The Esri Performance Engineering team tests hardware, software and infrastructure platforms and systems to find solutions that work with our software stack but most importantly provide the best user experience possible. Input from customers assists us in finding solutions, testing and evaluating the technology, and in turn publishing information to our users. Nutanix is a software-based platform that allows users to run a virtualized infrastructure, with a variety of hypervisors (VMware-ESXi, Citrix-XenServer, Nutanix-AHV).
What is Nutanix, and how does it work?
See the video for a quick overview.
ArcGIS Pro users expect fast 3-D rendering, execute complex geoprocessing models, and perform speedy network analysis. To meet these demands, GPUs and virtualized GPUs will play a vital role in delivering a fast and responsive user experience. This is giving rise to new hardware, software and infrastructure options from GPUs, server hardware, and virtualized infrastructure.
Based on user interaction and working with the Nutanix team, Esri Performance Engineering tested a NX-3155G-G5 and NX-1065-G4 system with 5 nodes that were equipped with (2) Nvidia M10 GPUs. the hardware was tested using two different hypervisors, first with VMware’s ESXi 6.5, followed by the Nutanix Acropolis Hypervisor (AHV). Testing focused on usability and rendering quality. The VMs with ArcGIS Pro installed are assigned shared resources such as a GPU. The ability to use or have options of hypervisors is something that is unique to this platform. Nutanix is a hyper -converged infrastructure that delivers a simplified IT management experience., for ArcGIS users, this infrastructure allows an ability to expand a virtual environment by adding nodes while the Nutanix software subsystem does the rest. . Running the system is Prism, which is Nutanix’s “end-to-end” management console and more. For more information on Prism download the Nutanix bible but also check out the following link.

As previously mentioned, the Nutanix platform operates a variety of hypervisors which can in turn host a VDI (Virtual Desktop Infrastructure) with VMs. VMs with ArcGIS Pro installed are assigned shared resources such as a GPU. The ability to use or have options of hypervisors is something that is unique to this platform. Nutanix does not truly consider themselves a hardware supplier; they consider themselves more a software company. Nutanix is a hyper -converged infrastructure that delivers a simplified IT management experience. Ultimately, for ArcGIS users, this infrastructure allows an ability to expand a virtual environment by adding nodes while the Nutanix software subsystem does the rest. This is not fully bound by a hypervisor and can again be setup and run on multiple hypervisors (Microsoft Server 2016, VMware ESXi, Citrix Xen Server, or Nutanix AHV). Running the system is Prism, which is Nutanix’s “end-to-end” management console and more. For more information on Prism download the Nutanix bible but also check out the following link.
https://www.nutanix.com/products/prism/
https://docs.nvidia.com/grid/5.0/grid-vgpu-release-notes-nutanix-ahv/index.html
So how did the system perform?
With the Nutanix test system we noticed responsive performance that can also be attributed to the use of a NVIDIA Tesla M10 GPU, a GPUmodel that does not have the same amount of CUDA cores for processing as its counterpart the M60, however designed for maximum VM density. While running 3D rendering tests on 16VMs, the results of the Nutanix system with the two Nvidia M10 GPUs showed a strong system performance which with 16 VMs concurrently running, were using roughly 30% of the overall system capacity at the time. See the results in the charts below
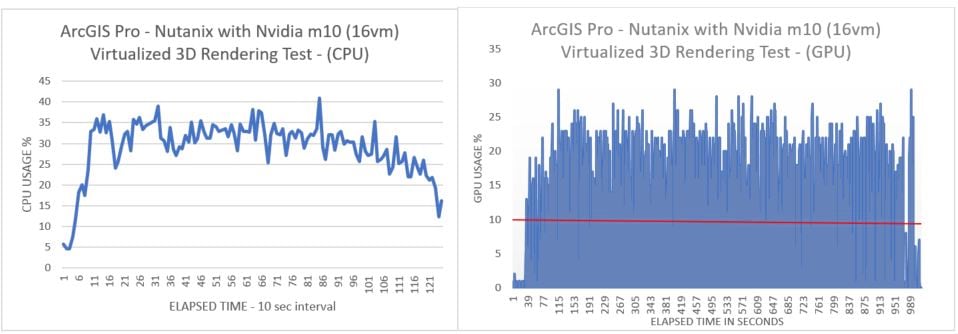
What do these results mean? This testing was only able to accommodate 16 sessions in our physical lab space, however with this kind of performance, it is possible to load a Nutanix node with 36-40 VMs and have an acceptable if not predictable user experience running processes such as 3D rendering. The dataset used for this testing is not the largest, nor is it the most complex 3d project, however it does visually render a large cityscape. This type of testing can impact the overall experience when rendering a similar dataset while using Windows 10 with other office products running. Given that dependency a VM can require the use of a NVIDIA 2Q profile, and avoid a loss of performance with the VM or a loss of functionality with ArcGIS Pro.
ArcGIS Pro is made for virtualized environments, and can fully leverage a well-provisioned system. As a personal observation, one thing that makes Nutanix stand out is the ease of deploying a host, which is then ready to deploy a vGPU, 3d ready VM, and run ArcGIS Pro. Using Esri software with Nutanix makes for a scalable architecture that can expand with the needs of GIS users, with 3D rendering and beyond.

Commenting is not enabled for this article.