Segmentation models help to identify objects such as trees, water bodies, and crop fields in satellite or aerial imagery and extract them as features. While automating this process greatly enhances geospatial workflows, training the models can be a very time consuming task. This is where Meta AI’s Segment Anything Model (SAM) comes in!
SAM is a foundational model developed to segment anything in an image without the need for additional training.
SAM has been added to our library of pretrained models, allowing you to use it seamlessly with ArcGIS. Since it was released, SAM has quickly become one of our most popular models.
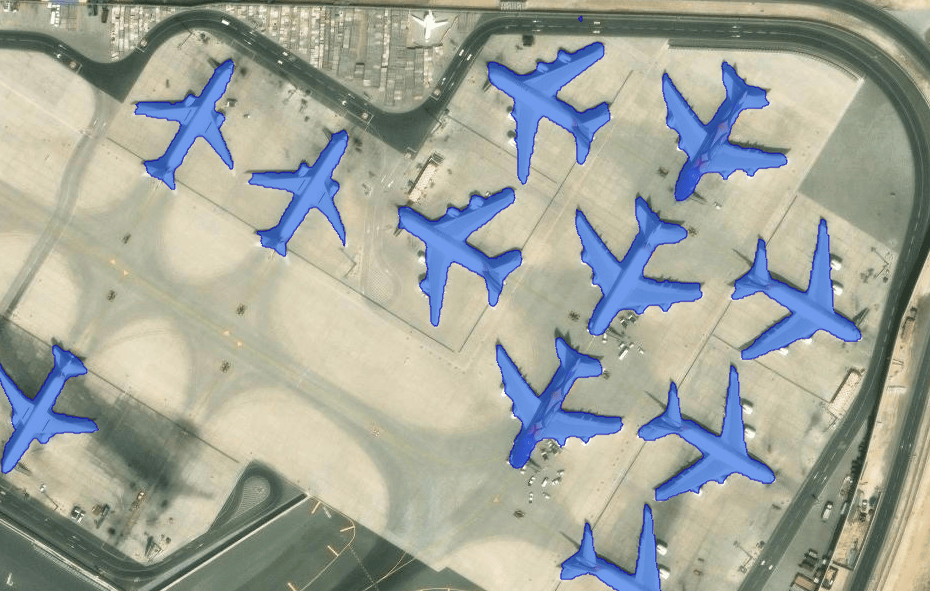
While SAM works great for many workflows, you may find that SAM alone doesn’t always suit your specific needs.
Have you ever wished you could indicate which type of object to extract as features, or wanted to fine-tune the model on your data? In her plenary demo, Priyanka will share how you can do just that.
Text SAM
In a scene with many types of objects such as buildings, roads, and trees, SAM will segment everything regardless of the object type. Depending on your workflow, you may wish for the model to only extract buildings from the imagery.
This is why we have released the Text SAM model as a deep learning package. Text SAM combines SAM with another model, Grounding DINO, which detects objects using text prompts. The Text SAM model allows you to input any free-form text that describes your object of interest. The model will then extract features based on the text you provide.
In her demo, Priyanka will run Text SAM as a geoprocessing tool from ArcGIS Pro.
