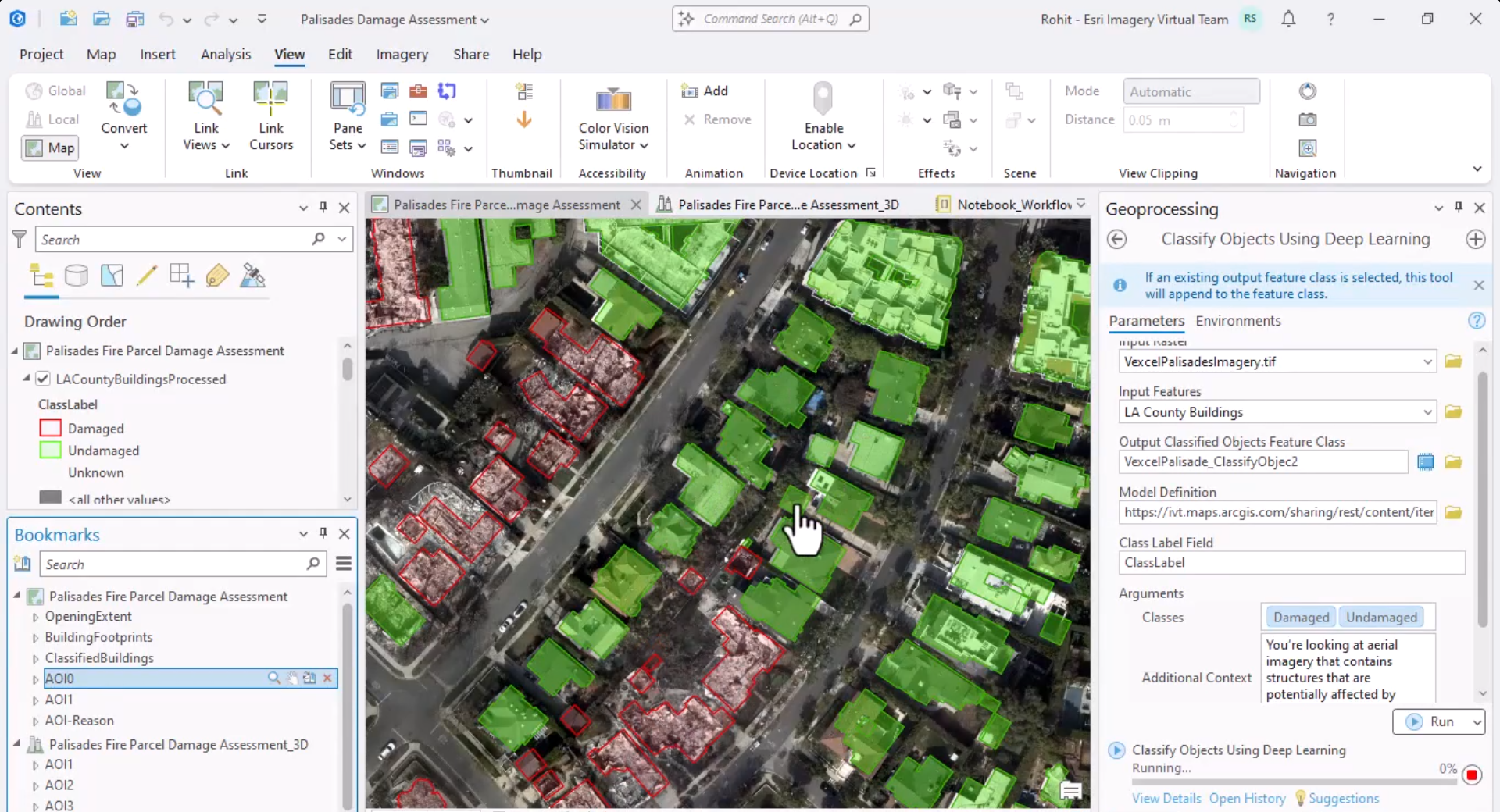
Since the classification takes a few hours, Rohit shows the result he obtained when he ran the tool before the plenary. The result shows that the model identified approximately 7000 damaged buildings.
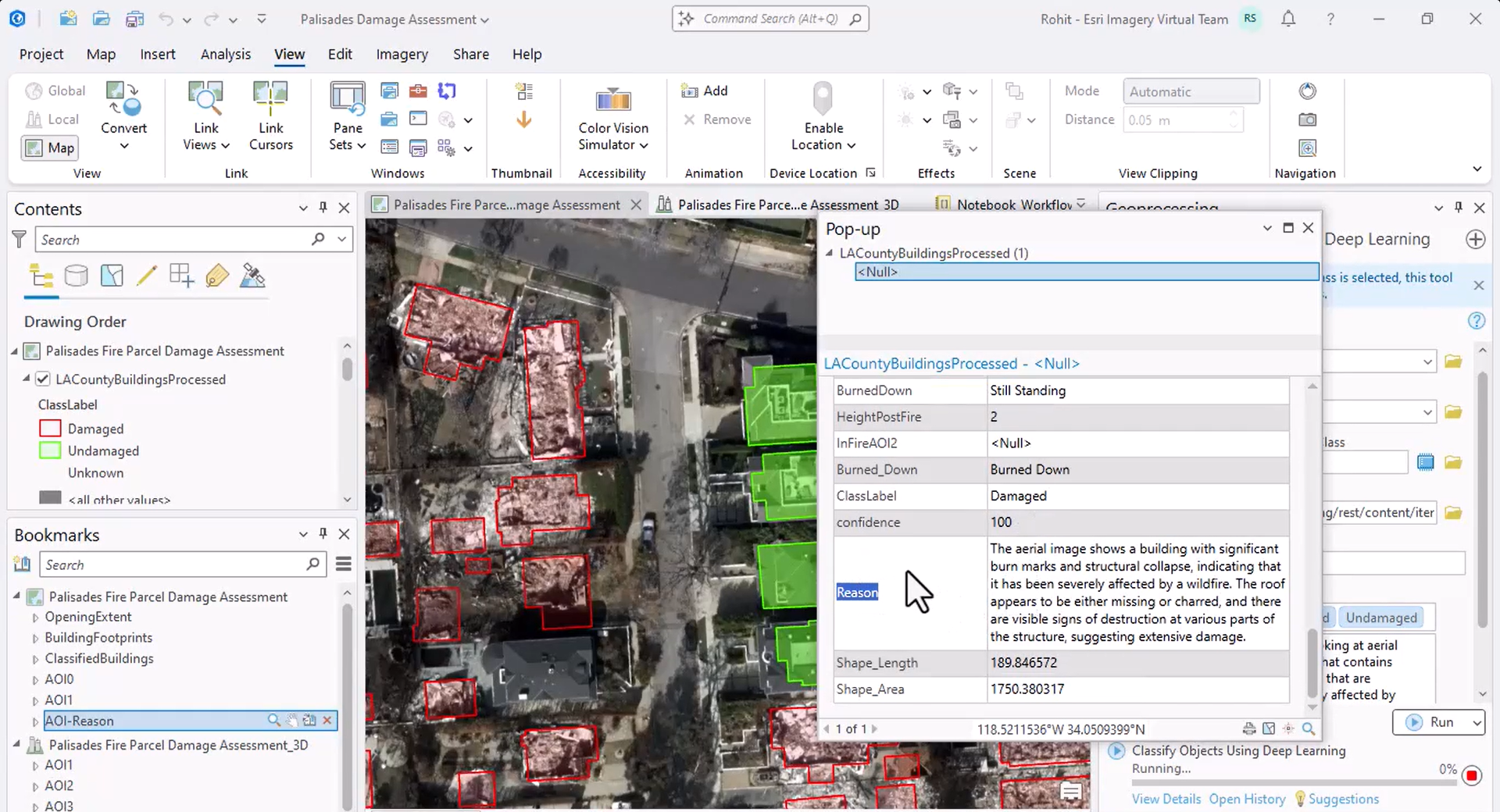
Additionally, the model explains how it determined whether a building is damaged.
Next, he opens a 3D scene that better shows the extent of the damage.