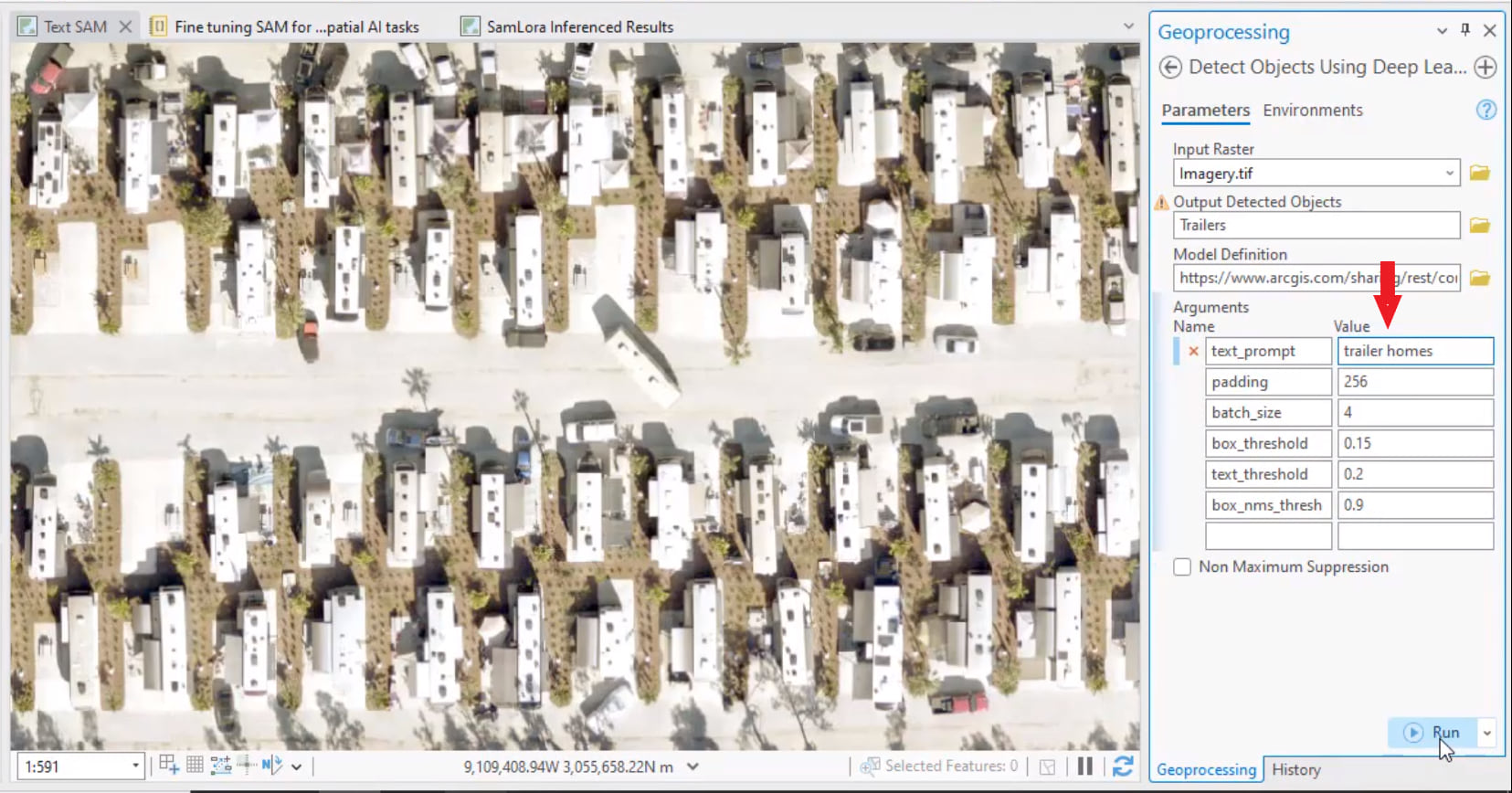

Priyanka has entered trailer homes as the object of interest she wants the model to identify in her input imagery. Let’s see what happens when she runs the model.
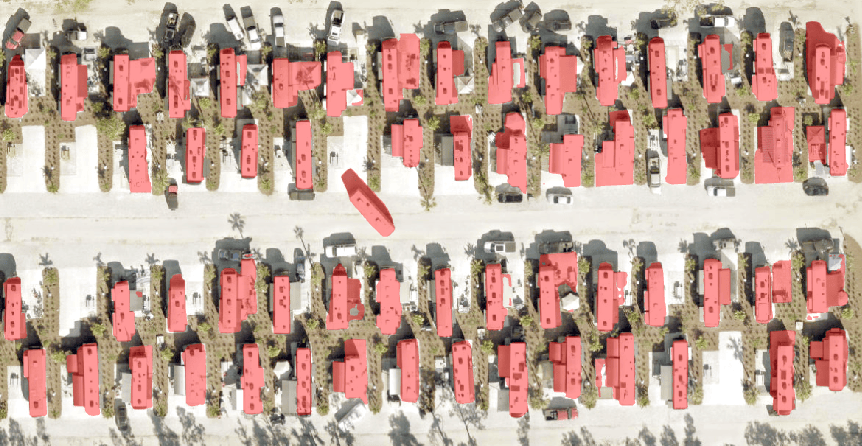
The model has successfully identified the trailers. It has even included a trailer outside of its presumed parking spot, differentiating it from other vehicles on the road!