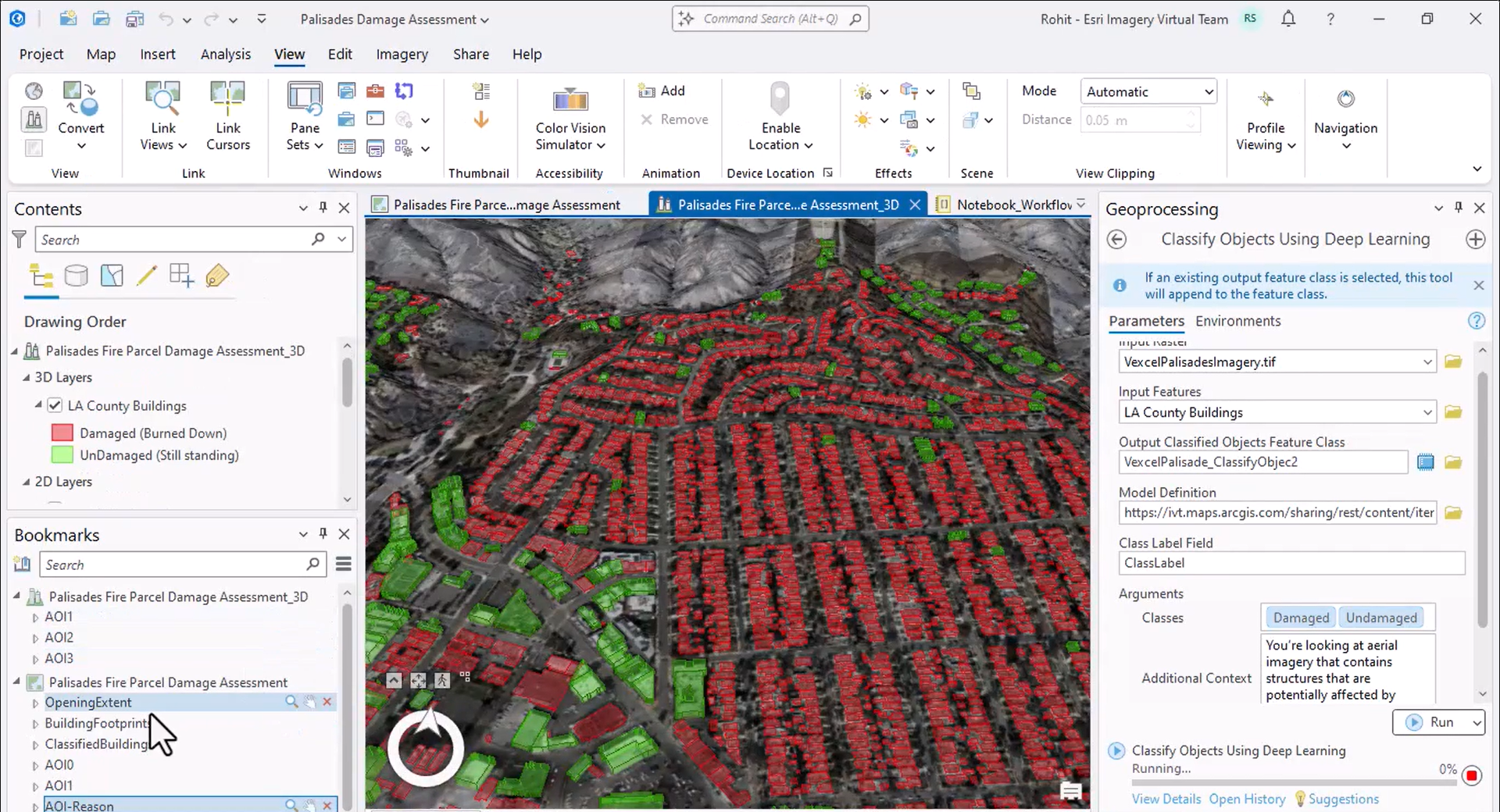
Finally, he shows how the classification can be automated through ArcPy and ArcGIS Notebooks, mainly using natural language and very little code.
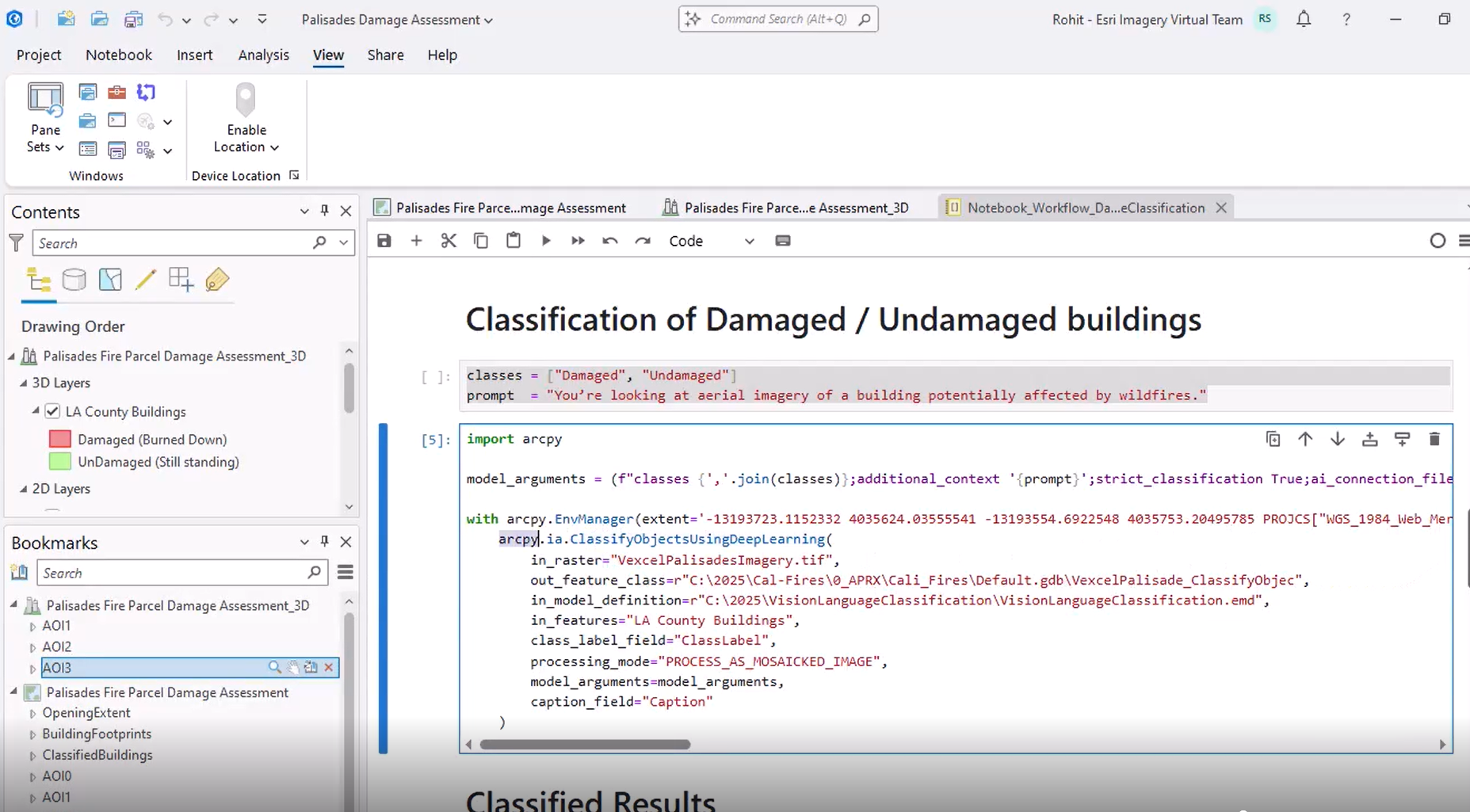
In a scenario where understanding both image and text prompts was crucial, Rohit employed the Vision Language Context-Based Classification model to extract insights that would have been difficult or impossible to find manually. To learn more about the model, see the ArcGIS pretrained models documentation.


Commenting is not enabled for this article.