SAMLoRA model
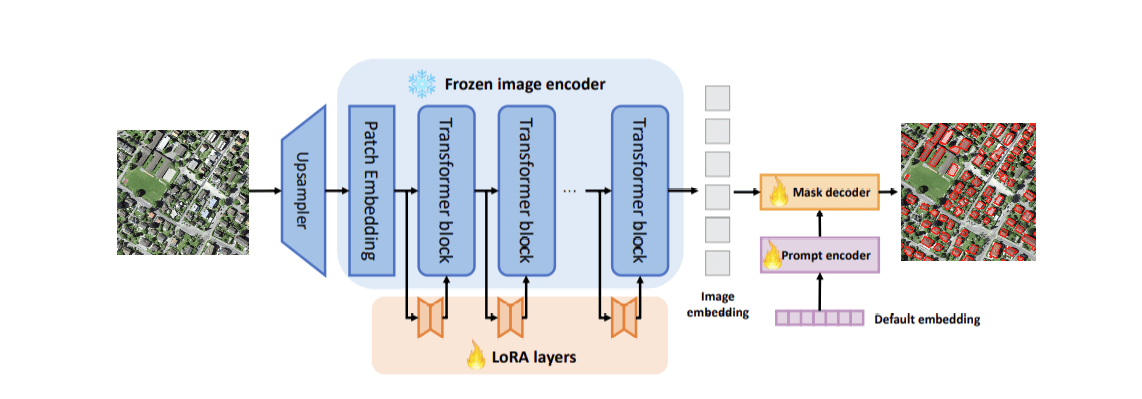
SAM is designed to work with 3-band, natural color RGB imagery. To finetune it on other data types that normally require massive computing resources such as synthetic-aperture radar (SAR) data, elevation data, and multispectral imagery, we now have the SAMLoRA model.
The SAMLoRA model, available in the arcgis.learn module, applies the low-rank-adaptation (LoRA) technique to the SAM model and finetunes it for geospatial imagery segmentation. LoRA is a training technique that enables few-shot learning, significantly reducing the number of trainable parameters.
In her demo, Priyanka extracts building footprints by using the SAMLoRA model finetuned on elevation data with just a handful of images.
Instead of needing a GPU cluster and several days of training, she’s able to do this in under 30 minutes on her laptop GPU.
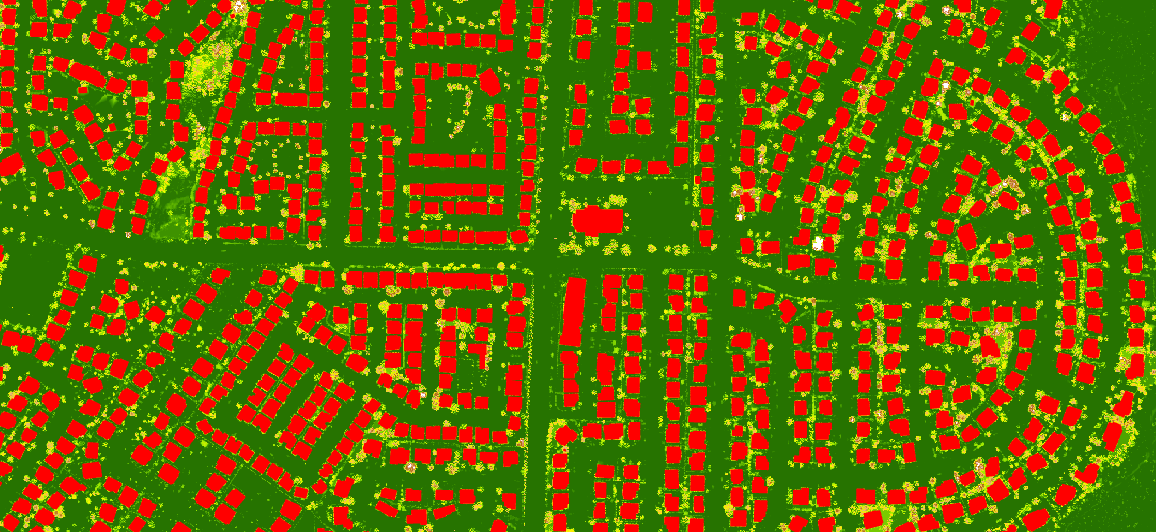
The model has successfully identified the building footprints.
Additional resources
In her demo, Priyanka has highlighted how SAM as a deep learning package can be used in your workflows, how you can prompt SAM using text inputs to segment specific features and imagery, and how you can fine-tune SAM on your data.
We are excited to see how you leverage SAM in your workflows! For more information on how to get started, explore the following:

Commenting is not enabled for this article.